alpha-Synuclein [Cys Glu134, p Ser129] Antibody (J18) - BSA Free
Novus Biologicals, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # NBP3-18266
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody


Conjugate
Catalog #
Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Human, Mouse
Applications
Dot Blot, ELISA, Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry, Western Blot
Label
Unconjugated
Antibody Source
Monoclonal Rabbit IgG Clone # J18
Format
BSA Free
Concentration
1 mg/ml
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Human alpha-Synuclein AA 124-134: AYEMP-pS-EEGYQ-Cys
Modification
p Ser129, Cys Glu134
Localization
Cytoplasm|Cytosol|Membrane|Nucleus|Cell Junction|Synapse
Specificity
Binds to phosphorylated serine 129 on alpha synuclein. Does not detect unphosphorylated serine 129 alpha synuclein
Clonality
Monoclonal
Host
Rabbit
Isotype
IgG
Scientific Data Images for alpha-Synuclein [Cys Glu134, p Ser129] Antibody (J18) - BSA Free
Western Blot: alpha-Synuclein [p Ser 129] Antibody (J18) [NBP3-18266] - Western Blot analysis of Human Alpha Synuclein showing detection of alpha-Synuclein protein using Rabbit Anti-alpha-Synuclein Monoclonal Antibody, Clone J18 (NBP3-18266). Lane 1: MW ladder. Lane 2: 0.5 ug human alpha synuclein monomer (SPR-321). Lane 3: 2 ug human alpha synuclein monomer (SPR-321). Lane 4: 0.5 ug human alpha synuclein PFFs (SPR-322). Lane 5: 2 ug human alpha synuclein PFFs (SPR-322). Lane 6: 15 ug human Parkinson's Disease brain lysate.. Block: 5% BSA in TBST. Primary Antibody: Rabbit Anti-alpha-Synuclein Monoclonal Antibody (NBP3-18266) at 1:500 for 2 hours at RT with shaking. Secondary Antibody: Goat anti-mouse IgG:HRP at 1:4000 for 1 hour at RT with shaking. Color Development: Chemiluminescent for HRP (Moss) for 5 min in RT. NBP3-18266 does not detect unphosphorylated alpha synuclein.
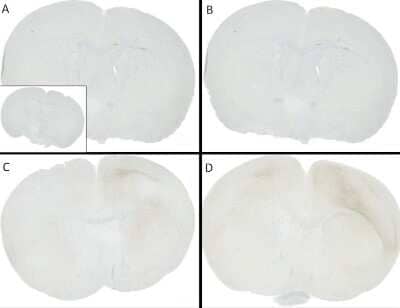
Immunohistochemistry: alpha-Synuclein [p Ser 129] Antibody (J18) [NBP3-18266] - C57/BL6 mice were injected with sonicated recombinant mouse alpha synuclein monomers or fibrils at 8 weeks of age. Mice were unilaterally injected in the dorsal striatum (bregma AP + 0.2 mm, L +/1 2.0 mm, V - 3.0 mm) and sacrificed 30 days post-injection. (A) 1.25 uL mouse alpha synuclein monomers. (B) 2.5 uL mouse alpha synuclein monomers. (C) 2.5 ug alpha synuclein PFFs. (C) 5 ug alpha synuclein PFFs Inset: PBS (negative control). Primary antibody: Anti-alpha-Synuclein (NBP3-18266) at 1:10 000. Secondary antibody: anti-rabbit HRP. Mice injected with PFF displayed alpha synuclein staining in the striatum and cortex and contralateral to the injection site.
Western Blot: alpha-Synuclein [p Ser 129] Antibody (J18) [NBP3-18266] - Western Blot analysis of Mouse Brain showing detection of alpha-Synuclein protein using Rabbit Anti-alpha-Synuclein Monoclonal Antibody, Clone J18 (NBP3-18266). Lane 1: MW ladder. Lane 2: Mouse brain. Load: 15 ug. Block: 5% BSA in TBST. Primary Antibody: Rabbit Anti-alpha-Synuclein Monoclonal Antibody (NBP3-18266) at 1:500 for 2 hours at RT with shaking. Secondary Antibody: Goat anti-mouse IgG:HRP at 1:4000 for 1 hour at RT with shaking. Color Development: Chemiluminescent for HRP (Moss) for 5 min in RT. Multiple bands due to phosphorylation.
Applications for alpha-Synuclein [Cys Glu134, p Ser129] Antibody (J18) - BSA Free
Application
Recommended Usage
Western Blot
1:500
Application Notes
Optimal dilutions for assays should be determined by the user.
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Affinity purified
Formulation
PBS pH 7.4, 50% glycerol
Format
BSA Free
Preservative
0.09% Sodium Azide
Concentration
1 mg/ml
Shipping
The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below.
Stability & Storage
Store at -20C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
Background: alpha-Synuclein
A number of studies have revealed that alpha-synuclein aggregation is a hallmark feature in a number of neurodegenerative diseases, referred to as synucleinopathies (2-4). Alpha-synuclein protein aggregates are a large component of Lewy bodies that are present in Parkinson's disease (PD), Lewy body dementia (LBD), and multiple system atrophy (1-6). Research has shown phosphorylation of alpha-synuclein at Ser129 moves the protein from the nucleus to the cytoplasm and promotes fibril formation associated with synucleinopathies (1,2,5). Recent studies also suggest that alpha-synuclein accumulation can prevent mitochondrial import machinery causing mitochondrial dysfunction that is often observed in neurodegeneration (5). It is thought that preventing alpha-synuclein aggregation may prevent PD, thus alpha-synuclein is a target for many potential therapeutic interventions aimed at decreasing aggregate formation or increasing clearance (1,2,4-6).
References
1. Villar-Pique, A., Lopes da Fonseca, T., & Outeiro, T. F. (2016). Structure, function and toxicity of alpha-synuclein: the Bermuda triangle in synucleinopathies. Journal of neurochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13249
2. Emamzadeh F. N. (2016). Alpha-synuclein structure, functions, and interactions. Journal of research in medical sciences : the official journal of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences. https://doi.org/10.4103/1735-1995.181989
3. Burre J. (2015). The Synaptic Function of alpha-Synuclein. Journal of Parkinson's disease. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-150642
4. Lashuel, H. A., Overk, C. R., Oueslati, A., & Masliah, E. (2013). The many faces of alpha-synuclein: from structure and toxicity to therapeutic target. Nature reviews. Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3406
5. Rocha, E. M., De Miranda, B., & Sanders, L. H. (2018). Alpha-synuclein: Pathology, mitochondrial dysfunction and neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease. Neurobiology of disease. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2017.04.004
6. O'Leary, E. I., & Lee, J. C. (2019). Interplay between alpha-synuclein amyloid formation and membrane structure. Biochimica et biophysica acta. Proteins and proteomics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2018.09.012
Alternate Names
NACP, PARK1, PARK4, SNCA, Synuclein-alpha
Gene Symbol
SNCA
Additional alpha-Synuclein Products
Product Documents for alpha-Synuclein [Cys Glu134, p Ser129] Antibody (J18) - BSA Free
Product Specific Notices for alpha-Synuclein [Cys Glu134, p Ser129] Antibody (J18) - BSA Free
This product is for research use only and is not approved for use in humans or in clinical diagnosis. Primary Antibodies are guaranteed for 1 year from date of receipt.
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...