Human Insulin R/CD220 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF1544

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Applications
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
His28-Lys944
Accession # NP_001073285
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human Insulin R/CD220 Antibody
Detection of Insulin R/CD220 in Human Blood Monocytes by Flow Cytometry.
Human peripheral blood monocytes were stained with Goat Anti-Human/Mouse Insulin R/CD220 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1544, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (AB-108-C, open histogram) followed by Phycoerythrin-conjugated anti-Goat IgG (F0107). Staining was performed using our Staining Membrane-associated Proteins protocol.Insulin R/CD220 in Human Liver.
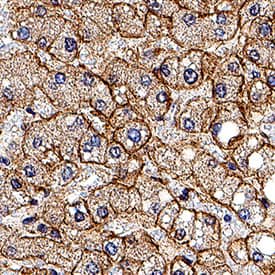
Insulin R/CD220 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human liver using Goat Anti-Human Insulin R/CD220 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1544) at 1 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Goat IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (VC004). Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (CTS013). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to cell membrane of hepatocytes. Staining was performed using our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.Insulin R/CD220 in Human Pancreas.
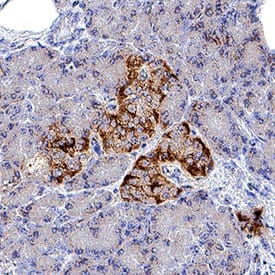
Insulin R/CD220 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human pancreas using Goat Anti-Human Insulin R/CD220 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1544) at 0.3 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Goat IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (VC004). Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (CTS013). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to cell membrane in islet cells. Staining was performed using our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.Applications for Human Insulin R/CD220 Antibody
CyTOF-ready
Flow Cytometry
Sample: Human peripheral blood monocytes
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human liver and immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human pancreas
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Human Insulin R/CD220 (Catalog # 1544-IR)
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Insulin R/CD220
The Insulin Receptor (INS R) and insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1 R) constitute a subfamily of receptor tyrosine kinases (1‑4). The two receptors share structural similarity as well as overlapping intracellular signaling events, and are believed to have evolved through gene duplication from a common ancestral gene. INS R cDNA encodes a type I transmembrane single chain preproprotein with a putative 27 amino acid residues (aa) signal peptide. The large INS R extracellular domain is organized into two successive homologous globular domains, which are separated by a Cysteine-rich domain, followed by three fibronectin type III domains. The intracellular region contains the kinase domain sandwiched between the juxtamembrane domain used for docking insulin-receptor substrates (IRS), and the carboxy-terminal tail that contains two phosphotyrosine-binding sites. After synthesis, the single chain INS R precursor is glycosylated, dimerized and transported to the Golgi apparatus where it is processed at a furin-cleavage site within the middle fibronectin type III domain to generate the mature disulfide-linked alpha2 beta2 tetrameric receptor. The alpha subunit is localized extracellularly and mediates ligand binding while the transmembrane beta subunit contains the cytoplasmic kinase domain and mediates intracellular signaling. As a result of alternative splicing, two INS R isoforms (A and B) that differ by the absence or presence, respectively, of a 12 aa residue sequence in the carboxyl terminus of the alpha subunit exist. Whereas the A isoform is predominantly expressed in fetal tissues and cancer cells, the B isoform is primarily expressed in adult differentiated cells. Both the A and B isoforms bind insulin with high-affinity, but the A isoform has considerably higher affinity for IGF‑I and IGF‑II. Ligand binding induces a conformational change of the receptor, resulting in ATP binding, autophosphorylation, and subsequent downstream signaling. INS R signaling is important in metabolic regulation, but may also contribute to cell growth, differentiation and apoptosis. Mutations in the INS R gene have been linked to insulin-resistant diabetes mellitus, noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and leprechaunism, an extremely rare disorder characterized by abnormal resistance to insulin that results in a variety of distinguishing characteristics, including growth delays and abnormalities affecting the endocrine system. INS R is highly conserved between species, rat INS R shares 94% and 97% aa sequence homology with the human and mouse receptor, respectively.
References
- Nakae, J. et al. (2001) Endoc. Rev. 22:818.
- De Meyts, P. and J. Whittaker (2002) Nature Rev. Drug Disc. 1:769.
- Kim, J.J. and D. Accili (2002) Growth Hormone and IGF Res. 12:84.
- Sciacca, L. et al. (2003) Endocrinology 144:2650.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Insulin R/CD220 Products
Product Documents for Human Insulin R/CD220 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human Insulin R/CD220 Antibody
For research use only