Human CCL22/MDC Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB336

Key Product Details
Validated by
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Gly25-Gln93
Accession # O00626.1
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Endotoxin Level
Scientific Data Images for Human CCL22/MDC Antibody
Chemotaxis Induced by CCL22/MDC and Neutralization by Human CCL22/MDC Antibody.
Recombinant Human CCL22/MDC (Catalog # 336-MD) chemoattracts the BaF3 mouse pro-B cell line transfected with human CCR4 in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). The amount of cells that migrated through to the lower chemotaxis chamber was measured by Resazurin (Catalog # AR002). Chemotaxis elicited by Recombinant Human CCL22/MDC (10 ng/mL) is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Mouse Anti-Human CCL22/MDC Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB336). The ND50 is typically 0.6-3.0 µg/mL.Detection of Human CCL22/MDC by Western Blot
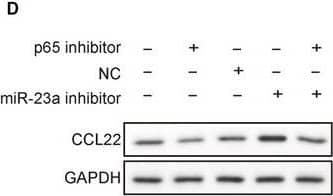
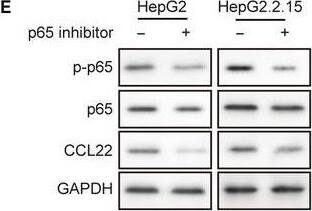
MiR‐23a inhibitor reversed p65 inhibition effects on HBV‐positive xenograft tumor growth. A, Xenografted tumors were harvested after different treatments. B and C, p65 inhibitor treatment significantly retarded tumor growth and miR‐23a inhibitor promoted tumor growth as indicated by the tumor weight and size. The therapeutic effects of p65 inhibitor were abolished by cotreatment with miR‐23a inhibitor. D, CCL22 protein levels from each group were detected by western blotting. E, Statistical results in D. p65 inhibitor led to reduction of CCL22 protein level but miR‐23a inhibitor increased CCL22 level in tumor tissues. F, p65 inhibitor led to reduction of CCL22 mRNA level but miR‐23a inhibitor increased CCL22 mRNA level in tumor tissues. MiR‐23a inhibitor reversed p65 inhibition effects on CCL22 level in tumor tissues. Error bars represented mean ± SD. *P < .05 and **P < .01 Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31769216), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Detection of Human CCL22/MDC by Western Blot
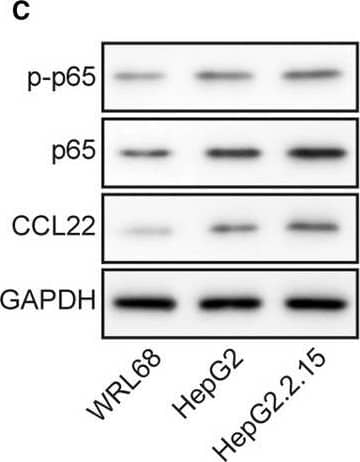
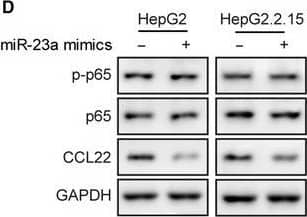
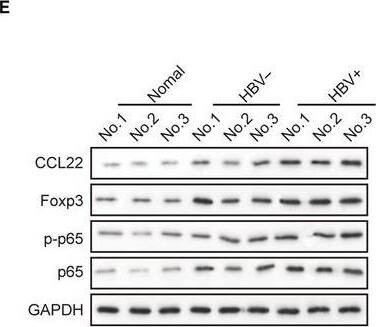
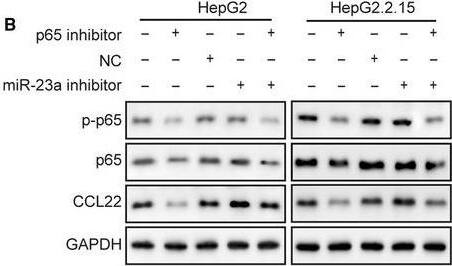
MiR‐23a, p‐p65, p65, and CCL22 levels were dysregulated in HCC cell lines. A, RT‐qPCR revealed that miR‐23a expression was lowest in the HBV‐positive HepG2.2.15 cell line. B, Highest mRNA level of CCL22 was observed in HepG2.2.15. C, Protein levels of p‐p65, p65, and CCL22 in three cell lines were determined by Western blotting. D, The gray scale analysis of p‐p65, p65, CCL22 and ratio of p‐p65/p65 in three cell lines. Expression of CCL22, p‐p65, and p65 were higher in HBV+ HepG2.2.15 cells than their parental HBV‐ HepG2 cells and normal WRL68 cells. Error bars represented mean ± SD. **P < .01 and *P < .05 Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31769216), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Human CCL22/MDC Antibody
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Human CCL22/MDC (Catalog # 336-MD)
Neutralization
Human CCL22/MDC Sandwich Immunoassay
Reviewed Applications
Read 2 reviews rated 4 using MAB336 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: CCL22/MDC
CCL22, also named stimulated T cell chemotactic protein (STCP-1) and MDC, is a CC chemokine initially isolated from clones of monocyte-derived macrophages. Human CCL22 cDNA encodes a precursor protein of 93 amino acid residues with a 24 amino acid residue predicted signal peptide that is cleaved to yield a 69 amino acid residue mature 8 kDa protein. At the amino acid sequence level, CCL22 shows less than 35% identity to other CC chemokine family members. Human CCL22 is expressed in dendritic cells, macrophages and activated monocytes. In addition, CCL22 expression is also detected in the tissues of thymus, lymph node and appendix. The gene for human CCL22 has been mapped to chromosome 16 rather than chromosome 17 where the genes for many human CC chemokines are clustered. Recombinant or chemically synthesized mature CCL22 has been shown to induce chemotaxis or Ca2+ mobilization in dendritic cells, IL-2 activated NK cells, and activated T lymphocytes. A CD8+ T lymphocyte-derived secreted soluble activity that suppresses infection by primary non-syncytium-inducing and syncytium-inducing HIV-1 isolates and the T cell line-adapted isolate HIV-1IIIB, has been identified as CCL22. Based on amino-terminal sequence analysis, the major CD8+ T lymphocyte-derived CCL22 protein yielded an amino-terminal sequence of YGANM, which is two amino acid residues shorter than the predicted mature CCL22. The difference in potency between the two mature CCL22 isoforms has not been determined.
References
- Godiska, R. et al. (1997) J. Exp. Med. 185:1595.
- Chang, M-S. et al. (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272:25229.
- Pal, R. et al. (1997) Science 278:5338.
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional CCL22/MDC Products
Product Documents for Human CCL22/MDC Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human CCL22/MDC Antibody
For research use only