Human HGFR/c-MET Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB5694

Key Product Details
Validated by
Species Reactivity
Applications
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Glu1120-Val1271
Accession # P08581
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human HGFR/c-MET Antibody
Detection of Human HGF R/c‑MET by Western Blot.
Western blot shows lysates of HeLa human cervical epithelial carcinoma cell line. Gels were loaded with 3 x 105cells (lane 1), 2 x 105cells (lane 2), and 1 x 105cells (lane 3). PVDF membrane was probed with 1 µg/mL Mouse Anti-Human HGF R/c-MET Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB5694) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF007). A specific band for HGF R/c-MET was detected at approximately 145 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.Western Blot Shows Human HGF R/c‑MET Specificity by Using Knockout Cell Line.
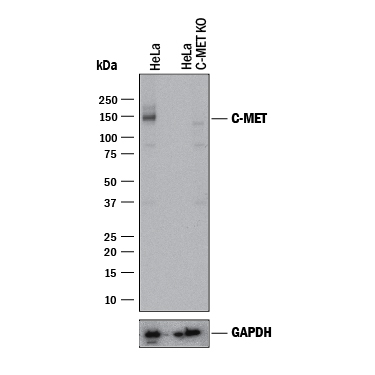
Western blot shows lysates of HeLa human cervical epithelial carcinoma parental cell line and HGF R/c-MET knockout HeLa cell line (KO). PVDF membrane was probed with 2 µg/mL of Mouse Anti-Human HGF R/c-MET Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB5694) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF018). A specific band was detected for HGF R/c-MET at approximately 150-200 kDa (as indicated) in the parental HeLa cell line, but is not detectable in knockout HeLa cell line. GAPDH (Catalog # MAB5718) is shown as a loading control. This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.Applications for Human HGFR/c-MET Antibody
Knockout Validated
Western Blot
Sample: HeLa human cervical epithelial carcinoma cell line
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: HGFR/c-MET
HGF R, also known as Met (from N-methyl-N’-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine induced), is a glycosylated receptor tyrosine kinase that plays a central role in epithelial morphogenesis and cancer development. HGF R is synthesized as a single chain precursor which undergoes cotranslational proteolytic cleavage. This generates a mature HGF R that is a disulfide-linked dimer composed of a 50 kDa extracellular alpha chain and a 145 kDa transmembrane beta chain (1, 2). The extracellular domain (ECD) contains a seven bladed beta-propeller sema domain, a cysteine-rich PSI/MRS, and four Ig-like E-set domains, while the cytoplasmic region includes the tyrosine kinase domain (3, 4). Proteolysis and alternate splicing generate additional forms of human HGF R which either lack of the kinase domain, consist of secreted extracellular domains, or are deficient in proteolytic separation of the alpha and beta chains (5-7). The sema domain, which is formed by both the alpha and beta chains of HGF R, mediates both ligand binding and receptor dimerization (3, 8). Ligand-induced tyrosine phosphorylation in the cytoplasmic region activates the kinase domain and provides docking sites for multiple SH2-containing molecules (9, 10). HGF stimulation induces HGF R downregulation via internalization and proteasome-dependent degradation (11). In the absence of ligand, HGF R forms non-covalent complexes with a variety of membrane proteins including CD44v6, CD151, EGF R, Fas, Integrin alpha6/ beta4, Plexins B1, 2, 3, and MSP R/Ron (12-19). Ligation of one complex component triggers activation of the other, followed by cooperative signaling effects (12-19). Formation of some of these heteromeric complexes is a requirement for epithelial cell morphogenesis and tumor cell invasion (12, 16, 17). Paracrine induction of epithelial cell scattering and branching tubulogenesis results from the stimulation of HGF R on undifferentiated epithelium by HGF released from neighboring mesenchymal cells (20). Genetic polymorphisms, chromosomal translocation, over-expression, and additional splicing and proteolytic cleavage of HGF R have been described in a wide range of cancers (1). Within the ECD, human HGF R shares 86-88% amino acid sequence identity with canine, mouse, and rat HGF R.
References
- Birchmeier, C. et al. (2003) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4:915.
- Corso, S. et al. (2005) Trends Mol. Med. 11:284.
- Gherardi, E. et al. (2003) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100:12039.
- Park, M. et al. (1987) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:6379.
- Crepaldi, T. et al. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269:1750.
- Prat, M. et al. (1991) Mol. Cell. Biol. 12:5954.
- Rodrigues, G.A. et al. (1991) Mol. Cell. Biol. 11:2962.
- Kong-Beltran, M. et al. (2004) Cancer Cell 6:75.
- Naldini, L. et al. (1991) Mol. Cell. Biol. 11:1793.
- Ponzetto, C. et al. (1994) Cell 77:261.
- Jeffers, M. et al. (1997) Mol. Cell. Biol. 17:799.
- Orian-Rousseau, V. et al. (2002) Genes Dev. 16:3074.
- Klosek, S.K. et al. (2005) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 336:408.
- Jo, M. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275:8806.
- Wang, X. et al. (2002) Mol. Cell 9:411.
- Trusolino, L. et al. (2001) Cell 107:643.
- Giordano, S. et al. (2002) Nat. Cell Biol. 4:720.
- Conrotto, P. et al. (2004) Oncogene 23:5131.
- Follenzi, A. et al. (2000) Oncogene 19:3041.
- Sonnenberg, E. et al. (1993) J. Cell Biol. 123:223.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional HGFR/c-MET Products
Product Documents for Human HGFR/c-MET Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human HGFR/c-MET Antibody
For research use only