Human/Mouse/Rat CD200 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF2724


Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Gln31-Gly232
Accession # P41217
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human/Mouse/Rat CD200 Antibody
Detection of Human, Mouse, and Rat CD200 by Western Blot.
Western blot shows lysates of human, mouse, and rat brain (cortex) tissue, human tonsil tissue, and human dendritic cells (mature). PVDF membrane was probed with 0.5 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat CD200 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2724) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF017). A specific band was detected for CD200 at approximately 42 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.CD200 in Human Placenta.
CD200 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human placenta using Goat Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat CD200 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2724) at 15 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.Detection of Human, Mouse, and Rat CD200 by Simple WesternTM.
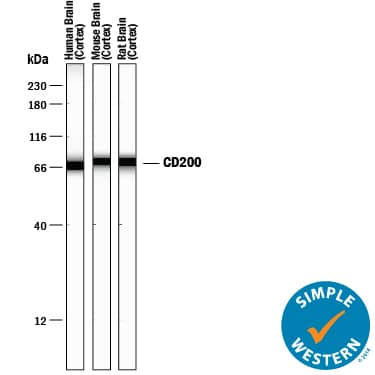
Simple Western lane view shows lysates of human, mouse, and rat brain (cortex) tissue, loaded at 0.2 mg/mL. A specific band was detected for CD200 at approximately 70-75 kDa (as indicated) using 10 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human/Mouse/Rat CD200 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2724) followed by 1:50 dilution of HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF109). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using the 12-230 kDa separation system.Applications for Human/Mouse/Rat CD200 Antibody
CyTOF-ready
Flow Cytometry
Sample: Human whole blood CD19+ B cells
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human placenta
Simple Western
Sample: Human, mouse, and rat brain (cortex) tissue
Western Blot
Sample: Human, mouse, and rat brain (cortex) tissue, human tonsil tissue, and human dendritic cells (mature)
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: CD200
CD200, also known as OX-2, is a 45 kDa transmembrane immunoregulatory protein that belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily (1, 2). The human CD200 cDNA encodes a 278 amino acid (aa) precursor that includes a 30 aa signal sequence, a 202 aa extracellular domain (ECD), a 27 aa transmembrane segment, and a 19 aa cytoplasmic domain. The ECD is composed of one Ig-like V-type domain and one Ig-like C2-type domain (3). A splice variant of CD200 has been described and has a truncated cytoplasmic tail. Within the ECD, human CD200 shares 76% aa sequence identity with mouse and rat CD200. CD200 is widely but not ubiquitously expressed (4). Its receptor (CD200R) is restricted primarily to mast cells, basophils, macrophages, and dendritic cells, which suggests myeloid cell regulation as the major function of CD200 (5-7). CD200 knockout mice are characterized by increased macrophage number and activation and are predisposed to autoimmune disorders (8). CD200 and CD200R associate via their respective N-terminal Ig-like domains (9). In myeloid cells, CD200R initiates inhibitory signals following receptor‑ligand contact (6, 7, 10). In T cells, however, CD200 functions as a costimulatory molecule independent of the CD28 pathway (11). Several additional CD200R-like molecules have been identified in human and mouse, but their capacity to interact with CD200 is controversial (12, 13). Several viruses encode CD200 homologs which are expressed on infected cells during the lytic phase (14, 15). Like CD200 itself, viral CD200 homologs also suppress myeloid cell activity, enabling increased viral propagation (5, 14-16).
References
- Gorczynski, R.M. (2005) Curr. Opin. Invest. Drugs 6:483.
- Barclay, A.N. et al. (2002) Trends Immunol. 23:285.
- McCaughan, G.W. et al. (1987) Immunogenetics 25:329.
- Wright, G.J. et al. (2001) Immunology 102:173.
- Shiratori, I. et al. (2005) J. Immunol. 175:4441.
- Cherwinski, H.M. et al. (2005) J. Immunol. 174:1348.
- Fallarino, F. et al. (2004) J. Immunol. 173:3748.
- Hoek, R.M. et al. (2000) Science 290:1768.
- Hatherley, D. and A.N. Barclay (2004) Eur. J. Immunol. 34:1688.
- Jenmalm, M.C. et al. (2006) J. Immunol. 176:191.
- Borriello, F. et al. (1997) J. Immunol. 158:4548.
- Gorczynski, R. et al. (2004) J. Immunol. 172:7744.
- Hatherley, D. et al. (2005) J. Immunol. 175:2469.
- Foster-Cuevas, M. et al. (2004) J. Virol. 78:7667.
- Cameron, C.M. et al. (2005) J. Virol. 79:6052.
- Langlais, C.L. et al. (2006) J. Virol. 80:3098.
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional CD200 Products
Product Documents for Human/Mouse/Rat CD200 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human/Mouse/Rat CD200 Antibody
For research use only