MKK7 Products
MAP Kinase Kinase 7 (MKK7), also known as MAP2K7, is a member of the dual-specificity MAP kinase kinase family with a predicted molecular weight of approximately 47.5 kDa. It is widely expressed in mammalian tissue and localizes to both the cytoplasm and the nucleus. The MKK7 protein contains three N-terminal D-sites, a central catalytic domain, and a C-terminal DVD domain. MAP kinase kinase kinases activate MKK7 via binding of the DVD domain and phosphorylation of a serine and threonine residue within the activation loop of the catalytic domain. MKK7 then utilizes its D-sites to bind and activate the JNK family of MAP kinases via phosphorylation. The genetic inactivation of MKK7 in mice results in embryonic lethality, indicating that MKK7 is an essential gene. Accordingly, MKK7 appears to be involved in the regulation of diverse physiological processes, including axon elongation, the circadian clock, embryonic stem cell differentiation, and liver regeneration. MKK7 function may also be important for the prevention of certain diseases. It has been shown to inhibit lung and mammary cancer via JNK1- and JNK2-dependent p53 stabilization. Additionally, reduced MKK7 function has been linked to the development of schizophrenia.
15 results for "MKK7" in Products
15 results for "MKK7" in Products
MKK7 Products
MAP Kinase Kinase 7 (MKK7), also known as MAP2K7, is a member of the dual-specificity MAP kinase kinase family with a predicted molecular weight of approximately 47.5 kDa. It is widely expressed in mammalian tissue and localizes to both the cytoplasm and the nucleus. The MKK7 protein contains three N-terminal D-sites, a central catalytic domain, and a C-terminal DVD domain. MAP kinase kinase kinases activate MKK7 via binding of the DVD domain and phosphorylation of a serine and threonine residue within the activation loop of the catalytic domain. MKK7 then utilizes its D-sites to bind and activate the JNK family of MAP kinases via phosphorylation. The genetic inactivation of MKK7 in mice results in embryonic lethality, indicating that MKK7 is an essential gene. Accordingly, MKK7 appears to be involved in the regulation of diverse physiological processes, including axon elongation, the circadian clock, embryonic stem cell differentiation, and liver regeneration. MKK7 function may also be important for the prevention of certain diseases. It has been shown to inhibit lung and mammary cancer via JNK1- and JNK2-dependent p53 stabilization. Additionally, reduced MKK7 function has been linked to the development of schizophrenia.
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #4E5 |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ELISA, ICC/IF, Flow |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2b Monoclonal Clone #324302 |
| Applications: | IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 kappa Monoclonal Clone #2G5 |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ELISA, ICC/IF, Func |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 kappa Monoclonal Clone #4D2 |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Monoclonal Clone #1T3M6 |
| Applications: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 kappa Monoclonal Clone #4E8 |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, MA, AP |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, MA, AP, PAGE |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 kappa Monoclonal Clone #6A4 |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA |
| Applications: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC |
Potent, selective inhibitor of MEK1 and 2
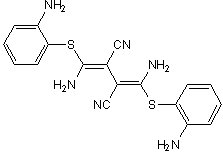
| Chemical Name: | 1,4-Diamino-2,3-dicyano-1,4-bis[2-aminophenylthio]butadiene |
Selective MEK inhibitor
| Alternate Names: | CI-1040 |
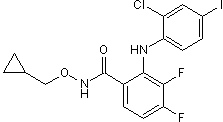
| Chemical Name: | 2-[(2-Chloro-4-iodophenyl)amino]-N-cyclopropylmethoxy)-3,4-difluorobenzamide |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |

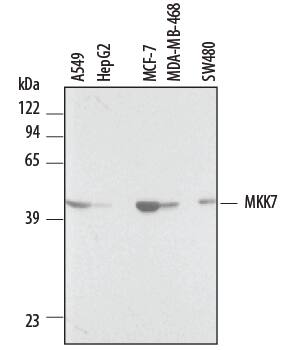

![Western Blot: MKK7/MEK7 Antibody (4E5)BSA Free [NBP2-37542] Western Blot: MKK7/MEK7 Antibody (4E5)BSA Free [NBP2-37542]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/MKK7-MEK7-Antibody-4E5-Western-Blot-NBP2-37542-img0002.jpg)
![Western Blot: MKK7/MEK7 Antibody (2G5) [H00005609-M04] Western Blot: MKK7/MEK7 Antibody (2G5) [H00005609-M04]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/MKK7-MEK7-Antibody-2G5-Western-Blot-H00005609-M04-img0006.jpg)
![Western Blot: MKK7/MEK7 Antibody (4D2) [H00005609-M02] Western Blot: MKK7/MEK7 Antibody (4D2) [H00005609-M02]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/MKK7-MEK7-Antibody-4D2-Western-Blot-H00005609-M02-img0006.jpg)
![Western Blot: MKK7/MEK7 Antibody (1T3M6) [NBP3-15456] Western Blot: MKK7/MEK7 Antibody (1T3M6) [NBP3-15456]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/MKK7-MEK7-Antibody-1T3M6-Western-Blot-NBP3-15456-img0001.jpg)
![Western Blot: MKK7/MEK7 Antibody (4E8) [H00005609-M01] Western Blot: MKK7/MEK7 Antibody (4E8) [H00005609-M01]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/MKK7-MEK7-Antibody-4E8-Western-Blot-H00005609-M01-img0002.jpg)
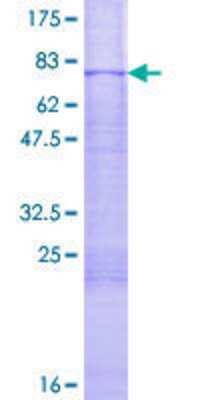
![Western Blot: MKK7/MEK7 [p Thr277] Antibody [NBP2-29678] Western Blot: MKK7/MEK7 [p Thr277] Antibody [NBP2-29678]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/MKK7-MEK7-[p-Thr277]-Antibody-Western-Blot-NBP2-29678-img0003.jpg)
![Western Blot: MKK7/MEK7 Antibody (6A4) [H00005609-M05] Western Blot: MKK7/MEK7 Antibody (6A4) [H00005609-M05]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/MKK7-MEK7-Antibody-6A4-Western-Blot-H00005609-M05-img0002.jpg)
![Western Blot: MKK7/MEK7 Overexpression Lysate [NBP2-05503] Western Blot: MKK7/MEK7 Overexpression Lysate [NBP2-05503]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/MEK7-Overexpression-Lysate-Adult-Normal-Western-Blot-NBP2-05503-img0001.jpg)
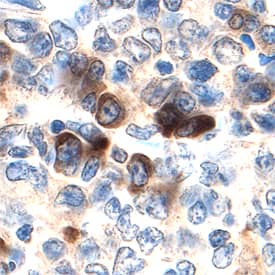
![Immunohistochemistry: MKK7/MEK7 Antibody [NBP1-87792] Immunohistochemistry: MKK7/MEK7 Antibody [NBP1-87792]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/MKK7-MEK7-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-NBP1-87792-img0003.jpg)