Human GDF-11/BMP-11 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB19581

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Asn299-Ser407
Accession # O95390
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human GDF-11/BMP-11 Antibody
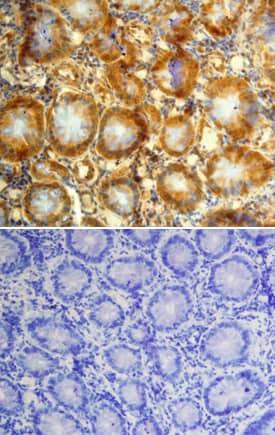
GDF‑11/BMP‑11 in Human Colon Cancer Tissue.
GDF-11/BMP-11 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human colon cancer tissue using Mouse Anti-Human GDF-11/BMP-11 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB19581) at 15 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Mouse HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS002) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Lower panel shows a lack of labeling when primary antibodies are omitted and tissue is stained only with secondary antibody followed by incubation with detection reagents. Specific staining was localized to epithelia of the colon. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.Detection of Mouse Human GDF-11/BMP-11 Antibody by Western Blot
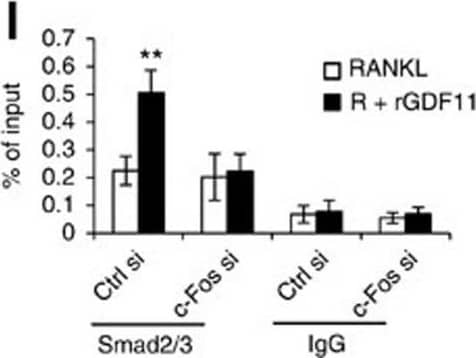
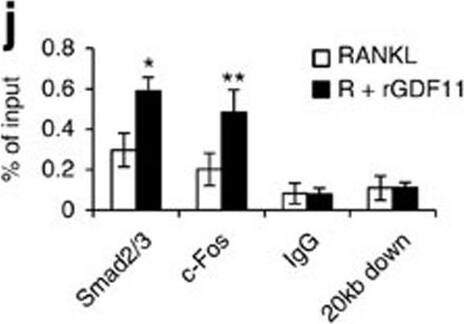
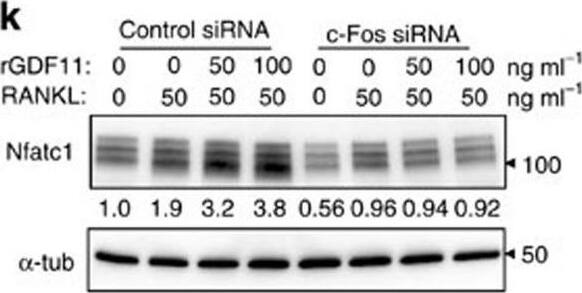
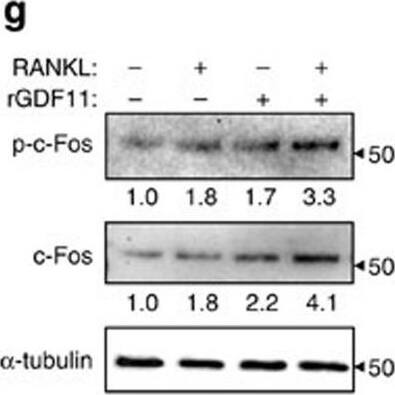
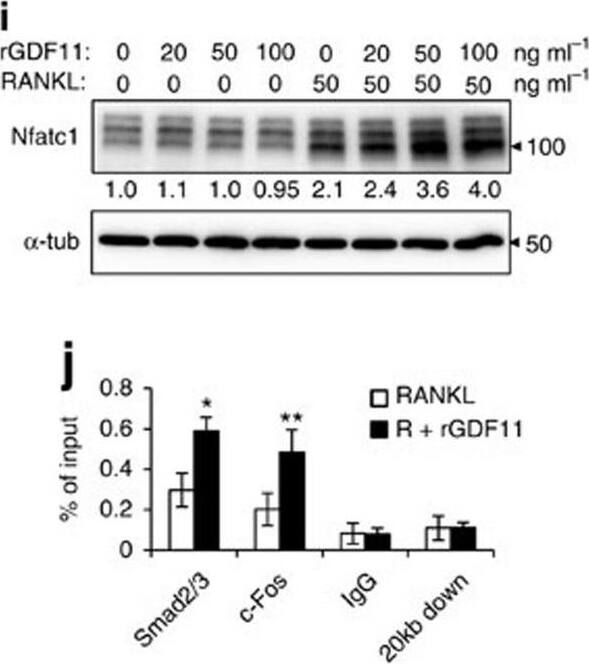
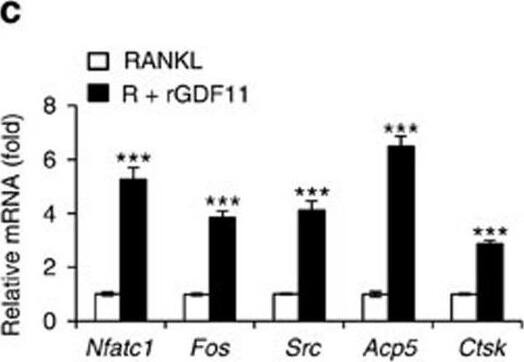
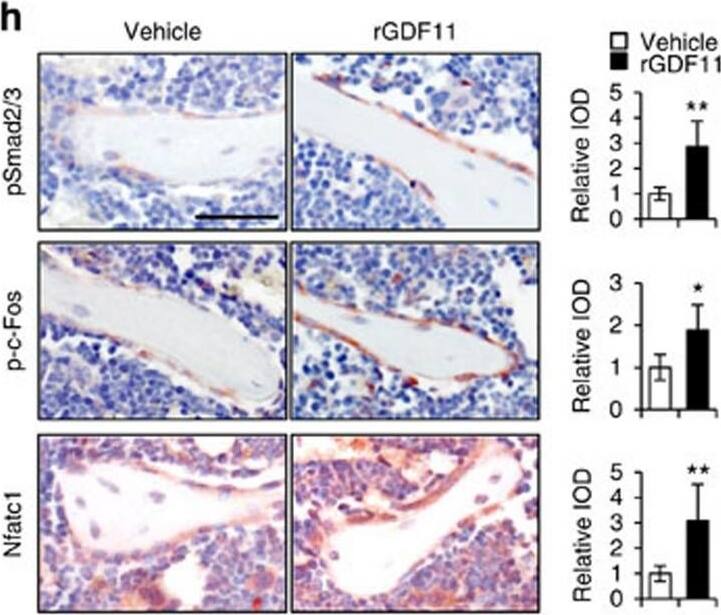
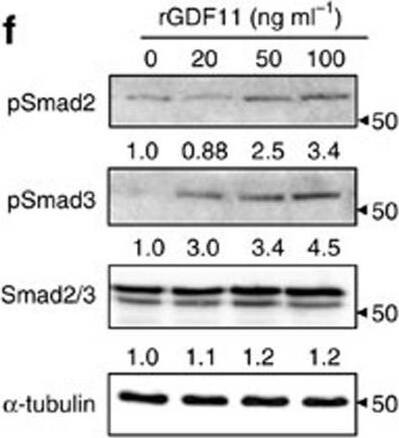
GDF11 activates Smad2/3-dependent TGF-beta pathway.(a) Gene expression levels of the BMMs stimulated without or with 100 ng ml−1 rGDF11 for 24 h (three biological replicates per group). 467 genes (red) were upregulated and 679 genes (black) were downregulated. 100 ng ml−1 M-CSF was present in all settings. (b) Heatmap of the osteoclastogenesis associated genes. (c) Quantitative RT-PCR confirmed the increased expression of osteoclast key marker genes. Results are shown as mean±s.d.; n=3. ***P<0.001 by t test. (d) KEGG pathway analysis indicated the altered function of TGF-beta pathway. (e) Heatmap of the TGF-beta pathway associated genes. (f) Western blot analysis indicated that rGDF11 stimulated the phosphorylation of Smad2/3 in BMMs in 30 min. (g) Western blot analysis demonstrated that rGDF11 amplified the RANKL-induced expression of c-Fos. BMMs were starved overnight and then treated for 4 h. (h) Representative images of immunohistochemical staining. rGDF11 injections increased the phosphorylation of Smad2/3 and c-Fos, as well as the expression of Nfatc1 in vivo. Femurs were collected ∼2 h after the last injection of rGDF11. Scale bar, 50 μm. (i) Western blot analysis indicated that rGDF11 stimulated the RANKL-induced expression of Nfatc1. BMMs were treated for 2 days. (j) ChIP assay revealed that rGDF11 induced the co-occupancy of Smad2/3 and c-Fos to the binding region of Nfatc1. Results are shown as mean±s.d.; n=3. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 by t test. (k) Western blot analysis of Nfatc1. Depletion of c-Fos eliminated the rGDF11 induced expression of Nfatc1. (l) ChIP assay. Depletion of c-Fos abolished rGDF11 triggered binding of Smad2/3 to Nfatc1. Results are shown as mean±s.d.; n=3. **P<0.01 by t test. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27653144), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Detection of Mouse Human GDF-11/BMP-11 Antibody by Western Blot
GDF11 activates Smad2/3-dependent TGF-beta pathway.(a) Gene expression levels of the BMMs stimulated without or with 100 ng ml−1 rGDF11 for 24 h (three biological replicates per group). 467 genes (red) were upregulated and 679 genes (black) were downregulated. 100 ng ml−1 M-CSF was present in all settings. (b) Heatmap of the osteoclastogenesis associated genes. (c) Quantitative RT-PCR confirmed the increased expression of osteoclast key marker genes. Results are shown as mean±s.d.; n=3. ***P<0.001 by t test. (d) KEGG pathway analysis indicated the altered function of TGF-beta pathway. (e) Heatmap of the TGF-beta pathway associated genes. (f) Western blot analysis indicated that rGDF11 stimulated the phosphorylation of Smad2/3 in BMMs in 30 min. (g) Western blot analysis demonstrated that rGDF11 amplified the RANKL-induced expression of c-Fos. BMMs were starved overnight and then treated for 4 h. (h) Representative images of immunohistochemical staining. rGDF11 injections increased the phosphorylation of Smad2/3 and c-Fos, as well as the expression of Nfatc1 in vivo. Femurs were collected ∼2 h after the last injection of rGDF11. Scale bar, 50 μm. (i) Western blot analysis indicated that rGDF11 stimulated the RANKL-induced expression of Nfatc1. BMMs were treated for 2 days. (j) ChIP assay revealed that rGDF11 induced the co-occupancy of Smad2/3 and c-Fos to the binding region of Nfatc1. Results are shown as mean±s.d.; n=3. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 by t test. (k) Western blot analysis of Nfatc1. Depletion of c-Fos eliminated the rGDF11 induced expression of Nfatc1. (l) ChIP assay. Depletion of c-Fos abolished rGDF11 triggered binding of Smad2/3 to Nfatc1. Results are shown as mean±s.d.; n=3. **P<0.01 by t test. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27653144), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Human GDF-11/BMP-11 Antibody
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human colon cancer tissue
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: GDF-11/BMP-11
Growth Differentiation Factor 11 (GDF-11), also known as BMP-11, is a member of the TGF-beta superfamily and is highly related to GDF-8. GDF-11 encodes a 407 amino acid (aa) prepropeptide which contains a signal sequence for secretion and an RXXR proteolytic processing site to yield a 109 aa residue carboxy-terminal mature protein (1). Mature GDF-11 contains the canonical 7-cysteine motif common to other TGF-beta superfamily members; however, like the TGF-beta s, Activins and GDF-8, GDF-11 also contains one extra pair of cysteine residues. At the amino acid sequence level, mature human, mouse, rat and chicken GDF-11 are 99‑100% identical. GDF-11 and GDF-8 share 90% amino acid sequence identity within the mature protein. As detected by in situ hybridization, GDF-11 is expressed in diverse regions of the mouse embryo: tailbud, somitic precursors, limbs, mandibular and branchial arches, dorsal neural tube, odontoblasts, nasal epithelium, and particular regions of the brain (1, 2). Likewise, a targeted deletion of GDF-11 in mice results in a spectrum of abnormalities including palatal malformation, vertebral defects, elongated trunks with a reduced or absent tail, missing or malformed kidneys, and an increased number of neurons in the olfactory epithelium (2-5). An intriguing finding in the knockout mice was that the trunk elongation was due to an increase in the number of thoracic vertebrae (4). This implicates GDF-11 as the first secreted factor to influence the specification of segmental identity in vertebrates (3). In fact, GDF-11 does regulate expression of segmental transcription factors, the Hox genes (6). GDF-11 signals through the Activin type II receptors and induces phosphorylation of Smad2 to mediate axial patterning (7). Despite the strong expression in the limb throughout development, no limb abnormalities were found in the knockout mice. However, in vitro micromass studies indicate that GDF-11 inhibits myogenic and chondrogenic cell differentiation and may impact formation and development of the limb skeleton (6).
References
- Gamer, L.W. et al. (1999) Dev. Biol. 208: 222.
- Nakashima, M. et al. (1999) Mech. Dev. 80:185.
- Gad, J.M. and P.P.L. Tam (1999) Curr. Biol. 9:R783.
- McPherron, A.C. et al. (1999) Nat. Genet. 22:260.
- Esquela, A.F. and S.J. Lee (2003) Dev. Biol. 257:356.
- Gamer, L.W. et al. (2001) Dev. Biol. 229:407.
- Oh, S.P. et al. (2002) Genes & Dev. 16:274.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional GDF-11/BMP-11 Products
Product Documents for Human GDF-11/BMP-11 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human GDF-11/BMP-11 Antibody
For research use only