CHREBP-Antibody---BSA-Free-Chromatin-Immunoprecipitation-NB400-135-img0018.jpg
Western Blot: CHREBP AntibodyBSA Free [NB400-135]
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - CHREBP Antibody [NB400-135] - Detection of ChREBP in 20 ug of human hepatocyte lysate using NB400-135. 5-10 second film exposure.
Western Blot: CHREBP AntibodyBSA Free [NB400-135]
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - CHREBP Antibody [NB400-135] - Detection of ChREBP in liver nuclear extracts from well-fed rats. 7% SDS-PAGE gel, 1:1000 dilution of NB400-135. Photo courtesy of Dr. Uyeda, UT Southwestern University.
Western Blot: CHREBP AntibodyBSA Free [NB400-135]
CHREBP-Antibody---BSA-Free-Western-Blot-NB400-135-img0019.jpg
Western Blot: CHREBP AntibodyBSA Free [NB400-135]
CHREBP-Antibody---BSA-Free-Western-Blot-NB400-135-img0020.jpg
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135]
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - CHREBP Antibody [NB400-135] - HeLa cells were fixed for 10 minutes using 10% formalin and permeabilized for 5 minutes using 1X TBS + 0.5% Triton X-100. The cells were incubated with anti-ChREBP (NB400-135) at a 1:200 dilution overnight at 4C and detected with an anti-rabbit DyLight 488 (Green) at a 1:500 dilution. Alpha tubulin was used as a co-stained at 1:1000 and detected with an anti-mouse DyLight 550 (Red) at a 1:500. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (Blue). Cells were imaged using a 40X objective.
Immunohistochemistry: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135]
Immunohistochemistry: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - CHREBP Antibody [NB400-135] - Analysis of CHREBP in mouse liver using DAB with hematoxylin counterstain.
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135]
CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free-Knockout Validated-NB400-135-img0024.jpg
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] -
Analysis of protein levels in livers transfected with GK and GKA456V. Livers excised from mice in postabsorptive state were homogenized and resolved by Western blot. (a, b) Representative blots from three independent experiments. The densitometric analysis is presented (N = 4, *P < 0.05 versus pControl, ***P < 0.001 versus pGKA456V). (c) Liver sections of 5-hour fasted mice injected with pControl, pGK, or pGKA456V were immunostained with Glc6Pase antibody. TO-PRO-3 was used to visualize nuclei.
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] -
Immunoblot analysis of livers from control & L-Chrebp−/− mice subjected to fasting & refeeding with a high-sucrose diet. Littermate control & L-Chrebp−/− mice (same as those described in supplemental Tables S2A & S2B) were subjected to fasting & refeeding. The nonfasted (N) groups were fed chow diet ad libitum. The fasted (F) group was fasted 12 h, & the refed (R) group was fasted for 12 h & then refed with 60% (w/w) high-sucrose diet for 12 h prior to study. Liver whole-cell lysates & membrane fractions were prepared individually, & equal amounts of protein from each mouse of the same group (four per group) were pooled. Aliquots (40 μg for whole-cell lysates & 30 μg for membrane fractions) of the pooled protein were subjected to SDS-PAGE & immunoblot analysis. Immunoblot analysis of Insig-1 & Insig-2 were carried out using membrane fractions. Whole-cell lysates were used to detect other proteins. The precursor & nuclear forms of SREBPs are denoted as P & N, respectively. Calnexin was used as loading control. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0022227520331369), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] -
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - Raffinose stimulates transcription of genes involved in epidermal barrier function in HaCaT cells.(a & b) HaCaT cells were treated with vehicle, 1 μM or 10 μM raffinose (Raf), or 1 μM TO901317 (T17) for 24 h. Expressions of transcripts (a) & proteins (b) were analyzed by qRT-PCR or western blotting, respectively. FLG; filaggrin. IVL; involucrin, LOR; loricrin, AQP3; aquaporin3. (c) HaCaT cells were transfected with siGFP control, siLXR alpha, or siLXR beta, & then treated with 1 μM raffinose for 24 h. Expression of proteins was analyzed by western blotting. The original blots are shown in Supplementary Fig. S9. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28266648), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] -
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - Impaired hepatic SIRT1-FoxO signaling in L-G6pc-/- mice.(A) Western blots & densitometry analysis (n = 5), & quantification of mRNA for hepatic SIRT1 & FoxO3a (n = 8). (B) Hepatic NAD+ levels (n = 9). (C) Western blots & densitometry analysis of PPAR-gamma, PPAR-alpha & beta-actin (n = 5). (D) Immunohistochemical analysis of hepatic ChREBP & quantification of nuclear ChREBP-translocated cells (n = 4). Scale bar, 25 μm. (E) Quantification of mRNA for hepatic Acaca, Fasn & Elovl6 by real-time RT-PCR (n = 6). (F) Western blots of acetylated & total FoxO3a after immunoprecipitation of nuclear extracts using anti-FoxO3a, & quantification of the acetylated FoxO3a/total FoxO3a (n = 5). Data represent the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28558013), licensed under a CC0-1.0 license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] -
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - Expressing recombinant ChREBP beta in Rictor-deficient adipocytes rescues expression of DNL enzymes.Western blot of indicated proteins in differentiated adipocytes with or without Rictor deletion transfected with various rescue constructs that were stably expressed in cells before differentiation. ‘*' indicates ChREBP beta based on molecular weight. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms11365), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] -
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - Hepatic expression of mRNAs encoding carbohydrate response element-binding protein (ChREBP) (a), liver pyruvate kinase (LPK) (c), & microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTTP) (d), & nuclear ChREBP protein (b) in water-control, 10% fructose solution-control, & fructose pair-fed oleanolic acid- (OA-) treated rats at week 10. Animals were administered with OA (25 mg/kg/day) or vehicle (OA: 0 mg/kg, 5% Gum Arabic) by oral gavage daily for 10 weeks. mRNA was determined by real-time PCR. Protein expression was determined by Western blot. Data are means ± SEM (n = 6 each group). *P < 0.05. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23737835), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] -
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - LXR mediate the induction of lipogenesis induced by an oleic acid-rich diet.(A) Hepatic Acly, Acaca, Acacb, Fasn, Elovl6, Scd1 mRNA levels quantified by qPCR. (B) Cytoplasmic protein expression levels of P-ACLY, ACLY, ACC, ELOVL6, SCD1, FASN & beta-ACTIN assayed by Western Blotting. (C) Fads1, Fads2, Elovl5, Gpat, Pnpla3 & Lpk mRNA quantification assayed by qPCR. (D) Srebp-1c & Chrebp mRNA quantification assayed by qPCR. (E) Cytoplasmic & nuclear expression levels of LXR, SREBP-1c & ChREBP assayed by Western Blotting. Data are the mean±SEM of values measured in LXR+/+ & LXR-/- mice fed REF or OLIV diet. a Significant genotype effect. b Significant difference versus REF diet (n = 6 mice per group). Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28732092), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] -
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - Analysis of protein levels in livers transfected with GK & GKA456V. Livers excised from mice in postabsorptive state were homogenized & resolved by Western blot. (a, b) Representative blots from three independent experiments. The densitometric analysis is presented (N = 4, *P < 0.05 versus pControl, ***P < 0.001 versus pGKA456V). (c) Liver sections of 5-hour fasted mice injected with pControl, pGK, or pGKA456V were immunostained with Glc6Pase antibody. TO-PRO-3 was used to visualize nuclei. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22194744), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] -
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - ChREBP knockdown inhibited glycolysis, lipogenesis & p21 in HT29 cells. (A) Inhibited relative mRNA expression of ChREBP alpha & ChREBP beta normalized to B2M after control or ChREBP siRNA transfection for 48 hours. (B) Western-blot of ChREBP, phospho-p53 & p21 & their quantification on the right. beta-actin was served as a loading control. Proteins were extracted from cells transfected with sicontrol & siChREBP after 48 hours. The quantification of western blot was normalized to beta-actin. (C) Decreased relative mRNA expression of glycolytic & lipogenic genes, normalized to B2M. (D) Relative mRNA expression of p53 & p21, normalized to B2M. (E) Relative mRNA expression of cell Cyclins, normalized to B2M. n = 4. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32144313), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] -
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - Ligand-activated LXR reduces ChREBP binding to chromatin. (A). Left panels: Local pattern of LXR-ChREBP co-occupancy. Browser view of LXR & ChREBP tracks in the promoter region of Lpk (Pklr), Txnip, Fasn & Scd1. Square brackets indicate the scale maxima of ChIP/input ratios. Arrows indicate the genomic locations of quantitative RT-PCR primers. Right panel: AML12 cells transfected with ChREBP alpha/Mlx gamma & LXR alpha/RXR alpha were treated with DMSO (0.1%) or GW3965 (10 µM) for 18 h. ChREBP or LXR binding to genomic location indicated in the right panels were detected by ChIP using antibodies against ChREBP, LXR or IgG as negative control. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3–5). Significant differences are shown as * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 compared to ChIP-IgG & #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 between DMSO & GW3965 groups. ns, not significant. (B). CoIP of LXR alpha & ChREBP alpha, expressed in COS-1 cells cultured in 25 mM glucose, treated with DMSO (0.1%) or GW3965 (1 µM) for 18 h. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with ChREBP antibody (n = 3). Input & immunoprecipitated proteins were immunoblotted with ChREBP or LXR alpha antibodies. One representative western blot is shown. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32414201), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] -
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - Induction of hepatic Srebp-1 & carbohydrate response element-binding protein (Chrebp) beta expression by dietary glucose is reduced in LXR alpha−/− mice. (A) Hepatic gene expression of Lxr alpha/ beta, Srebp-1, & Chrebp alpha/ beta was analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR & normalized to Tbp; (B) Cytosolic & nuclear lysates were immunoblotted with antibodies against LXR, SREBP-1, & ChREBP with alpha-Tubulin & Lamin A as loading controls. Each lane represents independent mice from each group. One representative western blot is shown (n = 3). Data represent the mean ± SEM (n = 5). Significant differences were found using two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test (fasted vs. fructose fed & fasted vs. glucose fed RNA data were analyzed separately). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 compared to fasted. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 compared to LXR alpha+/+ mice. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (http://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/9/7/678), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] -
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - Decreased glucose uptake & Chrebp beta-driven DNL is a primary consequence of Rictor loss in adipocytes.(a) Western blots of indicated proteins at different days of differentiation using Rictor iKO primary adipocytes (described in Methods). (b) Oil Red O staining of differentiated adipocytes. (c) The relative mRNA level of ChREBP beta in differentiated cells at various time points. n=3. (d) 2-DG uptake in differentiated adipocytes without or with insulin stimulation. n=3. (e) The C14-glucose-derived FA in differentiated adipocytes. n=3. (f) The C14-glucose derived triglyceride (TAG) in differentiated adipocytes. n=3. (g) Relative glut4 expression in differentiated cells at various time points. n=3. (h) Relative glut4 expression in sWAT. n=8. (i) Glycerol release in differentiated adipocytes under basal & isoproterenol (Iso) stimulation. n=4. (j) Glycerol release in ex vivo pgWAT under basal & isoproterenol stimulation. n=6. Data were analysed by Student's t-test. Values are expressed as mean+s.e.m. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms11365), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] -
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - RetSat controls ChREBP activity & glucose sensing in primary hepatocytes. Primary mouse hepatocytes were treated with Control or RetSat siRNA for 48 h, (a, left) ChREBP mRNA expression determined by qPCR, & RetSat & ChREBP protein levels determined by immunoblotting (a, right). left, Data are shown as mean ± 11s.d., n = 3 independent transfections of hepatocyte cultures from the same mouse. Two independent experiments yielded similar results. b Hepatocytes were treated as described in a & mRNA expression of a selection of known ChREBP target genes visualized in a heatmap. c Primary hepatocytes were depleted of RetSat using two siRNA’s targeting different sites of the RetSat transcript for 48 h, & expression of the indicated genes analyzed by qPCR. Data are shown as mean ± s.d., n = 6 independent transfections of hepatocyte cultures from two different mice; *P < 0.05 between siControl und siRetSat by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post test. An independent experiment yielded similar results. d Hepatocytes treated with Control or RetSat siRNA were transfected with a ChoRE-Luc reporter, exposed to low & high glucose concentrations as indicated, & analyzed for luciferase activity. e Hepatocytes treated with Control or RetSat siRNA were exposed to low & high glucose concentrations as indicated, & mRNA expression determined by qPCR. In d, e, data are shown as mean ± s.d., n = 6 independent transfections of hepatocyte cultures from two mice; two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post test revealed significances between low & high glucose concentrations (#P < 0.05) & between siControl & siRetSat (*P < 0.05). An independent experiment yielded similar results Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-017-00430-w), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] -
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - LXR alpha & ChREBP alpha interact via key activation domains. (A). Top panel: Schematic representation of the ChREBP alpha full-length (FL), ChREBP beta & the low glucose inhibitory domain (LID) protein. Bottom panel: CoIP of LXR alpha & ChREBP alpha, ChREBP beta or LID, expressed in COS-1 cells cultured in 25 mM glucose. The ChREBP expression plasmids were transfected with a DNA ratio of ChREBP alpha:ChREBP beta:LID = 1:6:1, to obtain comparable protein levels. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with ChREBP, FLAG (for LID) or LXR alpha antibodies & input & immunoprecipitated proteins immunoblotted with the same antibodies (n = 3). One representative western blot is shown. LID, low-glucose inhibitory domain; GRACE, glucose-response activation conserved element; bHLH, basic helix-loop-helix domain: ZIP, leucine zipper. (B). Top panel: Schematic representation of the LXR alpha FL & truncations. Bottom panel: CoIP of ChREBP alpha & LXR alpha FL or truncations expressed in COS-1 cells cultured in 25 mM glucose. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with ChREBP antibody (n = 3). Input & immunoprecipitated proteins were immunoblotted with ChREBP or FLAG (for LXR alpha FL & truncations) antibodies. One representative western blot is shown. NTD, N-terminal domain; DBD, DNA-binding domain; LBD, ligand-binding domain. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32414201), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] -
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - FXR inhibits glucose-induced proglucagon expression(a) Proglucagon qPCR on cDNA from GLUTag cells starved for 12h with lactate (10 mmol L−1) & then incubated for 24h in lactate (10 mmol L−1), glucose (5.6 mmol L−1) or 2-deoxyglucose (5.6 mmol L−1) media containing DMSO, GW4064 (5 μmol L−1) or CDCA (100 μmol L−1) (n=3; performed 3 times). Data are represented as mean +/− SD. Two-Way ANOVA analysis followed by Bonferronni’s posthoc test. ***P≤0.001: effect of GW4064 & CDCA on proglucagon mRNA levels in each medium conditions. §§§P≤0.001: effect of glucose on proglucagon mRNA levels in DMSO, GW4064 & CDCA conditions. (b) Chrebp qPCR on cDNA from FACS-sorted proglucagon-negative & proglucagon-positive cells from the ileum (ileum L−; ileum L+) & colon (colon L−; colon L+) of GLU-VENUS mice (lower panel; n=3) & ChREBP protein expression from cytoplasm & nucleus extract from GLUTag cells (upper panel; performed 3 times). Data are represented as mean +/− SD. Student t-test. *P≤0.05 & **P≤0.01 (c) ChREBP & FXR western-blots after FXR immunoprecipitation on lysates from cytoplasm & nucleus of GLUTag cells treated or not with GW4064 (5 μmol L-1) in presence or not of glucose (5.6 mmol L−1) (performed 2 times). (d) Proglucagon qPCR on cDNA from GLUTag cells electroporated with a siCtrl or siChrebp, starved for 12h with lactate (10 mmol L−1) & then incubated for 24h in lactate 10 mmol L−1 (Glc −) or glucose 5.6 mmol L−1 (Glc +) media supplemented with DMSO or GW4064 (5 μmol L−1) (n=3; performed 3 times). Data are represented as mean +/− SD. Two-Way ANOVA analysis followed by Bonferronni’s posthoc test. *P≤0.05 & **P≤0.01: effect of treatments on each transfection condition. §§§P≤0.001: effect of siChrebp in each treatment condition. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms8629), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] -
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - Dietary fructose induces nuclear O-GlcNAc signaling. (A) Simplified schematic overview of the hexosamine signaling pathway including the rate limiting enzyme GFAT & O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT); (B) High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis of hepatic UDP-GlcNAc levels. Left panel: Example of a typical running profile w/ or w/out injection of UDP-GlcNAc standard (Std.) is shown. Right panel: Quantification of the HPLC data normalized to protein concentration; (C) Hepatic expression of the Ogt gene & cytosolic & nuclear OGT protein analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR & western blotting/Image J & normalized to Tbp, alpha-tubulin, & Lamin A, respectively. Data represent the mean ± SEM (n = 5); (D) Cytosolic & nuclear lysates immunoblotted w/ anti-O-GlcNAc antibody (RL2) w/ alpha-Tubulin & Lamin A as loading controls. Each lane represents independent mice from each group. One representative western blot is shown (n = 2); (E) Nuclear lysates subjected to wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) beads to precipitate O-GlcNAcylated proteins. WGA enriched samples (upper panel) & input lysates (bottom panel) immunoblotted w/ antibodies detecting O-GlcNAcylated proteins (RL2), LXR & ChREBP. Each lane represents independent mice from experimental groups. Representative western blots are shown (n = 2); (F) ChREBP binding to carbohydrate response element (ChoRE) containing region of the L-pk promoter & negative control sequence (NC) 2216–2288 bp into L-pk gene after ChoRE sequence detected by chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) using antibodies against ChREBP or IgG as a control. Data represent the mean ± SEM (n = 5). Significant differences found using two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test. ** p < 0.01 compared to fasted. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (http://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/9/7/678), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] -
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - Correction of hepatic G6Pase-alpha deficiency normalizes autophagy.L-G6pc-/- mice were treated with 1 x 1012 vp/kg of rAAV-G6PC at 4 WP & analyzed at 12 WP. (A) Hepatic G6Pase-alpha activity in control (n = 7), L-G6pc-/- (n = 7), & rAAV-treated L-G6pc-/- (AAV/ L-G6pc-/-, n = 8) mice. (B) Liver weights in control (n = 10), L-G6pc-/- (n = 5), & AAV/ L-G6pc-/- (n = 8) mice. (C) The levels of hepatic metabolites in control, L-G6pc-/- & AAV/ L-G6pc-/- (n = 8) mice. (D) Fasting glucose test (FGT) profile of control (n = 13), L-G6pc-/- (n = 6) & AAV/ L-G6pc-/- (n = 8) mice. (E) Western blots of hepatic SIRT1, FoxO3a, LC3B, p62 & beta-actin & densitometry analysis (n = 8). (F) Hematoxylin & eosin (H&E) stained liver sections, & immunohistochemical analysis of hepatic ChREBP & quantification of nuclear ChREBP-translocated cells in control, L-G6pc-/-, & rAAV-treated L-G6pc-/- (AAV/ L-G6pc-/-) mice (n = 4). The insets present higher magnification views. Scale bar, 25 μm. Data represent the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28558013), licensed under a CC0-1.0 license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] -
Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - Phf2 expression is increased in the liver of obese patients with benign hepatic steatosis & positively correlates with insulin sensitivity. Human liver biopsies from lean subjects with no fatty liver (NoFL) or obese patients with simple steatosis or NASH were obtained from the ABOS cohort. a Representative Western blot analysis of Phf2, ChREBP, SCD1, Nrf2, Gpx4, & alpha-SMA expression (n = 10 per group). b ChIP experiments for H3K9me2 levels & for the recruitment of ChREBP & the RNA polII at the SCD1 & Nrf2 promoter (n = 10 per group). c MUFA/SFA ratio reflecting SCD1 activity (n = 10 per group). d Expression of Nrf2 & Nrf2-regulated genes (n = 10 per group). e Levels of carbonylated proteins (n = 10 per group). f Expression of coll-Ia1, alpha-SMA, & TIMP-1 (n = 10 per group). All error bars represent mean ± SEM. Statistical analyses were made using Anova, followed by Bonferonni’s test. *Obese with steatosis compared to lean with noFL; P < 0.01. **Obese with steatosis compared to obese with NASH; P < 0.05 Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-018-04361-y), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.

![Western Blot: CHREBP AntibodyBSA Free [NB400-135] Western Blot: CHREBP AntibodyBSA Free [NB400-135]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/CHREBP-Antibody---BSA-Free-Western-Blot-NB400-135-img0023.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/CHREBP-Antibody---BSA-Free-Immunocytochemistry-Immunofluorescence-NB400-135-img0021.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/CHREBP-Antibody---BSA-Free-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NB400-135-img0016.jpg)
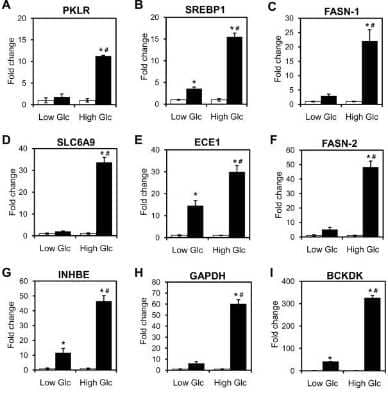
![Western Blot: CHREBP AntibodyBSA Free [NB400-135] Western Blot: CHREBP AntibodyBSA Free [NB400-135]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/CHREBP-Antibody---BSA-Free-Western-Blot-NB400-135-img0007.jpg)
![Western Blot: CHREBP AntibodyBSA Free [NB400-135] Western Blot: CHREBP AntibodyBSA Free [NB400-135]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/CHREBP-Antibody---BSA-Free-Western-Blot-NB400-135-img0010.jpg)
![Western Blot: CHREBP AntibodyBSA Free [NB400-135] Western Blot: CHREBP AntibodyBSA Free [NB400-135]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/CHREBP-Antibody---BSA-Free-Western-Blot-NB400-135-img0019.jpg)
![Western Blot: CHREBP AntibodyBSA Free [NB400-135] Western Blot: CHREBP AntibodyBSA Free [NB400-135]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/CHREBP-Antibody---BSA-Free-Western-Blot-NB400-135-img0020.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/CHREBP-Antibody---BSA-Free-Immunocytochemistry-Immunofluorescence-NB400-135-img0017.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] Immunohistochemistry: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/CHREBP-Antibody---BSA-Free-Immunohistochemistry-NB400-135-img0013.jpg)
![Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] Knockout Validated: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free-Knockout Validated-NB400-135-img0024.jpg)
![Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb400-135_rabbit-polyclonal-chrebp-antibody-271220231253379.jpg)
![Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb400-135_rabbit-polyclonal-chrebp-antibody-210202423452438.jpg)
![Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb400-135_rabbit-polyclonal-chrebp-antibody-310202415291928.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb400-135_rabbit-polyclonal-chrebp-antibody-310202415171345.jpg)
![Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb400-135_rabbit-polyclonal-chrebp-antibody-310202415171318.jpg)
![Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb400-135_rabbit-polyclonal-chrebp-antibody-31020241529337.jpg)
![Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb400-135_rabbit-polyclonal-chrebp-antibody-31020241534316.jpg)
![Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb400-135_rabbit-polyclonal-chrebp-antibody-310202415371929.jpg)
![Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb400-135_rabbit-polyclonal-chrebp-antibody-31020241528455.jpg)
![Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb400-135_rabbit-polyclonal-chrebp-antibody-310202416171431.jpg)
![Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb400-135_rabbit-polyclonal-chrebp-antibody-3102024161891.jpg)
![Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb400-135_rabbit-polyclonal-chrebp-antibody-310202416163714.jpg)
![Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb400-135_rabbit-polyclonal-chrebp-antibody-310202416165648.jpg)
![Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb400-135_rabbit-polyclonal-chrebp-antibody-310202416175271.jpg)
![Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb400-135_rabbit-polyclonal-chrebp-antibody-31020241616057.jpg)
![Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb400-135_rabbit-polyclonal-chrebp-antibody-310202416171465.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb400-135_rabbit-polyclonal-chrebp-antibody-310202416175247.jpg)
![Western Blot: CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free [NB400-135] - CHREBP Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb400-135_rabbit-polyclonal-chrebp-antibody-310202416163772.jpg)