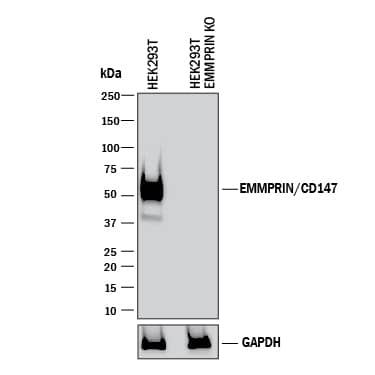
Detection of Human EMMPRIN/CD147 by Western Blot
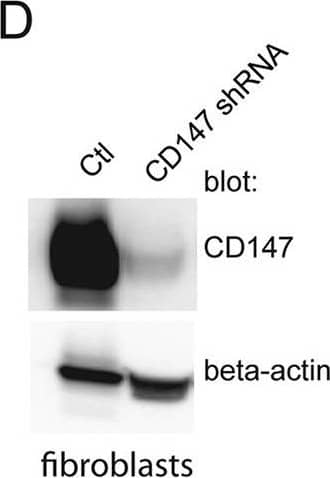
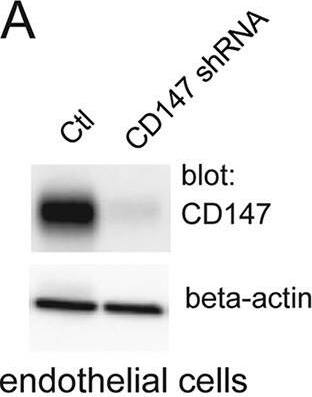
Silencing CD147 inhibits HCMV entry into endothelial cells. (A) Lysates from a control endothelial cell line (tAECs) transduced with an empty lentivirus vector (Ctl) or an endothelial cell line (tAECs) transduced with a lentivirus expressing a CD147-specific shRNA (CD147 shRNA; clone ID V3LHS_412785; Dharmacon) were analyzed in Western blot assays to determine the level of CD147 silencing. Membranes were probed with either anti-CD147 MAb 109403 or a rabbit polyclonal antibody against beta-actin (a loading control). (B) Human endothelial cells (tAECs) were transduced with an empty lentivirus vector (Ctl, lacking any shRNA) or a lentivirus vector expressing an shRNA to CD147 (CD147 shRNA) and then selected by puromycin. The cells lines were then infected with HCMV strain BADrUL131, and the level of entry was assessed by monitoring GFP expression from at least three independent wells. (C) The lentivirus-transduced cell lines in panel B were infected with HSV-1 VP26-GFP and analyzed for GFP expression after 24 h. (D) Lysates from control fibroblasts transduced with an empty lentivirus vectors (Ctl) or CD147 shRNA-expressing fibroblasts (CD147 shRNA) were analyzed by Western blotting to characterize CD147 silencing as described for panel A. (E) Fibroblast cell lines that had been transduced with an empty lentivirus vector (Ctl) or a lentivirus vector expressing an shRNA to CD147 (CD147 shRNA) were established using puromycin and then infected with HCMV BADrUL131, after which the number of GFP-positive cells was analyzed. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/mBio.00781-18), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Human EMMPRIN/CD147 by Western Blot
Silencing CD147 inhibits HCMV entry into endothelial cells. (A) Lysates from a control endothelial cell line (tAECs) transduced with an empty lentivirus vector (Ctl) or an endothelial cell line (tAECs) transduced with a lentivirus expressing a CD147-specific shRNA (CD147 shRNA; clone ID V3LHS_412785; Dharmacon) were analyzed in Western blot assays to determine the level of CD147 silencing. Membranes were probed with either anti-CD147 MAb 109403 or a rabbit polyclonal antibody against beta-actin (a loading control). (B) Human endothelial cells (tAECs) were transduced with an empty lentivirus vector (Ctl, lacking any shRNA) or a lentivirus vector expressing an shRNA to CD147 (CD147 shRNA) and then selected by puromycin. The cells lines were then infected with HCMV strain BADrUL131, and the level of entry was assessed by monitoring GFP expression from at least three independent wells. (C) The lentivirus-transduced cell lines in panel B were infected with HSV-1 VP26-GFP and analyzed for GFP expression after 24 h. (D) Lysates from control fibroblasts transduced with an empty lentivirus vectors (Ctl) or CD147 shRNA-expressing fibroblasts (CD147 shRNA) were analyzed by Western blotting to characterize CD147 silencing as described for panel A. (E) Fibroblast cell lines that had been transduced with an empty lentivirus vector (Ctl) or a lentivirus vector expressing an shRNA to CD147 (CD147 shRNA) were established using puromycin and then infected with HCMV BADrUL131, after which the number of GFP-positive cells was analyzed. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/mBio.00781-18), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Human EMMPRIN/CD147 by Flow Cytometry
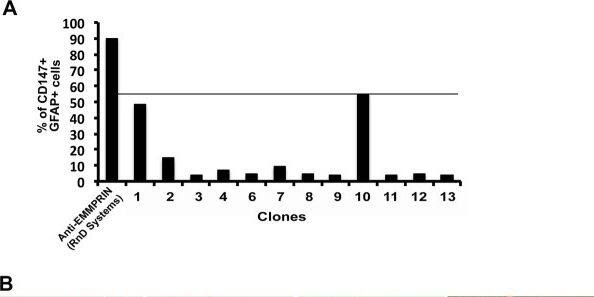
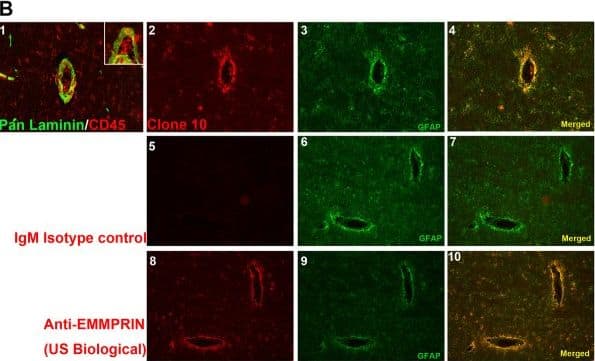
Clone 10 binding efficiency in human cells and tissue.(A) Using fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis, human fetal astrocytes stained for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) were additionally stained with hybridoma supernatants from several clones (1 to 13, no clone 5) and with the commercial anti-human extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) antibody (R&D Systems). (B) Immunofluorescence staining of postmortem multiple sclerosis (MS) brain samples for laminin/CD45 (1; higher magnification inset) and GFAP (3, 4, 6, 7, 9, 10), and with clone 10 (2, 4), IgM isotype control (5, 7) and commercial anti-EMMPRIN (US Biological, Table 1) antibodies (8, 10). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22480370), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
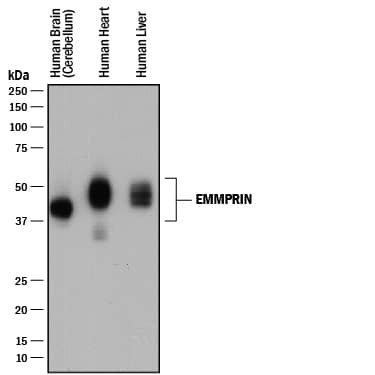
Detection of Mouse EMMPRIN/CD147 by Western Blot
Clone 10 binds most efficiently to extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) in western blots. Hybridoma supernatants from several clones are used in a western blot to detect 5 μg of recombinant human EMMPRIN (rhE; lane 1), 10 μg of mouse central nervous system (CNS) homogenate (m; lane 2) and 10 μg of human CNS homogenate (h; lane 3), EMMPRIN has an approximate molecular weight of 55 kDa. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22480370), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Human EMMPRIN/CD147 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
Clone 10 binding efficiency in human cells and tissue.(A) Using fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis, human fetal astrocytes stained for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) were additionally stained with hybridoma supernatants from several clones (1 to 13, no clone 5) and with the commercial anti-human extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) antibody (R&D Systems). (B) Immunofluorescence staining of postmortem multiple sclerosis (MS) brain samples for laminin/CD45 (1; higher magnification inset) and GFAP (3, 4, 6, 7, 9, 10), and with clone 10 (2, 4), IgM isotype control (5, 7) and commercial anti-EMMPRIN (US Biological, Table 1) antibodies (8, 10). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22480370), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Human EMMPRIN/CD147 by Western Blot
Inhibition of HCMV entry via anti-CD147 antibodies. (A) Human ARPE-19 epithelial cells were left untreated (No Ab) or were pretreated with MAbs specific for the transferrin receptor (TfR) or CD147 (MAbs 9B10, M61, 109403, 2F5, and 12G10) for 1 h at 37°C and then HCMV BADrUL131 was added to these cells in the presence of the MAbs for an additional 2 h at 37°C. The virus inoculum was removed, and the culture medium was replenished with fresh growth medium that contained the MAbs for 24 h, after which HCMV entry was assessed. (B) Human retinal epithelial cells were either left untreated or treated with antibodies as described above and then incubated with HSV-1 F-BAC VP26GFP, an HSV recombinant that express a GFP-tagged tegument protein. (C and D) Antibody inhibition assays were performed as described for panel A with HUVECs or fibroblast cells, respectively, and then challenged with HCMV BADrUL131. Under all experimental conditions, virus entry was quantified by counting GFP-positive from at least three independent wells, and these values compared to the numbers of GFP-positive cells among those not treated with antibodies. (E) Lysates from epithelial, endothelial, or fibroblast cells were analyzed by Western blotting to detect endogenous CD147 by probing membranes with anti-CD147 MAb 109403 or with polyclonal antibodies against beta-actin as a loading control. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/mBio.00781-18), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Human EMMPRIN/CD147 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
HCMV colocalizes with CD147 in early endosomes. ARPE-19 epithelial cells on glass slides were transduced with a baculovirus expressing a fluorescent-tagged early endosome marker, EEA-1. The cells were then incubated with HCMV UL32-GFP virus particles for 1 h at 4°C and then shifted to 37°C for 1 h. The cells were fixed and processed for immunofluorescent staining with an anti-CD147 MAb (109403) followed by a 649-conjugated secondary antibody to detect CD147 and then analyzed by deconvolution microscopy. (A and B) Representative images with arrows depict HCMV particles (green) colocalizing with CD147 (red) in EEA-1-labeled endosomes (blue). (C to E) More highly magnified images of HCMV particles (green) colocalizing with CD147 (red) and EEA-1-labeled endosomes (blue). The scale bars on the bottom left of each panel represent 1 µm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/mBio.00781-18), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Human EMMPRIN/CD147 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
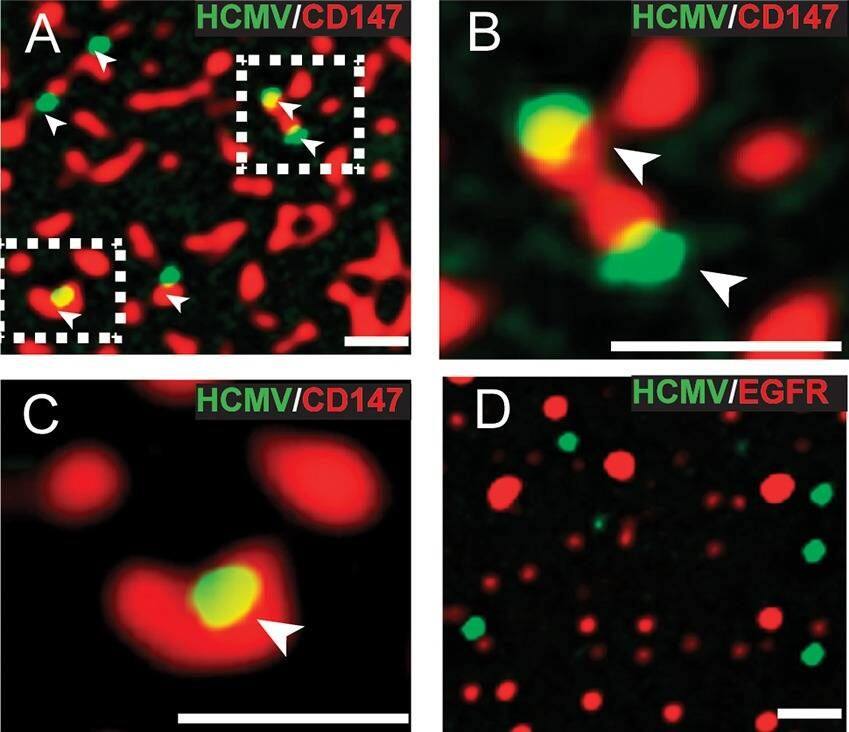
HCMV colocalizes with CD147 patches on the surface of ARPE-19 cells. (A) ARPE-19 cells on glass slides were incubated with anti-CD147 MAb 109403 and HCMV UL32-GFP virus particles at 4° for 1 h, then shifted to 37° for 15 min, and then fixed. The fixed cells were then incubated with goat anti-mouse–594 fluorescent secondary antibody to detect surface CD147 and then the cells were analyzed by deconvolution microscopy. Arrows indicate green fluorescent HCMV virus particles that overlapped with red fluorescent channel signal from CD147 surface patches. (B and C) Magnified images of the squared areas from panel A. (D) ARPE-19 cells were incubated with anti-EGFR MAb (LA1) and HCMV UL32-GFP virus particles at 4°C for 1 h, then shifted to 37°C for 15 min, fixed, and then processed to detect surface EGFR as described for panel A. The scale bars on the bottom right of each panel represent 1 µm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/mBio.00781-18), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Human EMMPRIN/CD147 by Western Blot
Effects of soluble CD147 on HCMV entry and binding to soluble HCMV glycoproteins. (A) A soluble form of CD147 that was fused to a polyhistidine epitope tag and purified from the tissue culture supernatant of plasmid-transfected 293E cells via use of nickel-agarose was analyzed by electrophoresis, polyacrylamide gel staining, and Coomassie brilliant blue stain. (B) Soluble CD147 was bound to nickel-coated plates and then analyzed in an ELISA. Individual wells were incubated with either a control MAb to transferrin (TfR) or CD147-specific MAbs 109403, 12G10, or 2F5, followed by goat anti-mouse–HRP conjugate. Controls also included incubation with secondary antibodies only (secondary). The bound antibodies were detected by chemiluminescence by adding Turbo-TMB ELISA substrate (Thermo Fisher), and absorbance was read using a precision plate reader (Molecular Dynamics). (C) HCMV BADrUL131 virus particles were incubated with soluble CD147 (sol. CD147+) at 100 µg ml−1 or no protein (sol. CD147 -) for 1 h at 37°C and then added to ARPE-19 epithelial cells or HUVECs for 2 h at 37°C. The virus inoclula were removed, and cells were incubated an additional 24 h before the numbers of GFP+ cells were assessed. Relative infectivity was calculated by comparing the numbers of GFP+ cells in soluble CD147 treated groups versus no-protein controls. (D) Soluble CD147 (black bars) or soluble PDGFR alpha (gray bars) were allowed to adsorb onto microtiter plates and then incubated with soluble gH/gL (dimer), trimer, or pentamer complexes. The plates were washed and then incubated with anti-gH MAb 14-4b, washed, and incubated with goat anti-mouse–HRP conjugate. Positive controls included anti-CD147 or anti-PDGFR alpha MAbs followed by secondary goat anti-mouse–HRP conjugate (CD147 pos. and PDGFR alpha pos.). Negative controls involved wells with adsorbed proteins incubated with secondary antibodies only (secondary). Chemiluminescence was detected as described for panel B. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/mBio.00781-18), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.