Human DC-SIGN+DC-SIGNR PE-conjugated Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # FAB1621P

Conjugate
Catalog #
Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Human
Cited:
Human
Applications
Validated:
Flow Cytometry
Cited:
Flow Cytometry
Label
Phycoerythrin (Excitation = 488 nm, Emission = 565-605 nm)
Antibody Source
Monoclonal Mouse IgG2A Clone # 120612
Product Specifications
Immunogen
NIH-3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line transfected with human DC-SIGNR
Accession # Q9H2X3
Accession # Q9H2X3
Specificity
Recognizes both human DC-SIGN and human DC-SIGNR on transfected cells. Does not react with parental mouse cells or irrelevant transfectants.
Clonality
Monoclonal
Host
Mouse
Isotype
IgG2A
Scientific Data Images for Human DC-SIGN+DC-SIGNR PE-conjugated Antibody
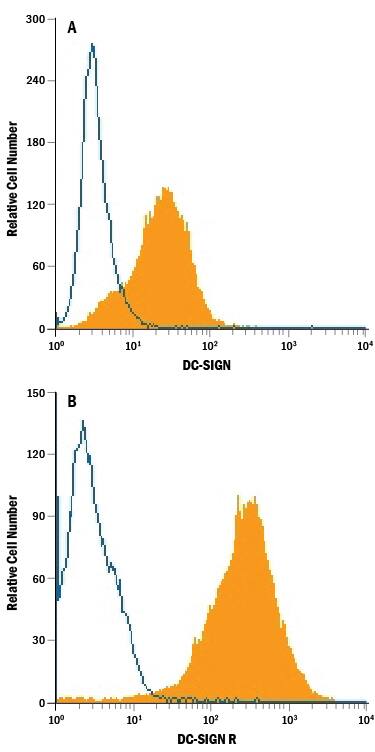
Detection of DC‑SIGN+DC‑SIGNR in NIH‑3T3 Mouse Cell Line Transfected with Human DC-SIGN and DC-SIGNR by Flow Cytometry.
NIH-3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line transfected with (A) human DC-SIGN and (B) human DC-SIGNR was stained with Mouse Anti-Human DC-SIGN+DC-SIGNR PE-conjugated Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB1621P, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # IC003P, open histogram). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.Applications for Human DC-SIGN+DC-SIGNR PE-conjugated Antibody
Application
Recommended Usage
Flow Cytometry
10 µL/106 cells
Sample: NIH‑3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line transfected with human DC-SIGN and human DC-SIGNR
Sample: NIH‑3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line transfected with human DC-SIGN and human DC-SIGNR
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Protein A or G purified from hybridoma culture supernatant
Formulation
Supplied in a saline solution containing BSA and Sodium Azide.
Shipping
The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below.
Stability & Storage
Protect from light. Do not freeze.
- 12 months from date of receipt, 2 to 8 °C as supplied.
Background: DC-SIGN+DC-SIGNR
References
- Geijtenbeek, T.B.H. et al. (2000) Cell 100:575.
- Geijtenbeek, T.B.H. et al. (2000) Cell 100:587.
- Yokoyama-Kobayashi, M.T. et al. (1999) Gene 228:161.
- Soilleux, E.J. et al. (2000) J. Immunol. 165:2937.
- Bashirova, A.A. et al. (2001) J. Exp. Med. 193:671.
- Mummidi, S. et al. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276:33196..
- Pohlman, S. et al. (2001) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:2670.
- Geijtenbeek, T.B.H. et al. (2000) Nature Immunol. 1:353.
Long Name
Dendritic Cell-specific ICAM-3-grabbing Non-integrin
Alternate Names
DCSIGN+DCSIGNR
Entrez Gene IDs
30835 (Human)
Gene Symbol
CD209
UniProt
Additional DC-SIGN+DC-SIGNR Products
Product Documents for Human DC-SIGN+DC-SIGNR PE-conjugated Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human DC-SIGN+DC-SIGNR PE-conjugated Antibody
For research use only
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...