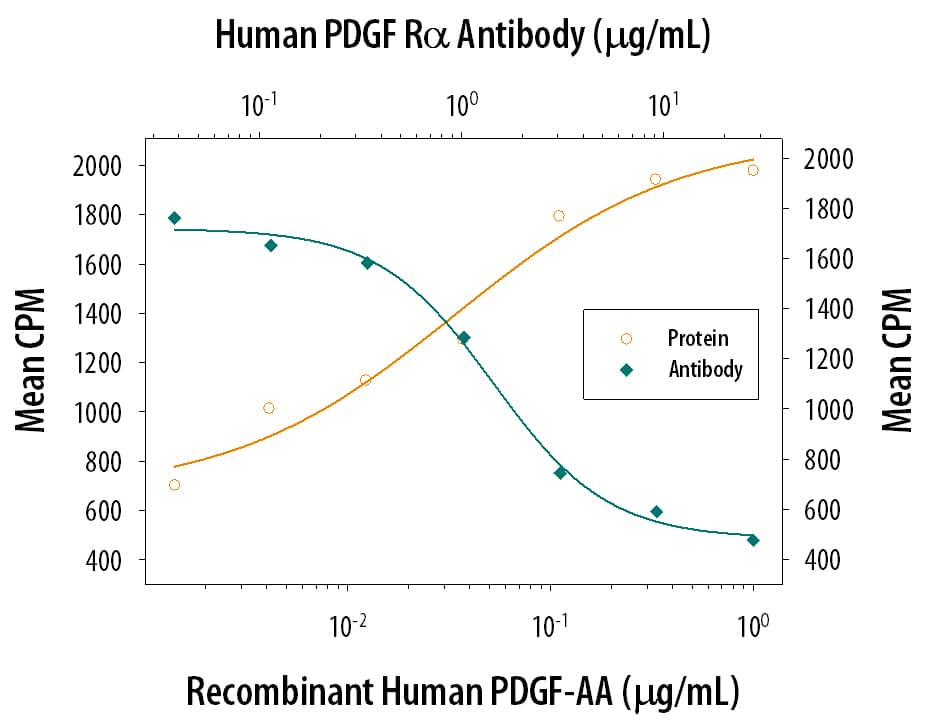
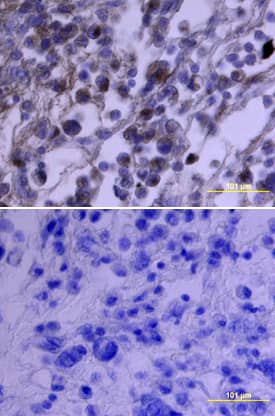
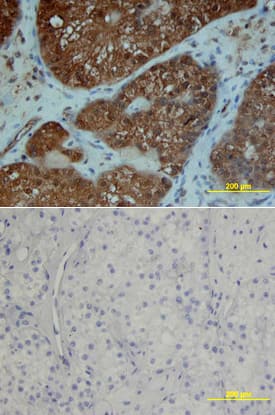
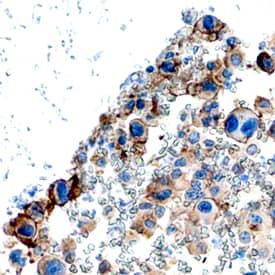
PDGF R alpha in Human Osteosarcoma.
PDGF Ra was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human osteosarcoma using Goat Anti-Human PDGF Ra Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF-307-NA) at 3 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog #
CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to plasma membranes. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.
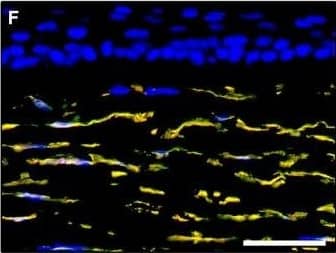
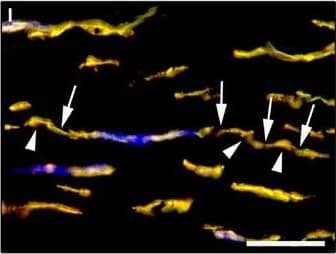
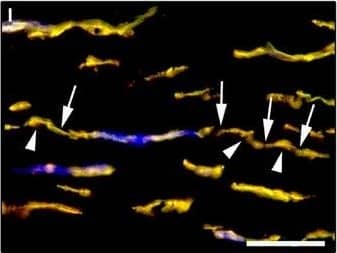
Detection of Human PDGFR alpha by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
Representative light and fluorescence microscopy photomicrographs of normal human corneal sections. (A–C) CD34 immunoperoxidase‐based immunohistochemistry with haematoxylin counterstain. (A) CD34‐positive stromal cells are orderly arranged and parallel to the corneal surface. (B and C) At higher magnification, the CD34‐positive stromal cells appear as spindle‐shaped cells with a small oval body and typically two long and thin moniliform cell processes characterized by the alternation of slender segments (arrows) and knobs/dilations (arrowheads) along their length. (D–I) Double immunofluorescence labelling for CD34 (red) and PDGFR alpha (green) with DAPI (blue) counterstain for nuclei. Colocalization of CD34 and PDGFR alpha in stromal cells gives rise to yellow staining either in the anterior corneal stroma (D–F) or in the deeper corneal stromal layer (G–I). CD34+/PDGFR alpha+ stromal cells display cell morphologies very evocative for telocytes: a small cell body with very long prolongations (telopodes) characterized by a moniliform silhouette with the alternation of podoms (arrowheads) and podomers (arrows). (J–L) Double immunofluorescence labelling for CD34 (red) and c‐kit (green) with DAPI (blue) counterstain for nuclei. Either in the subepithelial corneal stroma or in the deeper stromal layer, numerous CD34‐positive stromal cells coexpress c‐kit. Inset: Higher magnification view of CD34+/c‐kit+ corneal stromal cells. Scale bar: 50 μm (A, D–F and J–L), 25 μm (B, C and G–I). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28714595), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
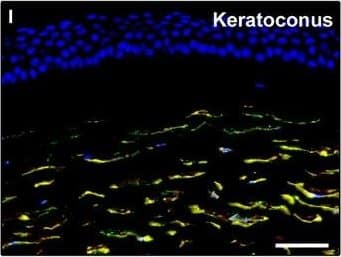
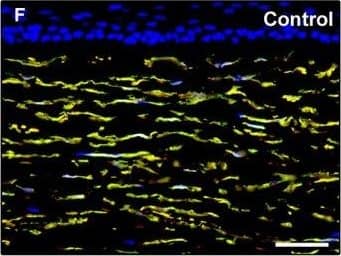
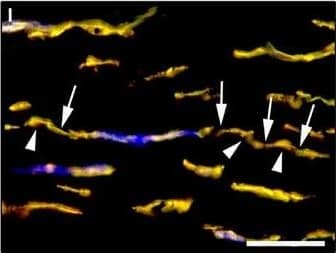
Detection of Human PDGFR alpha by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
Representative light and fluorescence microscopy photomicrographs of normal and keratoconic human corneal sections. (A and B) CD34 immunoperoxidase‐based immunohistochemistry with haematoxylin counterstain. (A) In control normal corneas, CD34‐positive stromal cells displaying morphological features of telocytes are orderly arranged and parallel to the corneal surface. (B) In keratoconus, a patchy loss of CD34‐positive stromal cells is mostly evident in the anterior corneal stroma. Insets: Higher magnification views of CD34‐positive corneal stromal cells. (C) Results of quantitative analysis of CD34‐positive telocyte counts per high‐power field in the corneal stroma of healthy controls (n = 6) and patients with keratoconus (n = 6). Data are mean ± S.D. *P < 0.001 versus control. (D–I) Double immunofluorescence labelling for CD34 (red) and PDGFR alpha (green) with DAPI (blue) counterstain for nuclei. (D–F) In control normal corneas, CD34+/PDGFR alpha+ stromal cells (telocytes) are orderly distributed throughout the stromal compartment. (G–I) In keratoconic corneas, a patchy loss of CD34+/PDGFR alpha+ stromal cells (telocytes) is mainly evident in the subepithelial stroma. (J and K) Double immunofluorescence labelling for CD34 (red) and c‐kit (green) with DAPI (blue) counterstain for nuclei. (J) In control normal corneas, numerous CD34+/c‐kit+ stromal cells (telocytes) are present throughout the stromal layer. (K) In keratoconic corneas, the CD34+/c‐kit+ stromal cell subpopulation is almost completely lost. (L) Results of quantitative analysis of c‐kit‐positive telocyte counts per high‐power field in the corneal stroma of healthy controls (n = 6) and patients with keratoconus (n = 6). Data are mean ± S.D. *P < 0.001 versus control. TC: telocytes; hpf: high‐power field. Scale bar: 100 μm (A and B), 50 μm (D–K). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28714595), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
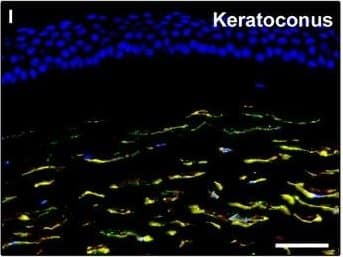
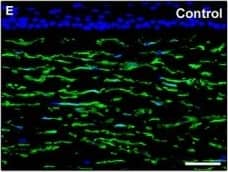
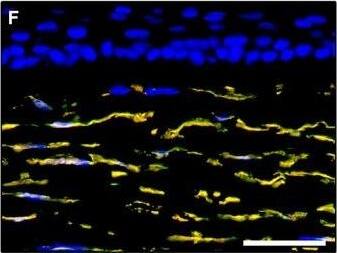
Detection of Human PDGFR alpha by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
Representative light and fluorescence microscopy photomicrographs of normal and keratoconic human corneal sections. (A and B) CD34 immunoperoxidase‐based immunohistochemistry with haematoxylin counterstain. (A) In control normal corneas, CD34‐positive stromal cells displaying morphological features of telocytes are orderly arranged and parallel to the corneal surface. (B) In keratoconus, a patchy loss of CD34‐positive stromal cells is mostly evident in the anterior corneal stroma. Insets: Higher magnification views of CD34‐positive corneal stromal cells. (C) Results of quantitative analysis of CD34‐positive telocyte counts per high‐power field in the corneal stroma of healthy controls (n = 6) and patients with keratoconus (n = 6). Data are mean ± S.D. *P < 0.001 versus control. (D–I) Double immunofluorescence labelling for CD34 (red) and PDGFR alpha (green) with DAPI (blue) counterstain for nuclei. (D–F) In control normal corneas, CD34+/PDGFR alpha+ stromal cells (telocytes) are orderly distributed throughout the stromal compartment. (G–I) In keratoconic corneas, a patchy loss of CD34+/PDGFR alpha+ stromal cells (telocytes) is mainly evident in the subepithelial stroma. (J and K) Double immunofluorescence labelling for CD34 (red) and c‐kit (green) with DAPI (blue) counterstain for nuclei. (J) In control normal corneas, numerous CD34+/c‐kit+ stromal cells (telocytes) are present throughout the stromal layer. (K) In keratoconic corneas, the CD34+/c‐kit+ stromal cell subpopulation is almost completely lost. (L) Results of quantitative analysis of c‐kit‐positive telocyte counts per high‐power field in the corneal stroma of healthy controls (n = 6) and patients with keratoconus (n = 6). Data are mean ± S.D. *P < 0.001 versus control. TC: telocytes; hpf: high‐power field. Scale bar: 100 μm (A and B), 50 μm (D–K). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28714595), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
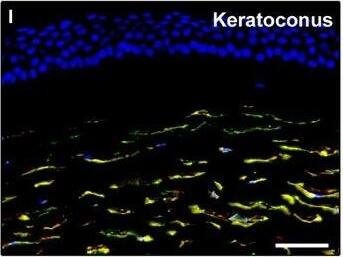
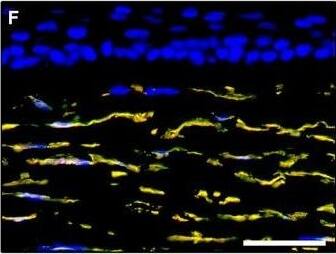
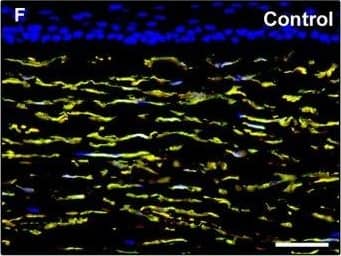
Detection of Human PDGFR alpha by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
Representative light and fluorescence microscopy photomicrographs of normal and keratoconic human corneal sections. (A and B) CD34 immunoperoxidase‐based immunohistochemistry with haematoxylin counterstain. (A) In control normal corneas, CD34‐positive stromal cells displaying morphological features of telocytes are orderly arranged and parallel to the corneal surface. (B) In keratoconus, a patchy loss of CD34‐positive stromal cells is mostly evident in the anterior corneal stroma. Insets: Higher magnification views of CD34‐positive corneal stromal cells. (C) Results of quantitative analysis of CD34‐positive telocyte counts per high‐power field in the corneal stroma of healthy controls (n = 6) and patients with keratoconus (n = 6). Data are mean ± S.D. *P < 0.001 versus control. (D–I) Double immunofluorescence labelling for CD34 (red) and PDGFR alpha (green) with DAPI (blue) counterstain for nuclei. (D–F) In control normal corneas, CD34+/PDGFR alpha+ stromal cells (telocytes) are orderly distributed throughout the stromal compartment. (G–I) In keratoconic corneas, a patchy loss of CD34+/PDGFR alpha+ stromal cells (telocytes) is mainly evident in the subepithelial stroma. (J and K) Double immunofluorescence labelling for CD34 (red) and c‐kit (green) with DAPI (blue) counterstain for nuclei. (J) In control normal corneas, numerous CD34+/c‐kit+ stromal cells (telocytes) are present throughout the stromal layer. (K) In keratoconic corneas, the CD34+/c‐kit+ stromal cell subpopulation is almost completely lost. (L) Results of quantitative analysis of c‐kit‐positive telocyte counts per high‐power field in the corneal stroma of healthy controls (n = 6) and patients with keratoconus (n = 6). Data are mean ± S.D. *P < 0.001 versus control. TC: telocytes; hpf: high‐power field. Scale bar: 100 μm (A and B), 50 μm (D–K). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28714595), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Human PDGFR alpha by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
Representative light and fluorescence microscopy photomicrographs of normal human corneal sections. (A–C) CD34 immunoperoxidase‐based immunohistochemistry with haematoxylin counterstain. (A) CD34‐positive stromal cells are orderly arranged and parallel to the corneal surface. (B and C) At higher magnification, the CD34‐positive stromal cells appear as spindle‐shaped cells with a small oval body and typically two long and thin moniliform cell processes characterized by the alternation of slender segments (arrows) and knobs/dilations (arrowheads) along their length. (D–I) Double immunofluorescence labelling for CD34 (red) and PDGFR alpha (green) with DAPI (blue) counterstain for nuclei. Colocalization of CD34 and PDGFR alpha in stromal cells gives rise to yellow staining either in the anterior corneal stroma (D–F) or in the deeper corneal stromal layer (G–I). CD34+/PDGFR alpha+ stromal cells display cell morphologies very evocative for telocytes: a small cell body with very long prolongations (telopodes) characterized by a moniliform silhouette with the alternation of podoms (arrowheads) and podomers (arrows). (J–L) Double immunofluorescence labelling for CD34 (red) and c‐kit (green) with DAPI (blue) counterstain for nuclei. Either in the subepithelial corneal stroma or in the deeper stromal layer, numerous CD34‐positive stromal cells coexpress c‐kit. Inset: Higher magnification view of CD34+/c‐kit+ corneal stromal cells. Scale bar: 50 μm (A, D–F and J–L), 25 μm (B, C and G–I). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28714595), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Human PDGFR alpha by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
Representative light and fluorescence microscopy photomicrographs of normal and keratoconic human corneal sections. (A and B) CD34 immunoperoxidase‐based immunohistochemistry with haematoxylin counterstain. (A) In control normal corneas, CD34‐positive stromal cells displaying morphological features of telocytes are orderly arranged and parallel to the corneal surface. (B) In keratoconus, a patchy loss of CD34‐positive stromal cells is mostly evident in the anterior corneal stroma. Insets: Higher magnification views of CD34‐positive corneal stromal cells. (C) Results of quantitative analysis of CD34‐positive telocyte counts per high‐power field in the corneal stroma of healthy controls (n = 6) and patients with keratoconus (n = 6). Data are mean ± S.D. *P < 0.001 versus control. (D–I) Double immunofluorescence labelling for CD34 (red) and PDGFR alpha (green) with DAPI (blue) counterstain for nuclei. (D–F) In control normal corneas, CD34+/PDGFR alpha+ stromal cells (telocytes) are orderly distributed throughout the stromal compartment. (G–I) In keratoconic corneas, a patchy loss of CD34+/PDGFR alpha+ stromal cells (telocytes) is mainly evident in the subepithelial stroma. (J and K) Double immunofluorescence labelling for CD34 (red) and c‐kit (green) with DAPI (blue) counterstain for nuclei. (J) In control normal corneas, numerous CD34+/c‐kit+ stromal cells (telocytes) are present throughout the stromal layer. (K) In keratoconic corneas, the CD34+/c‐kit+ stromal cell subpopulation is almost completely lost. (L) Results of quantitative analysis of c‐kit‐positive telocyte counts per high‐power field in the corneal stroma of healthy controls (n = 6) and patients with keratoconus (n = 6). Data are mean ± S.D. *P < 0.001 versus control. TC: telocytes; hpf: high‐power field. Scale bar: 100 μm (A and B), 50 μm (D–K). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28714595), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Human PDGFR alpha by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
Representative light and fluorescence microscopy photomicrographs of normal and keratoconic human corneal sections. (A and B) CD34 immunoperoxidase‐based immunohistochemistry with haematoxylin counterstain. (A) In control normal corneas, CD34‐positive stromal cells displaying morphological features of telocytes are orderly arranged and parallel to the corneal surface. (B) In keratoconus, a patchy loss of CD34‐positive stromal cells is mostly evident in the anterior corneal stroma. Insets: Higher magnification views of CD34‐positive corneal stromal cells. (C) Results of quantitative analysis of CD34‐positive telocyte counts per high‐power field in the corneal stroma of healthy controls (n = 6) and patients with keratoconus (n = 6). Data are mean ± S.D. *P < 0.001 versus control. (D–I) Double immunofluorescence labelling for CD34 (red) and PDGFR alpha (green) with DAPI (blue) counterstain for nuclei. (D–F) In control normal corneas, CD34+/PDGFR alpha+ stromal cells (telocytes) are orderly distributed throughout the stromal compartment. (G–I) In keratoconic corneas, a patchy loss of CD34+/PDGFR alpha+ stromal cells (telocytes) is mainly evident in the subepithelial stroma. (J and K) Double immunofluorescence labelling for CD34 (red) and c‐kit (green) with DAPI (blue) counterstain for nuclei. (J) In control normal corneas, numerous CD34+/c‐kit+ stromal cells (telocytes) are present throughout the stromal layer. (K) In keratoconic corneas, the CD34+/c‐kit+ stromal cell subpopulation is almost completely lost. (L) Results of quantitative analysis of c‐kit‐positive telocyte counts per high‐power field in the corneal stroma of healthy controls (n = 6) and patients with keratoconus (n = 6). Data are mean ± S.D. *P < 0.001 versus control. TC: telocytes; hpf: high‐power field. Scale bar: 100 μm (A and B), 50 μm (D–K). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28714595), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Human PDGFR alpha by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
Representative light and fluorescence microscopy photomicrographs of normal human corneal sections. (A–C) CD34 immunoperoxidase‐based immunohistochemistry with haematoxylin counterstain. (A) CD34‐positive stromal cells are orderly arranged and parallel to the corneal surface. (B and C) At higher magnification, the CD34‐positive stromal cells appear as spindle‐shaped cells with a small oval body and typically two long and thin moniliform cell processes characterized by the alternation of slender segments (arrows) and knobs/dilations (arrowheads) along their length. (D–I) Double immunofluorescence labelling for CD34 (red) and PDGFR alpha (green) with DAPI (blue) counterstain for nuclei. Colocalization of CD34 and PDGFR alpha in stromal cells gives rise to yellow staining either in the anterior corneal stroma (D–F) or in the deeper corneal stromal layer (G–I). CD34+/PDGFR alpha+ stromal cells display cell morphologies very evocative for telocytes: a small cell body with very long prolongations (telopodes) characterized by a moniliform silhouette with the alternation of podoms (arrowheads) and podomers (arrows). (J–L) Double immunofluorescence labelling for CD34 (red) and c‐kit (green) with DAPI (blue) counterstain for nuclei. Either in the subepithelial corneal stroma or in the deeper stromal layer, numerous CD34‐positive stromal cells coexpress c‐kit. Inset: Higher magnification view of CD34+/c‐kit+ corneal stromal cells. Scale bar: 50 μm (A, D–F and J–L), 25 μm (B, C and G–I). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28714595), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Human PDGFR alpha by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
Representative light and fluorescence microscopy photomicrographs of normal human corneal sections. (A–C) CD34 immunoperoxidase‐based immunohistochemistry with haematoxylin counterstain. (A) CD34‐positive stromal cells are orderly arranged and parallel to the corneal surface. (B and C) At higher magnification, the CD34‐positive stromal cells appear as spindle‐shaped cells with a small oval body and typically two long and thin moniliform cell processes characterized by the alternation of slender segments (arrows) and knobs/dilations (arrowheads) along their length. (D–I) Double immunofluorescence labelling for CD34 (red) and PDGFR alpha (green) with DAPI (blue) counterstain for nuclei. Colocalization of CD34 and PDGFR alpha in stromal cells gives rise to yellow staining either in the anterior corneal stroma (D–F) or in the deeper corneal stromal layer (G–I). CD34+/PDGFR alpha+ stromal cells display cell morphologies very evocative for telocytes: a small cell body with very long prolongations (telopodes) characterized by a moniliform silhouette with the alternation of podoms (arrowheads) and podomers (arrows). (J–L) Double immunofluorescence labelling for CD34 (red) and c‐kit (green) with DAPI (blue) counterstain for nuclei. Either in the subepithelial corneal stroma or in the deeper stromal layer, numerous CD34‐positive stromal cells coexpress c‐kit. Inset: Higher magnification view of CD34+/c‐kit+ corneal stromal cells. Scale bar: 50 μm (A, D–F and J–L), 25 μm (B, C and G–I). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28714595), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Human PDGFR alpha by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
Representative light and fluorescence microscopy photomicrographs of normal human corneal sections. (A–C) CD34 immunoperoxidase‐based immunohistochemistry with haematoxylin counterstain. (A) CD34‐positive stromal cells are orderly arranged and parallel to the corneal surface. (B and C) At higher magnification, the CD34‐positive stromal cells appear as spindle‐shaped cells with a small oval body and typically two long and thin moniliform cell processes characterized by the alternation of slender segments (arrows) and knobs/dilations (arrowheads) along their length. (D–I) Double immunofluorescence labelling for CD34 (red) and PDGFR alpha (green) with DAPI (blue) counterstain for nuclei. Colocalization of CD34 and PDGFR alpha in stromal cells gives rise to yellow staining either in the anterior corneal stroma (D–F) or in the deeper corneal stromal layer (G–I). CD34+/PDGFR alpha+ stromal cells display cell morphologies very evocative for telocytes: a small cell body with very long prolongations (telopodes) characterized by a moniliform silhouette with the alternation of podoms (arrowheads) and podomers (arrows). (J–L) Double immunofluorescence labelling for CD34 (red) and c‐kit (green) with DAPI (blue) counterstain for nuclei. Either in the subepithelial corneal stroma or in the deeper stromal layer, numerous CD34‐positive stromal cells coexpress c‐kit. Inset: Higher magnification view of CD34+/c‐kit+ corneal stromal cells. Scale bar: 50 μm (A, D–F and J–L), 25 μm (B, C and G–I). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28714595), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Human PDGFR alpha by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
Representative light and fluorescence microscopy photomicrographs of normal human corneal sections. (A–C) CD34 immunoperoxidase‐based immunohistochemistry with haematoxylin counterstain. (A) CD34‐positive stromal cells are orderly arranged and parallel to the corneal surface. (B and C) At higher magnification, the CD34‐positive stromal cells appear as spindle‐shaped cells with a small oval body and typically two long and thin moniliform cell processes characterized by the alternation of slender segments (arrows) and knobs/dilations (arrowheads) along their length. (D–I) Double immunofluorescence labelling for CD34 (red) and PDGFR alpha (green) with DAPI (blue) counterstain for nuclei. Colocalization of CD34 and PDGFR alpha in stromal cells gives rise to yellow staining either in the anterior corneal stroma (D–F) or in the deeper corneal stromal layer (G–I). CD34+/PDGFR alpha+ stromal cells display cell morphologies very evocative for telocytes: a small cell body with very long prolongations (telopodes) characterized by a moniliform silhouette with the alternation of podoms (arrowheads) and podomers (arrows). (J–L) Double immunofluorescence labelling for CD34 (red) and c‐kit (green) with DAPI (blue) counterstain for nuclei. Either in the subepithelial corneal stroma or in the deeper stromal layer, numerous CD34‐positive stromal cells coexpress c‐kit. Inset: Higher magnification view of CD34+/c‐kit+ corneal stromal cells. Scale bar: 50 μm (A, D–F and J–L), 25 μm (B, C and G–I). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28714595), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Human PDGFR alpha by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
Representative light and fluorescence microscopy photomicrographs of normal and keratoconic human corneal sections. (A and B) CD34 immunoperoxidase‐based immunohistochemistry with haematoxylin counterstain. (A) In control normal corneas, CD34‐positive stromal cells displaying morphological features of telocytes are orderly arranged and parallel to the corneal surface. (B) In keratoconus, a patchy loss of CD34‐positive stromal cells is mostly evident in the anterior corneal stroma. Insets: Higher magnification views of CD34‐positive corneal stromal cells. (C) Results of quantitative analysis of CD34‐positive telocyte counts per high‐power field in the corneal stroma of healthy controls (n = 6) and patients with keratoconus (n = 6). Data are mean ± S.D. *P < 0.001 versus control. (D–I) Double immunofluorescence labelling for CD34 (red) and PDGFR alpha (green) with DAPI (blue) counterstain for nuclei. (D–F) In control normal corneas, CD34+/PDGFR alpha+ stromal cells (telocytes) are orderly distributed throughout the stromal compartment. (G–I) In keratoconic corneas, a patchy loss of CD34+/PDGFR alpha+ stromal cells (telocytes) is mainly evident in the subepithelial stroma. (J and K) Double immunofluorescence labelling for CD34 (red) and c‐kit (green) with DAPI (blue) counterstain for nuclei. (J) In control normal corneas, numerous CD34+/c‐kit+ stromal cells (telocytes) are present throughout the stromal layer. (K) In keratoconic corneas, the CD34+/c‐kit+ stromal cell subpopulation is almost completely lost. (L) Results of quantitative analysis of c‐kit‐positive telocyte counts per high‐power field in the corneal stroma of healthy controls (n = 6) and patients with keratoconus (n = 6). Data are mean ± S.D. *P < 0.001 versus control. TC: telocytes; hpf: high‐power field. Scale bar: 100 μm (A and B), 50 μm (D–K). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28714595), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.