Immunohistochemistry: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116]
Immunohistochemistry: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) [NB100-116] - Immunohistochemical staining of APE1. A. Nuclear staining in the luminal epithelium of normal breast ducts and lobules. B. Low, and C. high nuclear APE1 expression in invasive breast cancer. (magnification x400). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (//dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0099528) licensed under a CC-BY license.
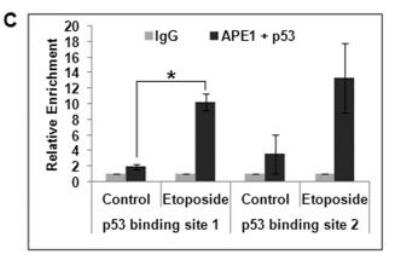
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP): APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) [NB100-116] - Association of p53 and APE1 on p53-binding sites in p21 promoter. Re-ChIP analysis (first IP with alpha-APE1 and the second IP with alpha-p53 antibody) showing simultaneous recruitment of APE1 and p53 in control vs. EPE treated cells; *: p value <0.05 (n=2) calculated based on APE1/p53 enriched DNA from control vs. etoposide treated cells. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0068467) licensed under a CC-BY license.
Simple Western: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2)BSA Free [NB100-116]
Simple Western: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) [NB100-116] - Image shows a specific band for APE1 in 0.1 mg/mL of HeLa lysate. This experiment was performed under reducing conditions using the 12-230kDa separation system. * Non-specific interaction with the 230 kDa Simple Western standard may be seen with this antibody.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116]
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) [NB100-116] - HeLa cells were fixed for 10 minutes using 10% formalin and then permeabilized for 5 minutes using 1X PBS + 0.05% Triton X-100. The cells were incubated with anti-APE (13B8E5C2) at 5 ug/mL overnight at 4C and detected with an anti-mouse DyLight 488 (Green) at a 1:500 dilution. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (Blue). Cells were imaged using a 40X objective.
Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2)BSA Free [NB100-116]
Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) [NB100-116] - Ovarian Cancer cell lines.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116]
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) [NB100-116] - Immunocytochemical detection of APE-ref-1 in breast cancer cell line MDA MB 231.
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116]
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) [NB100-116] - APE1 antibody was tested in human breast cancer xenograft using DAB with hematoxylin counterstain.
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] -
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - Association of APE1 & AP4 in p21 proximal promoter region.(A & B) ChIP Real Time PCR analysis showing relative enrichment of (A) APE1 & (B) AP4 in p21 proximal promoter containing AP4-responsive E-Box elements in HCT116p53null cells. (C) Re-ChIP (first IP with alpha-APE1 & the second IP with alpha-AP4 antibody) analysis showing simultaneous recruitment of APE1 & AP4 in this promoter region. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23874636), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] -
Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - Effect of APE1 on p21 activation in p53 WT cells.(A) Western analysis for APE1 level in WT APE1 & N delta42 APE1 overexpressing cells. (B) Real Time RT-PCR analysis showing relative quantitation of p21 transcript level in etoposide-treated WT APE1-overexpressing HCT116WT cells & N delta42 APE1 overexpressing cells; *: p value <0.05 (n = 2) calculated from control (empty vector transfection) vs. WT APE1 overexpression, WT APE1 overexpression along with etoposide treatment or N delta42 overexpression. (C) Luciferase activity in cells co-transfected with empty or WT APE1-expression vector & p21 promoter-luciferase construct; *: p value <0.05 (n = 2) calculated from control (empty vector transfection) vs. APE1 overexpression. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23874636), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] -
Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - Analysis of single strand break repair in MCF-7 monolayer & mammosphere cell populations. (a) Cells were exposed to 4 Gy 60Co gamma-radiation & the relative degree of single-strand breakage (SSB) was determined by alkaline single-cell gel electrophoresis (comet assay) immediately after exposure & at the times indicated after exposure. (b) The 'comets' (n of about 100) were categorized according to the NIH LISTSERV (Comet Assay Interest Group web site) in which type 1 comets display the least DNA damage & type 5 the most. The error bars represent the mean ± standard error of the mean in both panels. The comets of the unirradiated cells are labeled Cont. (c) Expression of proteins involved in SSB repair in response to ionizing radiation. Lysates were prepared from unirradiated cells & from cells harvested one hour after exposure to 1 or 10-Gy 60Co gamma-radiation & analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies against several SSB repair proteins. alpha-Actin served as a loading control. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (http://breast-cancer-research.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/bcr2583), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] -
Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - Intracellular APE1/Ref-1 was targeted to the plasma membrane in response to acetylation. (A & B) Whole cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using an anti-acetyl lysine antibody, followed by immunoblotting with the polyclonal anti-APE1/Ref-1 antibody. The blots were stripped & re-probed with anti-beta -actin & APE1/Ref-1 antibody to ensure equal protein loading. Similar results were obtained from replicate experiments. Column, mean (n = 3); bars, SE. *, p < 0.05, significantly different compared with control or between group by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test. (C,D) Membrane fractions or whole cell lysates were prepared from the TSA-treated cells. Immunoblotting for APE1/Ref-1 was performed using the polyclonal anti-APE1/Ref-1 antibody. Blots were stripped & re-probed with anti-N-cadherin & anti-beta -actin antibodies to control for differences in protein loading. Fold changes in the levels of APE1/Ref-1 in the plasma membrane fraction relative to the control are shown. †, indicates molecular marker (N-cadherin) of left image. Column mean (n = 3); bars, SE.*, p < 0.05 indicates a significantly different result compared with control or between groups by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31261750), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - AcAPE1 is exclusively associated w/ chromatin & remains bound to condensed chromosomes. (A & B) Asynchronous normal lung fibroblast IMR90 cells & lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells immunostained w/ anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1 Abs, counterstained w/ DAPI, & visualized by confocal microscopy & 3D SIM. (C) Colocalization of AcAPE1 w/ histone H3 or active enhancer-specific histone marker acetylated H3K27 (H3K27Ac). (D) BJ-hTERT cells serum starved for 72 h & then fixed at different time points. Cells immunostained w/ anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1 Abs & counterstained w/ anti-TO-PRO-3 iodide Ab. (E) Mitotic A549 cells immunostained w/ anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1 & visualized by 3D SIM. (F) BJ-hTERT cells either serum starved for 72 h (G0/G1 phase), treated w/ nocodazole (mitotic cells) or aphidicolin (G1/S phase synchronized cells), or untreated, & whole-cell extracts isolated using 150 mM or 300 mM salt-containing lysis buffer. Western blot analysis for anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1 levels performed. Anti-HSC70 used as loading control. (G) A proximal ligation assay performed w/ mouse anti-APE1 & rabbit anti-APE1 (mAPE1 & Rabbit-APE1), mouse anti-mouse APE1 & rabbit anti-AcAPE1 (mAPE1 & rAcAPE1), & rabbit anti-AcAPE1 & mouse anti-histone H3 (mHistone H3 & rAcAPE1) to confirm the chromatin association of AcAPE1. Mouse IgG (mIgG) & rabbit anti-AcAPE1 used as a control. At least 50 cells counted for PLA foci. (H) Colocalization of p300 & AcAPE1 on chromatin (DAPI). (I) HCT116 cells transfected w/ E1A & mutant E1A, & at 48 h after transfection, IF performed. Cells immunostained w/ anti-p300 & anti-APE1 or anti-AcAPE1 & counterstained w/ DAPI. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27994014), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] -
Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - XPF is epistatic to APE in the gemcitabine resistance. The expression of XPF and/or APE was suppressed by siRNAs in HeLa cells & the cellular sensitivity to gemcitabine was examined. XPF- or APE-suppressed HeLa cells (closed square & closed triangle, respectively) showed sensitivity to gemcitabine. Cosuppression of XPF & APE (closed circle with dashed line) resulted in the sensitivity to gemcitabine similar to the sensitivity induced by the suppression of XPF or APE individually. A control siRNA (siControl) was used as a control (open diamond). Three independent experiments were performed & averages of surviving fraction are plotted. The error bars show standard deviations. The differences in the gemcitabine sensitivity between the control cells & the cells treated with siXPF, siAPE, or siXPF+siAPE are statistically significant at 10 nM & 50 nM with p<0.05. The western blots showed a significant suppression of XPF (more than 95%) & ~75% reduction in the expression of APE with the siRNA treatment. The cosuppression experiments with two siRNAs, siXPF & siAPE, resulted in similar levels of suppression of each protein induced by individual siRNA (more than 95% reduction in XPF & ~85% reduction in APE). Tubulin was used as a protein loading control. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30941207), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - Plasma membrane associated APE1/Ref-1 is bound to ABCA1 in response to acetylation. Cells transiently expressing wild type APE1/Ref-1-FLAG or mutant APE1/Ref-1(K6/7R)-FLAG were treated with 1 µM TSA for 1 h. (A) Whole cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using the monoclonal anti-ABCA1 antibody, followed by immunoblot with the anti-FLAG antibody. (B) For reverse immunoprecipitation, cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-APE1/Ref-1 antibody followed by immunoblot analysis with the polyclonal anti-ABCA1 antibody. Blots were stripped & re-probed with anti-ABCA1 or FLAG antibodies to ensure equal protein loading & no contamination of cellular proteins. Similar results were observed in replicate experiments. Columns, mean (n = 2-3); bars, SE. *, p < 0.05 indicates a significantly different result from control cells according to unpaired t-tests. (C) The binding between APE1/Ref-1 & ABCA1 in the plasma membrane was visualized using with a Duolink II PLA system with primary polyclonal anti-APE1/Ref-1 & monoclonal anti-ABCA1 antibodies (PLA†). The PLA-specific fluorescence which represents the APE1/Ref-1-ABCA1 signal, & the DAPI nuclear staining are in red & blue, respectively. The experiment was repeated multiple times with similar results; the data shown here are from a representative experiment. Optical slices were examined using a 40× oil immersion objective with a 2× zoom factor. Scale bar, 20 µm (×80). Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31261750), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE1 acetylation enhances its stability on chromatin & its interaction with downstream BER proteins. (A) Colocalization of ligase III & AcAPE1 in A549 cells. Cells were immunostained with anti-ligase III & anti-AcAPE1 Abs. (B) WT or K5R mutant APE1-overexpressing HEK293T cells were treated with TSA-nicotinamide (NAM) for 6 h or not treated, & the nuclear extract was immunoprecipitated using anti-FLAG Ab & immunoblotted with anti-XRCC1 & anti-FLAG Abs. (C) A549 cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde before (top) or after treatment with Triton X-100 (0.5%) (middle) or Triton X-100 plus salt (100 mM KCl) (bottom) & immunostained with anti-APE1 or anti-AcAPE1 Abs & counterstained with DAPI. (D) Acetylation of APE1 induces a conformational change in APE1. The distinct intrinsic fluorescence emission spectra of APE1 & AcAPE1 at 280 nm are shown. A.U., absorbance units. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27994014), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - AcAPE1 is exclusively associated w/ chromatin & remains bound to condensed chromosomes. (A & B) Asynchronous normal lung fibroblast IMR90 cells & lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells immunostained w/ anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1 Abs, counterstained w/ DAPI, & visualized by confocal microscopy & 3D SIM. (C) Colocalization of AcAPE1 w/ histone H3 or active enhancer-specific histone marker acetylated H3K27 (H3K27Ac). (D) BJ-hTERT cells serum starved for 72 h & then fixed at different time points. Cells immunostained w/ anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1 Abs & counterstained w/ anti-TO-PRO-3 iodide Ab. (E) Mitotic A549 cells immunostained w/ anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1 & visualized by 3D SIM. (F) BJ-hTERT cells either serum starved for 72 h (G0/G1 phase), treated w/ nocodazole (mitotic cells) or aphidicolin (G1/S phase synchronized cells), or untreated, & whole-cell extracts isolated using 150 mM or 300 mM salt-containing lysis buffer. Western blot analysis for anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1 levels performed. Anti-HSC70 used as loading control. (G) A proximal ligation assay performed w/ mouse anti-APE1 & rabbit anti-APE1 (mAPE1 & Rabbit-APE1), mouse anti-mouse APE1 & rabbit anti-AcAPE1 (mAPE1 & rAcAPE1), & rabbit anti-AcAPE1 & mouse anti-histone H3 (mHistone H3 & rAcAPE1) to confirm the chromatin association of AcAPE1. Mouse IgG (mIgG) & rabbit anti-AcAPE1 used as a control. At least 50 cells counted for PLA foci. (H) Colocalization of p300 & AcAPE1 on chromatin (DAPI). (I) HCT116 cells transfected w/ E1A & mutant E1A, & at 48 h after transfection, IF performed. Cells immunostained w/ anti-p300 & anti-APE1 or anti-AcAPE1 & counterstained w/ DAPI. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27994014), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE1 is acetylated after binding to AP sites in the chromatin. (A) BJ-hTERT cells were treated with MX (50 mM) for the indicated times. IF was performed using anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1, & counterstaining with DAPI was used. (B) HCT116 cells were treated with various doses of MX for 30 min, IF was performed using anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1, & counterstaining with DAPI was used. (C) HCT116 cells were treated with 50 mM MX for 30 min, IF was performed using anti-OGG1, & counterstaining with DAPI was used. (D) BJ-hTERT cells pretreated with 50 mM MX for 30 min or not pretreated were exposed to MMS (2 mM) for 1 h. IF was performed using anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1, & counterstaining with DAPI was used. Confocal microscopy was used to visualize the AcAPE1 levels in control cells & cells treated with MMS or MX, or both. (E) ChIP with anti-OGG1 antibody followed by Western blotting (ChIP-on-Western) was performed to examine the association of AcAPE1 & ligase III on chromatin after induction of DNA damage with GO. (F) The association of AcAPE1 with the endogenous p21 promoter in control or MMS- or MX-treated cells was examined by promoter-directed ChIP using anti-AcAPE1. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27994014), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE1 is acetylated after binding to AP sites in the chromatin. (A) BJ-hTERT cells were treated with MX (50 mM) for the indicated times. IF was performed using anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1, & counterstaining with DAPI was used. (B) HCT116 cells were treated with various doses of MX for 30 min, IF was performed using anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1, & counterstaining with DAPI was used. (C) HCT116 cells were treated with 50 mM MX for 30 min, IF was performed using anti-OGG1, & counterstaining with DAPI was used. (D) BJ-hTERT cells pretreated with 50 mM MX for 30 min or not pretreated were exposed to MMS (2 mM) for 1 h. IF was performed using anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1, & counterstaining with DAPI was used. Confocal microscopy was used to visualize the AcAPE1 levels in control cells & cells treated with MMS or MX, or both. (E) ChIP with anti-OGG1 antibody followed by Western blotting (ChIP-on-Western) was performed to examine the association of AcAPE1 & ligase III on chromatin after induction of DNA damage with GO. (F) The association of AcAPE1 with the endogenous p21 promoter in control or MMS- or MX-treated cells was examined by promoter-directed ChIP using anti-AcAPE1. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27994014), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - AcAPE1 is exclusively associated w/ chromatin & remains bound to condensed chromosomes. (A & B) Asynchronous normal lung fibroblast IMR90 cells & lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells immunostained w/ anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1 Abs, counterstained w/ DAPI, & visualized by confocal microscopy & 3D SIM. (C) Colocalization of AcAPE1 w/ histone H3 or active enhancer-specific histone marker acetylated H3K27 (H3K27Ac). (D) BJ-hTERT cells serum starved for 72 h & then fixed at different time points. Cells immunostained w/ anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1 Abs & counterstained w/ anti-TO-PRO-3 iodide Ab. (E) Mitotic A549 cells immunostained w/ anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1 & visualized by 3D SIM. (F) BJ-hTERT cells either serum starved for 72 h (G0/G1 phase), treated w/ nocodazole (mitotic cells) or aphidicolin (G1/S phase synchronized cells), or untreated, & whole-cell extracts isolated using 150 mM or 300 mM salt-containing lysis buffer. Western blot analysis for anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1 levels performed. Anti-HSC70 used as loading control. (G) A proximal ligation assay performed w/ mouse anti-APE1 & rabbit anti-APE1 (mAPE1 & Rabbit-APE1), mouse anti-mouse APE1 & rabbit anti-AcAPE1 (mAPE1 & rAcAPE1), & rabbit anti-AcAPE1 & mouse anti-histone H3 (mHistone H3 & rAcAPE1) to confirm the chromatin association of AcAPE1. Mouse IgG (mIgG) & rabbit anti-AcAPE1 used as a control. At least 50 cells counted for PLA foci. (H) Colocalization of p300 & AcAPE1 on chromatin (DAPI). (I) HCT116 cells transfected w/ E1A & mutant E1A, & at 48 h after transfection, IF performed. Cells immunostained w/ anti-p300 & anti-APE1 or anti-AcAPE1 & counterstained w/ DAPI. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27994014), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - AcAPE1 is exclusively associated w/ chromatin & remains bound to condensed chromosomes. (A & B) Asynchronous normal lung fibroblast IMR90 cells & lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells immunostained w/ anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1 Abs, counterstained w/ DAPI, & visualized by confocal microscopy & 3D SIM. (C) Colocalization of AcAPE1 w/ histone H3 or active enhancer-specific histone marker acetylated H3K27 (H3K27Ac). (D) BJ-hTERT cells serum starved for 72 h & then fixed at different time points. Cells immunostained w/ anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1 Abs & counterstained w/ anti-TO-PRO-3 iodide Ab. (E) Mitotic A549 cells immunostained w/ anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1 & visualized by 3D SIM. (F) BJ-hTERT cells either serum starved for 72 h (G0/G1 phase), treated w/ nocodazole (mitotic cells) or aphidicolin (G1/S phase synchronized cells), or untreated, & whole-cell extracts isolated using 150 mM or 300 mM salt-containing lysis buffer. Western blot analysis for anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1 levels performed. Anti-HSC70 used as loading control. (G) A proximal ligation assay performed w/ mouse anti-APE1 & rabbit anti-APE1 (mAPE1 & Rabbit-APE1), mouse anti-mouse APE1 & rabbit anti-AcAPE1 (mAPE1 & rAcAPE1), & rabbit anti-AcAPE1 & mouse anti-histone H3 (mHistone H3 & rAcAPE1) to confirm the chromatin association of AcAPE1. Mouse IgG (mIgG) & rabbit anti-AcAPE1 used as a control. At least 50 cells counted for PLA foci. (H) Colocalization of p300 & AcAPE1 on chromatin (DAPI). (I) HCT116 cells transfected w/ E1A & mutant E1A, & at 48 h after transfection, IF performed. Cells immunostained w/ anti-p300 & anti-APE1 or anti-AcAPE1 & counterstained w/ DAPI. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27994014), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] -
Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - Repression of p21 by APE1 in p53-null cells & effect of ectopic p53 in this repression.(A & B) Real Time RT-PCR analysis showing relative quantitation of p21 transcript level in (A) HCT116p53null cells with WT & N delta42 APE1 overexpression; *: p value (n = 4) calculated from control (empty vector transfection) vs. WT or N delta42 APE1 overexpression, & (B) control (control siRNA) vs. APE1-depleted HCT116p53null cells; *: p value <0.05 (n = 4) calculated from control vs. APE1-depleted cells. (C) Effect of ectopic p53 expression on p21 transcript level in control vs. APE1-depleted HCT116p53null cells. First, cells were transfected with control siRNA or APE1 siRNA, the next day both the cell types were again transfected with empty vector or p53 expression vector & after 48 hrs the cells were harvested; signal from empty vector transfection in both control & APE1-depleted cells were set as reference samples; *: p value <0.05 (n = 3) calculated based on the effect of ectopic p53 expression over empty vector transfection in control vs. APE1-depleted cells. (D) Effect of APE1 depletion in control (empty vector transfected) vs. ectopic p53-expressing HCT116p53null cells; the same experiment was performed as in C but analyzed differently; signal from control siRNA-transfected cells in both empty vector transfected & ectopic p53 expressing cases were set as reference samples; *: p value <0.05 (n = 3) calculated based on the effect of APE1-depletion in empty vector transfected vs. ectopic p53 expressing cells. (E) Representative Western analysis of p53, APE1, p21 & alpha-Tubulin levels in the same HCT116p53null cells as in B–D. (F & G) Real Time RT-PCR analysis of p21 level in Saos2 cells as in C & D. *: p value <0.05 (n = 2). Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23874636), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE1 is acetylated after binding to AP sites in the chromatin. (A) BJ-hTERT cells were treated with MX (50 mM) for the indicated times. IF was performed using anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1, & counterstaining with DAPI was used. (B) HCT116 cells were treated with various doses of MX for 30 min, IF was performed using anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1, & counterstaining with DAPI was used. (C) HCT116 cells were treated with 50 mM MX for 30 min, IF was performed using anti-OGG1, & counterstaining with DAPI was used. (D) BJ-hTERT cells pretreated with 50 mM MX for 30 min or not pretreated were exposed to MMS (2 mM) for 1 h. IF was performed using anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1, & counterstaining with DAPI was used. Confocal microscopy was used to visualize the AcAPE1 levels in control cells & cells treated with MMS or MX, or both. (E) ChIP with anti-OGG1 antibody followed by Western blotting (ChIP-on-Western) was performed to examine the association of AcAPE1 & ligase III on chromatin after induction of DNA damage with GO. (F) The association of AcAPE1 with the endogenous p21 promoter in control or MMS- or MX-treated cells was examined by promoter-directed ChIP using anti-AcAPE1. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27994014), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] -
Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - Intracellular APE1/Ref-1 was targeted to the plasma membrane in response to acetylation. (A & B) Whole cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using an anti-acetyl lysine antibody, followed by immunoblotting with the polyclonal anti-APE1/Ref-1 antibody. The blots were stripped & re-probed with anti-beta -actin & APE1/Ref-1 antibody to ensure equal protein loading. Similar results were obtained from replicate experiments. Column, mean (n = 3); bars, SE. *, p < 0.05, significantly different compared with control or between group by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test. (C,D) Membrane fractions or whole cell lysates were prepared from the TSA-treated cells. Immunoblotting for APE1/Ref-1 was performed using the polyclonal anti-APE1/Ref-1 antibody. Blots were stripped & re-probed with anti-N-cadherin & anti-beta -actin antibodies to control for differences in protein loading. Fold changes in the levels of APE1/Ref-1 in the plasma membrane fraction relative to the control are shown. †, indicates molecular marker (N-cadherin) of left image. Column mean (n = 3); bars, SE.*, p < 0.05 indicates a significantly different result compared with control or between groups by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31261750), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - AcAPE1 is exclusively associated w/ chromatin & remains bound to condensed chromosomes. (A & B) Asynchronous normal lung fibroblast IMR90 cells & lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells immunostained w/ anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1 Abs, counterstained w/ DAPI, & visualized by confocal microscopy & 3D SIM. (C) Colocalization of AcAPE1 w/ histone H3 or active enhancer-specific histone marker acetylated H3K27 (H3K27Ac). (D) BJ-hTERT cells serum starved for 72 h & then fixed at different time points. Cells immunostained w/ anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1 Abs & counterstained w/ anti-TO-PRO-3 iodide Ab. (E) Mitotic A549 cells immunostained w/ anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1 & visualized by 3D SIM. (F) BJ-hTERT cells either serum starved for 72 h (G0/G1 phase), treated w/ nocodazole (mitotic cells) or aphidicolin (G1/S phase synchronized cells), or untreated, & whole-cell extracts isolated using 150 mM or 300 mM salt-containing lysis buffer. Western blot analysis for anti-APE1 & anti-AcAPE1 levels performed. Anti-HSC70 used as loading control. (G) A proximal ligation assay performed w/ mouse anti-APE1 & rabbit anti-APE1 (mAPE1 & Rabbit-APE1), mouse anti-mouse APE1 & rabbit anti-AcAPE1 (mAPE1 & rAcAPE1), & rabbit anti-AcAPE1 & mouse anti-histone H3 (mHistone H3 & rAcAPE1) to confirm the chromatin association of AcAPE1. Mouse IgG (mIgG) & rabbit anti-AcAPE1 used as a control. At least 50 cells counted for PLA foci. (H) Colocalization of p300 & AcAPE1 on chromatin (DAPI). (I) HCT116 cells transfected w/ E1A & mutant E1A, & at 48 h after transfection, IF performed. Cells immunostained w/ anti-p300 & anti-APE1 or anti-AcAPE1 & counterstained w/ DAPI. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27994014), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] -
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - Association of p53 & APE1 on p53-binding sites in p21 promoter.(A) p21 promoter structure showing p53 & AP4 binding sites. (B) ChIP Real Time PCR analysis showing relative enrichment (2− deltaCT) of APE1-immunoprecipitated DNA over that from control IgG in p21 promoter regions containing p53 binding sites 1 & 2 in HCT116WT cells. (C) Re-ChIP analysis (first IP with alpha-APE1 & the second IP with alpha-p53 antibody) showing simultaneous recruitment of APE1 & p53 in control vs. etoposide treated cells; *: p value <0.05 (n = 2) calculated based on APE1/p53 enriched DNA from control vs. etoposide treated cells. (D) Western analysis of FLAG immunoprecipitate (IP) to detect APE1-associated p53 & FLAG (APE1) from empty vector vs. FLAG-tagged WT APE1 or FLAG-tagged N delta33 APE1 transfected HCT116WT cells (left panel) & from control vs. etoposide-treated WT APE1-FLAG transfected cells (right panel). Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23874636), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] -
Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - Gemcitabine-induced recruitment of XPF to chromatin depends on APE. HCT116, APE-suppressed HCT116 (HCT116 shAPE), & XPF-deficient HCT116 (HCT116 g4-10) cells were treated with 1 μM of gemcitabine & chromatin fractions were isolated in the indicated time. The presence of XPF & APE was detected by western blots. The asterisk (∗) shows a cross-reacted protein with the anti-XPF antibody. Histone H2AX was used as a loading control. Gemcitabine-induced recruitment of XPF to chromatin (lanes 1-3) was compromised in HCT116 shAPE cell line (lanes 4-5). The chromatin-bound APE is not changed by the gemcitabine treatment (lanes 4-6, Supplementary Figure 5). A signal of XPF (and APE) was normalized with a signal of H2AX in each chromatin fraction using ImageJ software. Then a ratio of chromatin-bound XPF with gemcitabine to XPF in control was determined & depicted as bar graphs. Three independent experiments were performed & averages of the ratio at indicated time points were plotted. The error bars show standard deviations. Only the difference in the chromatin-bound XPF between chromatin from control experiments & chromatin that was incubated one hour with 1 μM gemcitabine is statistically significant in HCT116 (p<0.05). Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30941207), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.

![Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2)BSA Free [NB100-116] Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2)BSA Free [NB100-116]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/APE-Antibody-13B8E5C2-Western-Blot-NB100-116-img0014.jpg)
![Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] Knockdown Validated: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/APE-Antibody-13B8E5C2-Knockdown-Validated-NB100-116-img0016.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/APE-Antibody-13B8E5C2-Immunocytochemistry-Immunofluorescence-NB100-116-img0010.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] Immunohistochemistry: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/APE-Antibody-13B8E5C2-Immunohistochemistry-NB100-116-img0017.jpg)
![Simple Western: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2)BSA Free [NB100-116] Simple Western: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2)BSA Free [NB100-116]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/APE-Antibody-13B8E5C2-Simple-Western-NB100-116-img0012.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/APE-Antibody-13B8E5C2-Immunocytochemistry-Immunofluorescence-NB100-116-img0013.jpg)
![Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2)BSA Free [NB100-116] Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2)BSA Free [NB100-116]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/APE-Antibody-13B8E5C2-Western-Blot-NB100-116-img0008.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/APE-Antibody-13B8E5C2-Immunocytochemistry-Immunofluorescence-NB100-116-img0009.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/APE-Antibody-13B8E5C2-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NB100-116-img0001.jpg)
![Chromatin Immunoprecipitation: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-116_mouse-monoclonal-ape-antibody-13b8e5c2-310202415394546.jpg)
![Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-116_mouse-monoclonal-ape-antibody-13b8e5c2-310202415371965.jpg)
![Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-116_mouse-monoclonal-ape-antibody-13b8e5c2-310202415525298.jpg)
![Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-116_mouse-monoclonal-ape-antibody-13b8e5c2-310202415541999.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-116_mouse-monoclonal-ape-antibody-13b8e5c2-310202415533841.jpg)
![Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-116_mouse-monoclonal-ape-antibody-13b8e5c2-310202415523918.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-116_mouse-monoclonal-ape-antibody-13b8e5c2-31020241555225.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-116_mouse-monoclonal-ape-antibody-13b8e5c2-3102024165741.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-116_mouse-monoclonal-ape-antibody-13b8e5c2-31020241682167.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-116_mouse-monoclonal-ape-antibody-13b8e5c2-31020241612630.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-116_mouse-monoclonal-ape-antibody-13b8e5c2-310202415532029.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-116_mouse-monoclonal-ape-antibody-13b8e5c2-31020241612615.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-116_mouse-monoclonal-ape-antibody-13b8e5c2-310202415541968.jpg)
![Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-116_mouse-monoclonal-ape-antibody-13b8e5c2-3102024168212.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-116_mouse-monoclonal-ape-antibody-13b8e5c2-31020241682160.jpg)
![Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-116_mouse-monoclonal-ape-antibody-13b8e5c2-31020241683933.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-116_mouse-monoclonal-ape-antibody-13b8e5c2-310202415535126.jpg)
![Chromatin Immunoprecipitation: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-116_mouse-monoclonal-ape-antibody-13b8e5c2-31020241683929.jpg)
![Western Blot: APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free [NB100-116] - APE Antibody (13B8E5C2) - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb100-116_mouse-monoclonal-ape-antibody-13b8e5c2-310202415541910.jpg)