Human B7-H1/PD-L1 PerCP-conjugated Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # FAB1561C

Key Product Details
Validated by
Species Reactivity
Applications
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Phe19-Thr239
Accession # Q9NZQ7
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human B7-H1/PD-L1 PerCP-conjugated Antibody
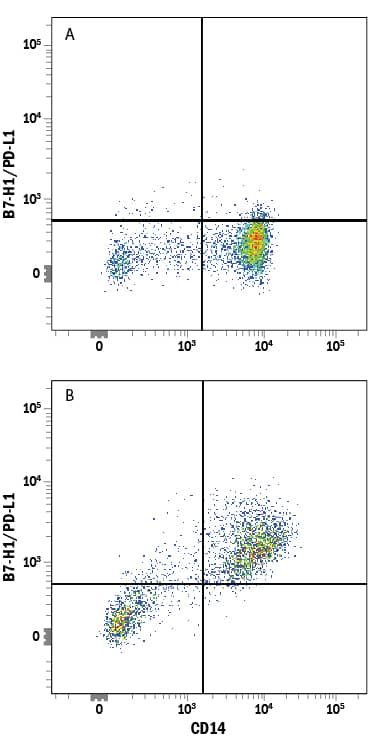
Detection of B7-H1/PD-L1 in Human PBMCs by Flow Cytometry.
Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) (A) resting or (B) treated with 1 µg/mL LPS overnight were stained with Mouse Anti-Human CD14 Fluorescein-conjugated Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB3832F) and Mouse Anti-Human B7-H1/PD-L1 PerCP-conjugated Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB1561C). Quadrant markers were set based on control antibody staining (Catalog # IC002C). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.Applications for Human B7-H1/PD-L1 PerCP-conjugated Antibody
Flow Cytometry
Sample: Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) treated with LPS
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, 2 to 8 °C as supplied.
Background: PD-L1/B7-H1
Human B7 homolog 1 (B7-H1), also called programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) and programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PDCD1L1), is a member of the growing B7 family of immune proteins that provide signals for both stimulating and inhibiting T cell activation. Other family members include B7-1, B7-2, B7-H2, PDL2 and B7-H3. B7 proteins are members of the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily. Their extracellular domains contain 2 Ig-like domains and all members have short cytoplasmic domains. Among the family members, there is about 20-25% amino acid identity. Human and mouse B7-H1 share approximately 70% amino acid sequence identity. B7-H1 has been identified as one of two ligands for programmed death-1 (PD-1), a member of the CD28 family of immunoreceptors. The B7-H1 gene encodes a 291 amino acid (aa) type I membrane precursor protein with a putative 18 aa signal peptide, a 220 aa extracellular domain, a 21 aa transmembrane region, and a 31 aa cytoplasmic domain. Human B7-H1 is constitutively expressed in several organs such as heart, skeletal muscle, placenta and lung, and in lower amounts in thymus, spleen, kidney and liver. B7-H1 expression is upregulated in a small fraction of activated T and B cells and a much larger fraction of activated monocytes. B7-H1 expression is also induced in dendritic cells and keratinocytes after IFN-gamma stimulation. Interaction of B7-H1 with PD-1 results in inhibition of TCR-mediated proliferation and cytokine production. The B7-H1:PD-1 pathway is involved in the negative regulation of some immune responses and may play an important role in the regulation of peripheral tolerance.
References
- Nishimura, H. and T. Honjo (2001) Trends Immunol. 22:265.
- Freeman, G.J. et al. (2000) J. Exp. Med. 192:1027.
- Latchman, Y. et al. (2001) Nat. Immunol. 2:261.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional PD-L1/B7-H1 Products
Product Documents for Human B7-H1/PD-L1 PerCP-conjugated Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human B7-H1/PD-L1 PerCP-conjugated Antibody
For research use only