Human/Mouse Phospho-HGFR/c-MET (Y1234/Y1235) Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF2480

Key Product Details
Validated by
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human/Mouse Phospho-HGFR/c-MET (Y1234/Y1235) Antibody
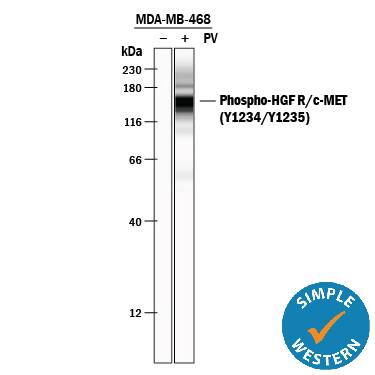
Detection of Human Phospho-HGF R/c-MET (Y1234/Y1235) by Western Blot.
Western blot shows Goat Anti-Human HGF R/c-MET Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF276) immunoprecipitate of MDA-MB-468 human breast cancer cell line untreated (-) or treated (+) with 100 µM pervanadate (PV) for 10 minutes. PVDF membrane was probed with 0.5 µg/mL of Rabbit Anti-Human/Mouse Phospho-HGF R/c-MET (Y1234/Y1235) Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2480), followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Rabbit IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF008). A specific band was detected for Phospho-HGF R/c-MET (Y1234/Y1235) at approximately 145 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.HGF R/c‑MET in SH-4 Human Cell Line.
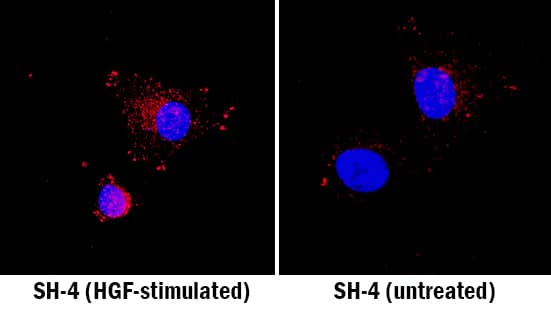
HGF R/c-MET was detected in immersion fixed SH-4 human melanoma cell line stimulated with HGF (left panel; positive staining) and non-stimulated (right panel; negative staining) using Rabbit Anti-Human/Mouse Phospho-HGF R/c-MET (Y1234/Y1235) Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2480) at 15 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Rabbit IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL004) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.HGF R/c-MET in Mouse Embryo.
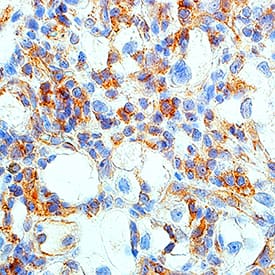
HGF R/c-MET was detected in immersion fixed frozen sections of mouse embryo (13 d.p.c.) using Rabbit Anti-Human/Mouse Phospho-HGF R/c-MET (Y1234/Y1235) Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2480) at 15 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Rabbit HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS005) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections.Applications for Human/Mouse Phospho-HGFR/c-MET (Y1234/Y1235) Antibody
CyTOF-reported
Immunocytochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed SH-4 human melanoma cell line
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed frozen sections of mouse embryo (E11-13), and immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human renal cell carcinoma tissue
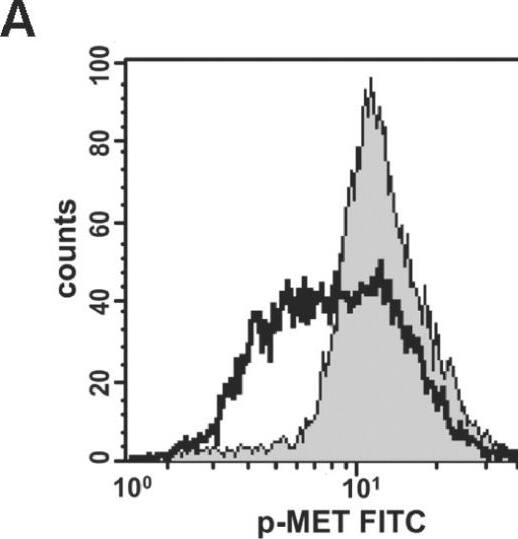
Intracellular Staining by Flow Cytometry
Sample: MCF‑7 human breast cancer cell line treated with pervanadate, fixed with paraformaldehyde, and permeabilized with methanol
Simple Western
Sample: MDA‑MB‑468 human breast cancer cell line treated with Pervanadate (PV)
Western Blot
Sample: Pervanadate-treated MDA-MB-468 human breast cancer cell line
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: HGFR/c-MET
HGF R, also known as Met (from N-methyl-N’-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine induced), is a glycosylated receptor tyrosine kinase that plays a central role in epithelial morphogenesis and cancer development. HGF R is synthesized as a single chain precursor which undergoes cotranslational proteolytic cleavage. This generates a mature HGF R that is a disulfide-linked dimer composed of a 50 kDa extracellular alpha chain and a 145 kDa transmembrane beta chain (1, 2). The extracellular domain (ECD) contains a seven bladed beta-propeller sema domain, a cysteine-rich PSI/MRS, and four Ig-like E-set domains, while the cytoplasmic region includes the tyrosine kinase domain (3, 4). Proteolysis and alternate splicing generate additional forms of human HGF R which either lack of the kinase domain, consist of secreted extracellular domains, or are deficient in proteolytic separation of the alpha and beta chains (5‑7). The sema domain, which is formed by both the alpha and beta chains of HGF R, mediates both ligand binding and receptor dimerization (3, 8). Ligand-induced tyrosine phosphorylation in the cytoplasmic region activates the kinase domain and provides docking sites for multiple SH2-containing molecules (9, 10). HGF stimulation induces HGF R downregulation via internalization and proteasome-dependent degradation (11). In the absence of ligand, HGF R forms noncovalent complexes with a variety of membrane proteins including CD44v6, CD151, EGF R, Fas, Integrin alpha6/ beta4, Plexins B1, 2, 3, and MSP R/Ron (12‑19). Ligation of one complex component triggers activation of the other, followed by cooperative signaling effects (12‑19). Formation of some of these heteromeric complexes is a requirement for epithelial cell morphogenesis and tumor cell invasion (12, 16, 17). Paracrine induction of epithelial cell scattering and branching tubulogenesis results from the stimulation of HGF R on undifferentiated epithelium by HGF released from neighboring mesenchymal cells (20). Genetic polymorphisms, chromosomal translocation, overexpression, and additional splicing and proteolytic cleavage of HGF R have been described in a wide range of cancers (1). Within the ECD, human HGF R shares 86%‑88% aa sequence identity with canine, mouse, and rat HGF R.
References
- Birchmeier, C. et al. (2003) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4:915.
- Corso, S. et al. (2005) Trends Mol. Med. 11:284.
- Gherardi, E. et al. (2003) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 100:12039.
- Park, M. et al. (1987) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 84:6379.
- Crepaldi, T. et al. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269:1750.
- Prat, M. et al. (1991) Mol. Cell. Biol. 12:5954.
- Rodrigues, G.A. et al. (1991) Mol. Cell. Biol. 11:2962.
- Kong-Beltran, M. et al. (2004) Cancer Cell 6:75.
- Naldini, L. et al. (1991) Mol. Cell. Biol. 11:1793.
- Ponzetto, C. et al. (1994) Cell 77:261.
- Jeffers, M. et al. (1997) Mol. Cell. Biol. 17:799.
- Orian-Rousseau, V. et al. (2002) Genes Dev. 16:3074.
- Klosek, S.K. et al. (2005) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 336:408.
- Jo, M. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275:8806.
- Wang, X. et al. (2002) Mol. Cell 9:411.
- Trusolino, L. et al. (2001) Cell 107:643.
- Giordano, S. et al. (2002) Nat. Cell Biol. 4:720.
- Conrotto, P. et al. (2004) Oncogene 23:5131.
- Follenzi, A. et al. (2000) Oncogene 19:3041.
- Sonnenberg, E. et al. (1993) J. Cell Biol. 123:223.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
Additional HGFR/c-MET Products
Product Documents for Human/Mouse Phospho-HGFR/c-MET (Y1234/Y1235) Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human/Mouse Phospho-HGFR/c-MET (Y1234/Y1235) Antibody
For research use only