Human Matriptase/ST14 Catalytic Domain Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF3946


Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Val615-Val855
Accession # Q9Y5Y6
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human Matriptase/ST14 Catalytic Domain Antibody
Detection of Matriptase/ST14 Catalytic Domain in PC‑3 Human Cell Line by Flow Cytometry.
PC-3 human prostate cancer cell line was stained with Sheep Anti-Human Matriptase/ST14 Catalytic Domain Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3946, filled histogram) or control antibody (5-001-A, open histogram), followed by NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Sheep IgG Secondary Antibody (NL010). To facilitate intracellular staining, cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde and permeabilized with saponin.Detection of Mouse Matriptase/ST14 by Simple Western
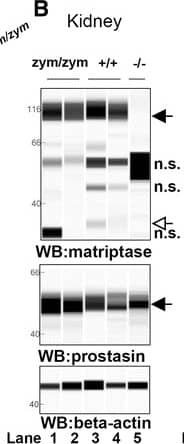
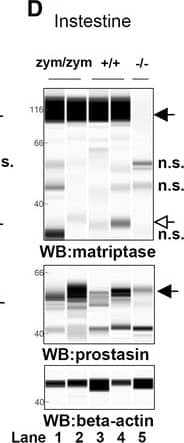
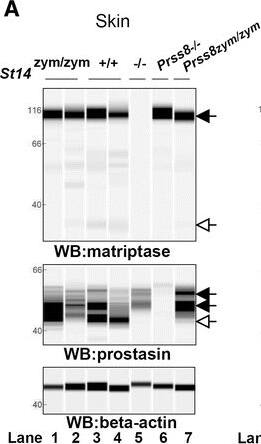
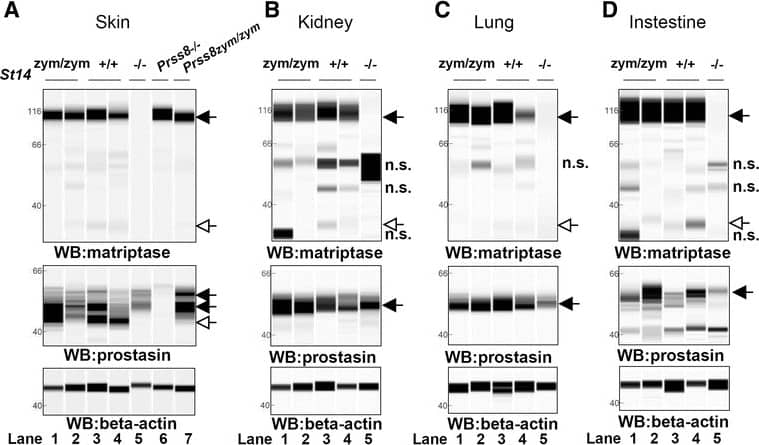
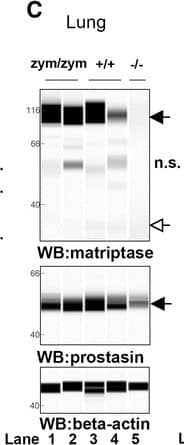
Zymogen-locked matriptase induces epidermal prostasin processing. Protein extracts from skin (a), kidney (b), lung (c), and intestine (d) from newborn St14zym/zym (lanes 1 and 2), St14+/+ (lanes 3 and 4), and St14–/– (lane 5) littermates were separated by capillary electrophoresis and probed with antibodies against matriptase (top panels), prostasin (middle panels), or beta-actin (bottom panels). Lanes 6 and 7 in (a) are skin extracts from prostasin null (Prss8–/–) and prostasin zymogen-locked (Prss8zym/zym) mice, respectively. Zymogens of matriptase and prostasin are indicated with filled arrows, and the activated forms are indicated with open arrows. n.s. non-specific. Positions of molecular weight markers (kDa) are indicated on the left. e Representative example of quantification of activated prostasin (open arrow) and zymogen prostasin (filled arrows) in protein extracts from skin from a newborn St14zym/zym mouse (top panel), St14+/+ mouse (second panel from top), and a newborn St14–/– mouse (second panel from bottom). Skin extracts from a newborn mouse expressing zymogen-locked (Prss8zym/zym) endogenous prostasin is included as reference (bottom panel). f Ratio of activated prostasin to total prostasin in skin extracts from newborn St14zym/zym (left bar, n = 7), St14+/+ (middle bar, n = 7), and St14–/– (right bar, n = 2) mice, quantified as in (e). Data are shown as mean ± SD. *P = 0.0011 was determined by one-way ANOVA, two-tailed. Additional file 1: Raw supporting data Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28571576), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Detection of Mouse Matriptase/ST14 by Simple Western
Zymogen-locked matriptase induces epidermal prostasin processing. Protein extracts from skin (a), kidney (b), lung (c), and intestine (d) from newborn St14zym/zym (lanes 1 and 2), St14+/+ (lanes 3 and 4), and St14–/– (lane 5) littermates were separated by capillary electrophoresis and probed with antibodies against matriptase (top panels), prostasin (middle panels), or beta-actin (bottom panels). Lanes 6 and 7 in (a) are skin extracts from prostasin null (Prss8–/–) and prostasin zymogen-locked (Prss8zym/zym) mice, respectively. Zymogens of matriptase and prostasin are indicated with filled arrows, and the activated forms are indicated with open arrows. n.s. non-specific. Positions of molecular weight markers (kDa) are indicated on the left. e Representative example of quantification of activated prostasin (open arrow) and zymogen prostasin (filled arrows) in protein extracts from skin from a newborn St14zym/zym mouse (top panel), St14+/+ mouse (second panel from top), and a newborn St14–/– mouse (second panel from bottom). Skin extracts from a newborn mouse expressing zymogen-locked (Prss8zym/zym) endogenous prostasin is included as reference (bottom panel). f Ratio of activated prostasin to total prostasin in skin extracts from newborn St14zym/zym (left bar, n = 7), St14+/+ (middle bar, n = 7), and St14–/– (right bar, n = 2) mice, quantified as in (e). Data are shown as mean ± SD. *P = 0.0011 was determined by one-way ANOVA, two-tailed. Additional file 1: Raw supporting data Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28571576), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Human Matriptase/ST14 Catalytic Domain Antibody
CyTOF-ready
Intracellular Staining by Flow Cytometry
Sample: PC-3 human prostate cancer cell line fixed with paraformaldehyde and permeabilized with saponin
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Human Matriptase/ST14 Catalytic Domain
Reviewed Applications
Read 2 reviews rated 5 using AF3946 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Matriptase/ST14
Human matriptase, encoded by the ST14 (suppression of tumorogenicity 14) gene, is also known as tumor associated differentially expressed gene 15 protein/TADG‑15), epithin, and membrane-type serine protease 1/MT-SP1 (1). Predicted to have a significant role in tumor biology, matriptase may be a novel target for anti-cancer therapy (2). However, expressed in most human epithelia, matriptase is also important in several physiological processes (1). For example, it activates prostasin to initiate a protease cascade that is essential for epidermal differentiation (3), and it converts a single-chain IGFBP-rp1 into the two-chain form (4).
Matriptase is a type II transmembrane serine protease with a complex modular structure (1). The 855 amino acid (aa) sequence of human matriptase consists of a cytoplasmic tail (aa 1-55), a transmembrane domain (aa 56-76), and an extracellular portion (aa 77-855). The latter contains the following domains: SEA (aa 86-201), two CUBs (aa 214-334 and 340-447), four LDLRAs (aa 452-486, 487-523, 524-560, and 566-603), and a serine protease (aa 615-855). The physiological activation of the single-chain zymogen requires the cleavage at the SEA domain within the ER or Golgi, association with HAI-1, which facilitates the transport of the protease to the cell surface, and auto-cleavage at QAR-V(615)VGG (1). The activated matriptase is inhibited by HAI-1, and the resulting HAI-1 complex can be shed from the cell surface (1). R&D Systems rhST14 corresponds to the catalytic domain, and is inhibited effectively by rhHAI-1 and rhHAI-2A (R&D Systems, Catalog # 1048-PI and 1106-PI).
References
- List, K. et al. (2006) Mol. Med. 12:1.
- Uhland, K. (2006) Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 63:2968.
- Netzel-Arnett, S. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:32941.
- Ahmed, S. et al. (2006) FEBS J. 273:615.
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Matriptase/ST14 Products
Product Documents for Human Matriptase/ST14 Catalytic Domain Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human Matriptase/ST14 Catalytic Domain Antibody
For research use only