Recombinant Human PILR-beta Fc Chimera Protein, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 9828-PR

Key Product Details
Source
Accession #
Structure / Form
Conjugate
Applications
Product Specifications
Source
| Human PILR-beta (Gln20-Ala189) Accession # Q9UKJ0-1 |
IEGRMD | Human IgG1 (Pro100-Lys330) |
| N-terminus | C-terminus |
Purity
Endotoxin Level
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Predicted Molecular Mass
SDS-PAGE
Activity
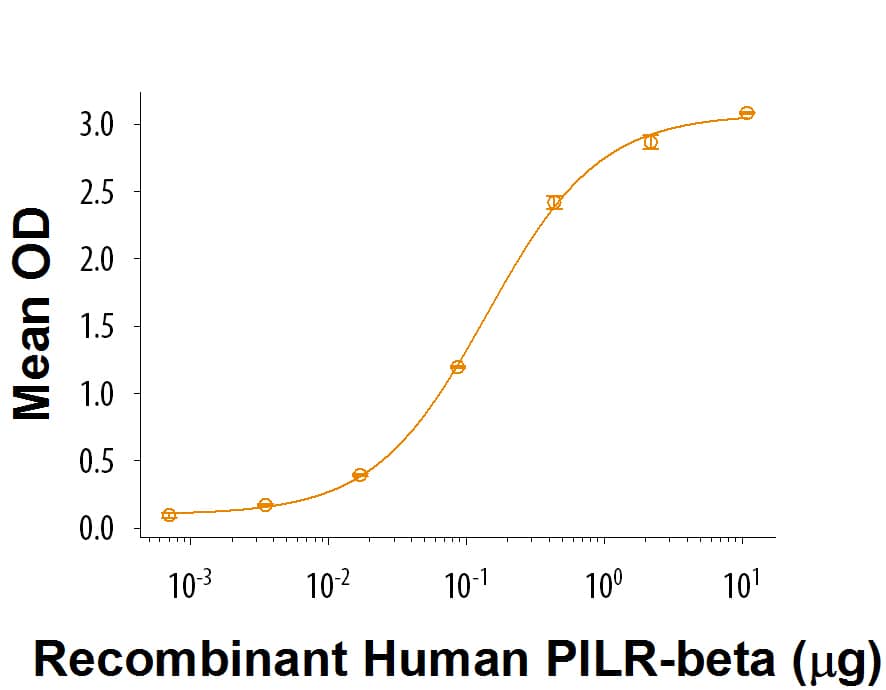
Recombinant Human CL-P1/COLEC12 (Catalog # 2690-CL) immobilized at 2 μg/mL, 100 μg/mL, can bind to Recombinant Human PILR‑ beta Fc Chimera with an ED50 of 0.12-0.72 μg/mL.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human PILR-beta Fc Chimera Protein, CF
Recombinant Human PILR-beta Fc Chimera Protein Bioactivity
When Recombinant Human CL-P1/COLEC12 (Catalog # 2690-CL) is coated at 2 µg/mL, Recombinant Human PILR-beta Fc Chimera (Catalog # 9828-PR) binds with an ED50 of 0.12-0.72 µg/mL.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
9828-PR
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution |
Reconstitute at 500 μg/mL in PBS.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: PILR-beta
Paired immunoglobulin-like type 2 receptor beta (PILR-beta) is a type I transmembrane (TM) glycoprotein belonging to the Ig superfamily. PILR-beta is the activating counterpart to the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM) containing PILR-alpha inhibitory receptor (1). Mature human PILR-beta is a 208 amino acid (aa) protein containing a 172 aa V-type Ig-like extracellular domain (ECD) with a siglec-like fold, a single TM, and a truncated cytoplasmic tail (2, 3). The TM of PILR-beta contains a positively-charged residue which interacts with immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation (ITAM)-bearing adaptor molecules (2). The ECD of mature human PILR-beta shares 40% aa sequence identity with its mouse counterpart. PILR-beta is expressed on myeloid cells, such as natural killer, macrophage, and dendritic cells, as well as resident cells of the central nervous system, such as microglial cells (2,4). It is a binding partner for DAP12 and CD99, and has been shown to play an important role in innate immunity and inflammation (4-6). The PILR-alpha / beta pair have also been shown to regulate cell signaling via association with SHP-1 (7). Experiments studying the effects of S. aureus and T. gondii infections in mice have shown that up-regulation of PILR-beta led to significantly lower survival rates while knock-down of PILR-beta or activation of PILR-alpha resulted in significantly less inflammation and increased pathogen clearance (4,5).
References
- Wilson, M.D. et al. (2006) Physiol. Genomics 27:201.
- Shiratori, I. et al. (2004) J. Exp. Med. 199:525.
- Lu, Q. et al. (2014) PNAS 111:8221.
- Tato, C.M. et al. (2012) PLoS One 7:e31690.
- Banerjee, A. et al. (2010) Infect. Immun. 78:1353.
- Tabata, S. et al. (2008) J. Biol. Chem. 283:8893.
- Mousseau, DD. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275:4467.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional PILR-beta Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human PILR-beta Fc Chimera Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human PILR-beta Fc Chimera Protein, CF
For research use only