Human SPARC-like 1/SPARCL1 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF2728

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Ile17-Phe664
Accession # Q8N4S1
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human SPARC-like 1/SPARCL1 Antibody
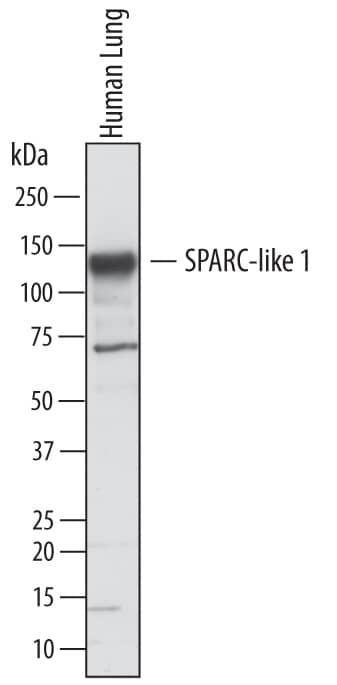
Detection of Human SPARC‑like 1/SPARCL1 by Western Blot.
Western blot shows lysates of human lung tissue. PVDF membrane was probed with 1 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human SPARC-like 1/ SPARCL1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2728) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF017). A specific band was detected for SPARC-like 1/SPARCL1 at approximately 130 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.SPARC‑like 1/SPARCL1 in Human Brain.
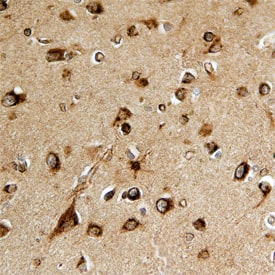
SPARC-like 1/SPARCL1 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human brain using Goat Anti-Human SPARC-like 1/SPARCL1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2728) at 15 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (Catalog # CTS013). Tissue was stained using the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to neurons. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.Detection of SPARC‑like 1/SPARCL1 in HL‑60 Human Cell Line by Flow Cytometry.
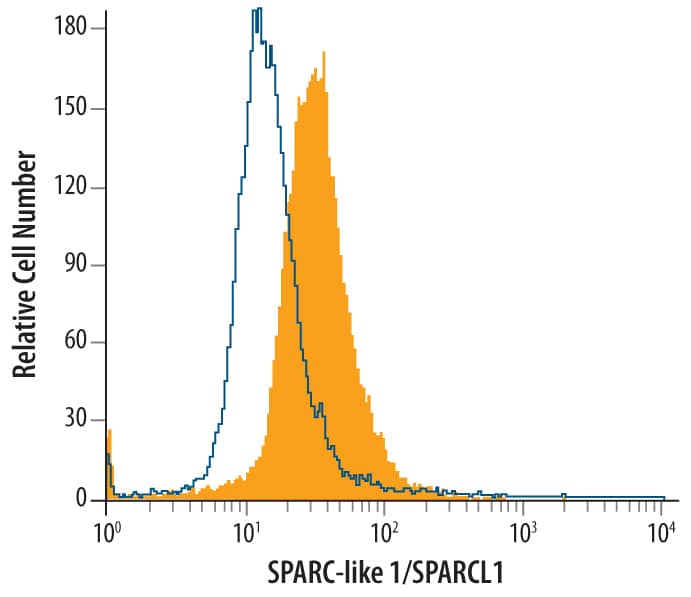
HL-60 human acute promyelocytic leukemia cell line was stained with Goat Anti-Human SPARC-like 1/SPARCL1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2728, filled histogram) or control antibody (Catalog # AB-108-C, open histogram), followed by Phycoerythrin-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0107). To facilitate intracellular staining, cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde and permeabilized with saponin.Applications for Human SPARC-like 1/SPARCL1 Antibody
CyTOF-ready
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human brain
Intracellular Staining by Flow Cytometry
Sample:
HL‑60 human acute promyelocytic leukemia cell line fixed with paraformaldehyde and permeabilized with saponin.
Western Blot
Sample: Human lung tissue
Reviewed Applications
Read 4 reviews rated 4.3 using AF2728 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: SPARC-like 1/SPARCL1
SPARCL1 (Secreted Protein, Acidic and Rich in Cysteines-like 1), also known as hevin, SC1 or MAST9, is a member of the SPARC family of extracellular glycoproteins (1, 2). SPARCL1 is an anti-adhesive protein that is widely expressed in tissues such as brain, heart, lung, muscle and kidney, but not liver (3, 4). Human SPARCL1 contains a 16 amino acid (aa) signal sequence and a 648 aa mature region with four domains: a 416 aa N-terminal acidic region, a 23 aa follistatin-like domain, a 55 aa kazal-like segment and a 48 aa EF-hand/calcium-binding domain (3, 4). SPARCL1 is predicted at 75 kDa, but migrates at ~130 kDa, which has been explained either by disulfide-linked homodimerization or by glycosylation and high acidity (3-5). Some truncated forms have been reported. In mouse, a 55 kDa C-terminal fragment is the only form in kidney and represents a portion of SPARCL1 in other tissues (6). In humans, a 25 kDa form is increased in liver tumors that are encapsulated, while the full-length form is downregulated in many epithelial cell-derived tumors (7, 8). SPARCL1 inhibits adhesion and spreading on a variety of substrates (5, 9). It is thought to cause antiadhesive signaling that terminates neuronal migration, consistent with production by glial and neuronal cells during development or in response to trauma (10). In tonsillar high endothelial venules (HEV), SPARCL1 may induce endothelial cell dissociation, promoting extravasation (3). SPARCL1 binds collagen; in mice, deletion causes dermal collagen fibrils that are smaller in diameter and deficient in decorin (6, 11). Human mature SPARCL1 shares 67%, 69%, 78%, 76%, 72%, and 72% aa identity with mouse, rat, equine, canine, porcine and bovine SPARCL1, respectively. The follistatin-like, kazal-like and calcium-binding domains of SPARCL1 show 61% aa identity with corresponding regions of SPARC.
References
- Framson, P.E. and E.H. Sage (2004) J. Cell. Biochem. 92:679.
- Sullivan, M.M. and E.H. Sage (2004) Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 36:991.
- Girard, J.P. and T.A. Springer (1995) Immunity 2:113.
- Bendik, I. et al. (1998) Cancer Res. 58:626.
- Brekken, R.A. et al. (2004) J. Histochem. Cytochem. 52:735.
- Hambrock, H.O. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278:11351.
- Lau, C.P. et al. (2006) J. Pathol. 210:469.
- Isler, S.G. et al. (2001) Int. J. Oncol. 18:521.
- Girard, J.P. and T.A. Springer (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271:4511.
- Gongidi, V. et al. (2004) Neuron 41:57.
- Sullivan, M.M. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:27621.
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional SPARC-like 1/SPARCL1 Products
Product Documents for Human SPARC-like 1/SPARCL1 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human SPARC-like 1/SPARCL1 Antibody
For research use only