Human LDLR Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB2148

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Ala22-Arg788
Accession # P01130
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human LDLR Antibody
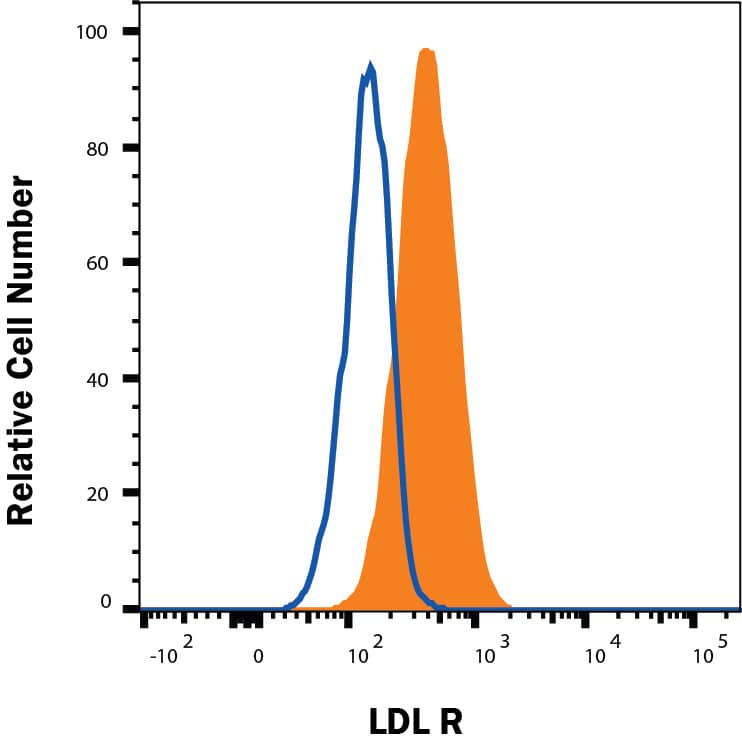
Detection of LDLR in HepG2 Human Cell Line by Flow Cytometry.
HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line was stained with Mouse Anti-Human LDLR Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB2148, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (MAB002, open histogram), followed by PE-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG F(ab')2Secondary Antibody (F0102B).Detection of LDLR in A172 cells by Flow Cytometry.
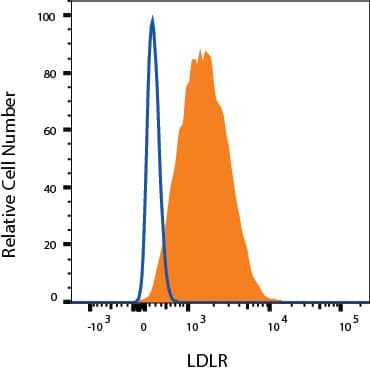
A172 cells were stained with Mouse Anti-Human LDLR Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB2148, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # MAB002, open histogram), followed by Fluorescein-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0103B). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.Detection of LDLR in U-118-MG cells by Flow Cytometry
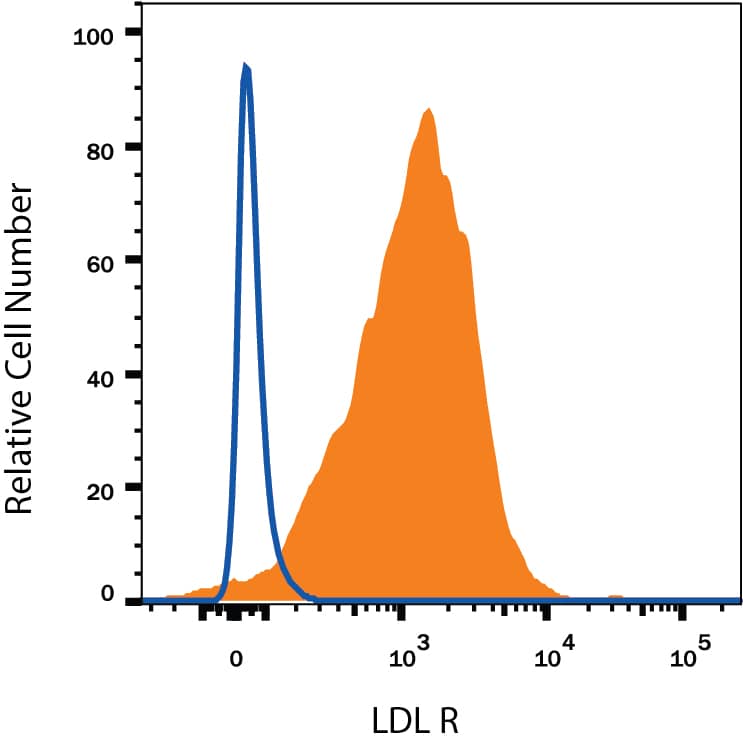
U-118-MG cells were stained with Mouse Anti-Human LDLR Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB2148, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # MAB002, open histogram) followed by Allophycocyanin-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0101B). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.Applications for Human LDLR Antibody
CyTOF-ready
Flow Cytometry
Sample: HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line, A172 human glioblastoma cell line, and U-118-MG human glioblastoma/astrocytoma cell line
Immunoprecipitation
Sample: Conditioned cell culture medium spiked with Recombinant Human LDLR (Catalog # 2148‑LD), see our available Western blot detection antibodies
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Human LDLR (Catalog # 2148-LD) under non-reducing conditions only
Human LDLR Sandwich Immunoassay
Reviewed Applications
Read 1 review rated 5 using MAB2148 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: LDLR
The Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor (LDLR) is the founding member of the LDLR family of scavenger receptors (1, 2). This family contains transmembrane molecules that are characterized by the presence of EGF repeats, complement-like repeats, and YWTD motifs that form beta-propellers. Although members of the family were originally thought to be endocytic receptors, it is now clear that some members interact with adjacent cell-surface molecules, expanding their range of activities (2). Human LDLR is synthesized as an 860 amino acid (aa) precursor that contains a 21 aa signal sequence, a 767 aa extracellular region, a 22 aa transmembrane segment and a 50 aa cytoplasmic tail (3). The extracellular region is complex. It consists of seven N-terminal complement-like cysteine-rich repeats that bind ligand. Cysteine residues in this region participate in intrachain disulfide bonds. This region is followed by three EGF-like repeats with a beta-propeller YWTD containing motif. The EGF-like repeats are responsible for ligand bonding and dissociation. Finally, there is a 50 aa membrane proximal Ser/Thr-rich region that serves as a carbohydrate attachment point (1, 3, 4). There is extensive O-linked and modest N-linked glycosylation. Thus the receptor’s predicted molecular weight of 93 kDa is increased to a native molecular weight of 120-160 kDa (3, 4). Within the 50 aa cytoplasmic tail, there is an NPXY motif that links the receptor to clathrin pits (1). The extracellular region of human LDLR is 51% aa identical to the extracellular region of human VLDLR, and 79% aa identical to the extracellular region of mouse LDLR. LDLR is constitutively expressed and binds ApoB of LDL and ApoE of VLDL (5). It is responsible for clearing 70% of plasma LDL in liver (5). Mutations in the LDLR gene cause the autosomal dominant disorder, familial hypercholesterolemia (6).
References
- Strickland, D.K. et al. (2002) Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 13:66.
- Nykjaer, A. and T.E. Willnow (2002) Trends Cell Biol. 12:273.
- Yamamoto, T. et al. (1984) Cell 39:27.
- Davis, C.G. et al. (1986) J. Biol. Chem. 261:2828.
- Defesche, J.C. (2004) Semin. Vasc. Med. 4:5.
- Varret, M. et al. (2008) Clin Genet. 73:1.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional LDLR Products
Product Documents for Human LDLR Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human LDLR Antibody
For research use only