Human
EpCAM/TROP-1 PE-conjugated Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # FAB960P

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Gln24-Lys265
Accession # CAA32870
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human EpCAM/TROP-1 PE-conjugated Antibody
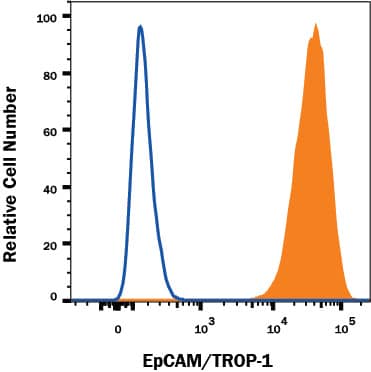
Detection of EpCAM/TROP‑1 in MCF‑7 Human Cell Line by Flow Cytometry.
MCF‑7 human breast cancer cell line was stained with Goat Anti-Human EpCAM/TROP‑1 PE‑conjugated Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB960P, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # IC108P, open histogram). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.Applications for Human EpCAM/TROP-1 PE-conjugated Antibody
Flow Cytometry
Sample: MCF‑7 human breast cancer cell line
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, 2 to 8 °C as supplied.
Background: EpCAM/TROP1
Epithelial Cellular Adhesion Molecule (EpCAM), also known as KS1/4, gp40, GA733-2, 17-1A, and TROP-1, is a 40 kDa transmembrane glycoprotein composed of a 242 amino acid (aa) extracellular domain with two epidermal-growth-factor-like (EGF-like) repeats within the cysteine-rich N-terminal region, a 23 aa transmembrane domain, and a 26 aa cytoplasmic domain. Human and mouse EpCAM share 82% aa sequence identity. In human, EpCAM also shares 49% aa sequence homology with TROP-2/EGP-1. During embryonic development, EpCAM is detected in fetal lung, kidney, liver, pancreas, skin, and germ cells. In adults, human EpCAM is detected in basolateral cell membranes of all simple, pseudo-stratified, and transitional epithelia, but is not detected in normal squamous stratified epithelia, mesenchymal tissue, muscular tissue, neuro-endocrine tissue, or lymphoid tissue (1). EpCAM expression has been found to increase in actively proliferating epithelia tissues and during adult liver regeneration (1, 2). EpCAM expression is also found to increase in human malignant neoplasias, with most carcinoma expressing EpCAM including those of arising from squamous epithelia (1). EpCAM has been shown function as a homophilic Ca2+ independent adhesion molecule (3). Homophilic adhesion via EpCAM requires the interaction of both EGF-like repeats, with the first EGF-like repeat mediating reciprocal interaction between EpCAM molecules on opposing cells, while the second repeat is involved in lateral interaction of EpCAM. Lateral interaction of EpCAM lead to the formation of dimers and tetramers (4). During homophilic adhesion the cytoplasmic tail of EpCAM interacts with the actin cytoskeleton via a direct association alpha-actinin (5).
References
- Balzar, M. et al. (1999) J. Mol. Med. 77:699.
- Boer, C.J. et al. (1999) J. Pathol. 188:201.
- Litvinow, S.V. et al. (1994) J. Cell Biol. 125:437.
- Balzar, M. et al. (2001) Mol. Cell. Biol. 21:2570.
- Balzar, M. et al. (1998) Mol. Cell. Biol. 18:4388.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional EpCAM/TROP1 Products
Product Documents for Human EpCAM/TROP-1 PE-conjugated Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human EpCAM/TROP-1 PE-conjugated Antibody
For research use only