Recombinant Human Siglec-11 Fc Chimera Protein, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 3258-SL

Key Product Details
Source
Accession #
Structure / Form
Conjugate
Applications
Product Specifications
Source
| Human Siglec-11 Asn17-His543 (Glu84Ala & Lys145Gln) Accession # AAK72907 |
IEGRMD | Human IgG1 (Pro100-Lys330) |
| N-terminus | C-terminus |
Purity
Endotoxin Level
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Predicted Molecular Mass
SDS-PAGE
Activity
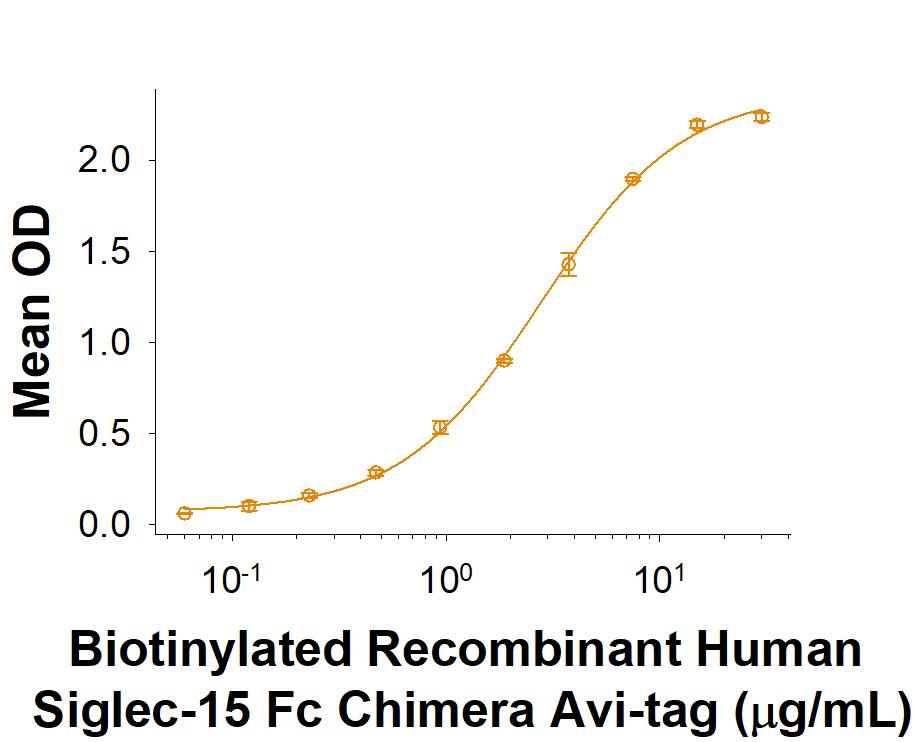
When Recombinant Human Siglec‑11 Fc Chimera is immobilized at 2 µg/mL (100 µL/well), it binds Biotinylated Recombinant Human Siglec‑15 Fc Chimera Avi-tag protein with an ED50 of 0.7-4.2 μg/mL.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human Siglec-11 Fc Chimera Protein, CF
Formulation, Preparation and Storage
3258-SL
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS. |
| Reconstitution |
Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in sterile PBS.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: Siglec-11
Siglecs (sialic acid binding Ig-like lectins) are I-type lectins that belong to the immunoglobulin superfamily. They are characterized by anN-terminal Ig-like V-set domain which mediates sialic acid binding, followed by a varying numbers of Ig-like C2-set domains. Siglecs-3 and 5 - 13 constitute the CD33/Siglec-3 related group, which are defined by their sequence homology and differential expression in the hematopoietic system (1-3). Mature human Siglec-11 consists of a 534 amino acid (aa) extracellular domain (ECD), a 23 aa transmembrane segment, and a 114 aa cytoplasmic domain. The ECD contains one Ig-like V-set domain, and three Ig-like C2-set domains. The cytoplasmic domain contains two immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs) (4). A splice variant of Siglec-11 has a deletion of nearly 100 aa in the extracellular juxtamembrane region. Among siglecs, the ECD of Siglec-11 is most closely related to that of Siglec-10 (82% aa sequence identity). The cytoplasmic domains of these proteins are only 20% identical. Siglec-11 is closely related to the pseudogenes Siglec-14 and Siglec-16 (4, 5). Human Siglec-11 shares 90%-96% aa sequence identity with Siglec-11 from great apes. Rodent orthologs of Siglec-11 have not been identified. In human, Siglec-11 is expressed in tissue macrophages, brain microglia, and inflammatory site monocytes (4). Strong microglial expression is specific to humans, as it is less prominent or absent in chimpanzees and orangutans (5). Siglec-11 forms 180 kDa disulfide-linked dimers. It shows a strong binding preference for sialic acid in alpha2-8 linkage which is unusual for siglecs (4). A conserved arginine in the Ig-like V-set domain only partially contributes to Siglec-11 ligand recognition, in contrast to its being required in other siglecs (4). Tyrosine phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic region of Siglec-11 promotes association with the phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2 (4).
References
- Varki, A. and T. Angata (2006) Glycobiology 16:1R.
- Crocker, P.R. (2005) Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 5:431.
- Crocker, P.R. (2002) Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 12:609.
- Angata, T. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277:24466.
- Hayakawa, T. et al. (2005) Science 309:1693.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Siglec-11 Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human Siglec-11 Fc Chimera Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human Siglec-11 Fc Chimera Protein, CF
For research use only