Human AMICA/JAML PE-conjugated Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # FAB34491P

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Leu20-Leu275
Accession # Q86YT9
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human AMICA/JAML PE-conjugated Antibody
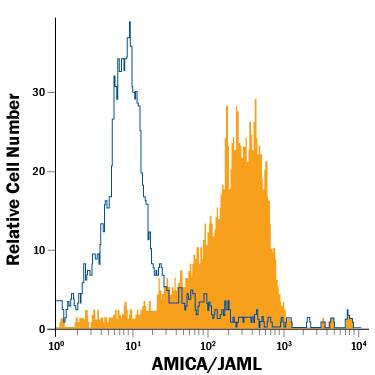
Detection of AMICA/JAML in Human Monocytes by Flow Cytometry.
Human monocytes were stained with Mouse Anti-Human AMICA/JAML PE-conjugated Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB34491P, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # IC003P, open histogram). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.Applications for Human AMICA/JAML PE-conjugated Antibody
Flow Cytometry
Sample: Human monocytes
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
Background: AMICA/JAML
AMICA (Adhesion Molecule, Interacting with CXADR Antigen 1), also known as JAML, is a 65 kDa, heavily glycosylated transmembrane protein that belongs to the junctional adhesion molecule (JAM) subset of the immunoglobulin superfamily (1). JAM family molecules contribute to intercellular connections within epithelial and endothelial cell layers, and mediate their interactions with various hemopoietic cells (1). The human AMICA cDNA encodes a 384 amino acid (aa) precursor that includes a 19 aa signal sequence, a 256 aa extracellular domain (ECD) with two Ig-like domains, a 21 aa transmembrane segment, and a 98 aa cytoplasmic domain (2). Alternative splicing may generate isoforms with N- and C-terminal deletions. In contrast to other JAM family proteins, AMICA does not contain a cytoplasmic PDZ-binding motif (3). Within the ECD, human AMICA shares 58% and 63% aa sequence identity with mouse and rat AMICA, respectively. It shares 18%‑20% aa sequence identity with the ECDs of human JAM-A, -B, -C, and JAM4. AMICA is expressed on the surface of granulocytes and monocytes and is upregulated during the differentiation of myeloid leukemia cells (2, 3). A motif in the ECD, which promotes dimerization of other JAM family proteins, is required for surface localization of AMICA (2). AMICA mediates the adhesion of monocytes to endothelial cells (2) and neutrophil migration across epithelial cell monolayers (3). This latter function involves specific interactions of AMICA with the coxsackie virus and adenovirus receptor (CXADR) in epithelial tight junctions (3). In particular, the membrane proximal Ig-like domain of AMICA binds the membrane-distal Ig-like domain of CXADR (3). AMICA does not appear to interact homophilically, as neutrophils adhere to immobilized CXADR but not to immobilized AMICA (3).
References
- Mandell, K.J. and C.A. Parkos (2005) Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 57:857.
- Moog-Lutz, C. et al. (2003) Blood 102:3371.
- Zen, K. et al. (2005) Mol. Biol. Cell 16:2694.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional AMICA/JAML Products
Product Documents for Human AMICA/JAML PE-conjugated Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human AMICA/JAML PE-conjugated Antibody
For research use only