Human EGFR F(ab')2 (Research Grade Depatuxizumab Biosimilar) Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB9583

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Applications
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human EGFR F(ab')2 (Research Grade Depatuxizumab Biosimilar) Antibody
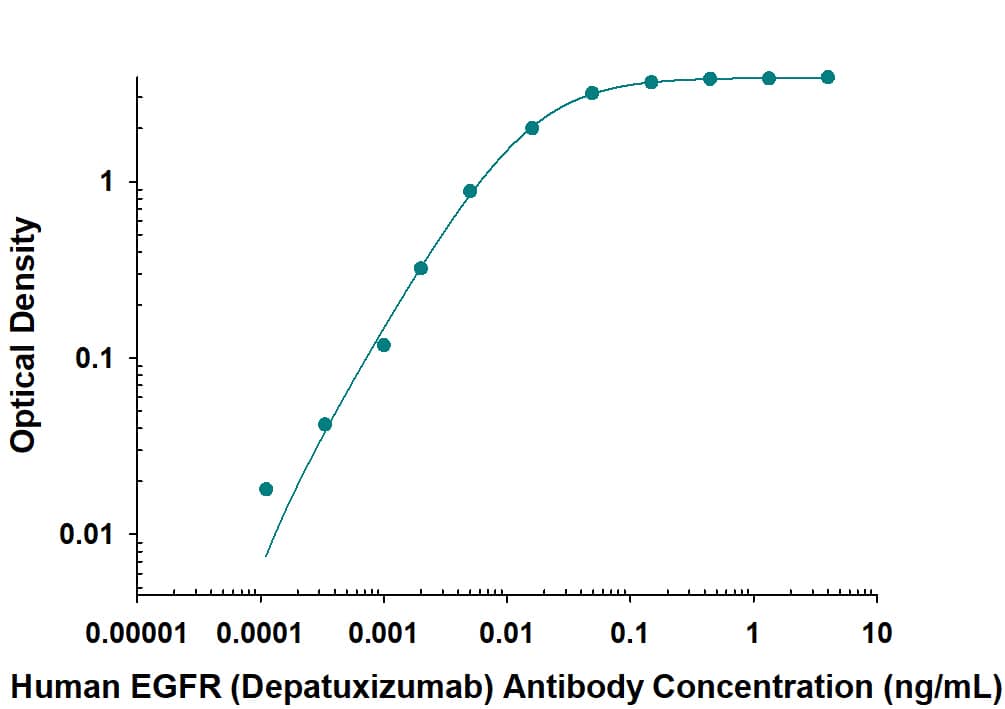
Human EGFR ELISA Standard Curve
Direct ELISA binding curve demonstrating the recognition of Human Anti-Human EGFR F(ab')2 (Research Grade Depatuxizumab Biosimilar) Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB9583) to EGFR. The target protein was coated onto the microplate well surface, followed by binding of the antibody. A goat anti-human HRP conjugate was used for detection.Applications for Human EGFR F(ab')2 (Research Grade Depatuxizumab Biosimilar) Antibody
ELISA
This antibody functions as an ELISA detection antibody for the specific antigen in direct ELISA. Colorimetric detection is performed after addition of a suitable substrate.
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: EGFR
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR), also named erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog 1 (ErbB1), is a member of the type I receptor tyrosine kinase superfamily. The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) subfamily of receptor tyrosine kinases comprises four members: EGFR (also known as HER1, ErbB1or ErbB), ErbB2 (Neu, HER2), ErbB3 (HER3), and ErbB4 (HER4). All family members are type I transmembrane glycoproteins that have an extracellular domain with two ligand binding cysteine rich domains, separated by a spacer region, and a cytoplasmic domain with a membrane proximal tyrosine kinase domain and a C-terminal tail with multiple tyrosine autophosphorylation sites. The human EGFR geneencodes a 1210 amino acid (aa) residue precursor with a 24 aa putative signal peptide, a 621 aa extracellular domain, a 23 aa transmembrane domain, and a 542 aa cytoplasmic domain. EGFR has been shown to bind a subset of the EGF family ligands, including EGF, amphiregulin, TGF alpha, betacellulin, epiregulin, heparin-binding EGF and neuregulin-2 alpha, in the absence of a coreceptor. Ligand binding induces EGFR homodimerization as well as heterodimerization with ErbB2, resulting in kinase activation, tyrosine phosphorylation and cell signaling. EGFR can also be recruited to form heterodimers with ligand-activated ErbB3 or ErbB4. EGFR signaling has been shown to regulate multiple biological functions including cell proliferation, differentiation, motility and apoptosis. In addition, EGFR signaling has also been shown to play a role in carcinogenesis (1-3).
References
- Daly, R.J. (1999) Growth Factors, 16:255.
- Schlessinger, J. (2000) Cell. 103:211.
- Maihle, N.J. et al. (2002) Cancer Treat. Res. 107:247.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
Additional EGFR Products
Product Specific Notices for Human EGFR F(ab')2 (Research Grade Depatuxizumab Biosimilar) Antibody
For research use only