Human TfR (Transferrin R) Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF2474

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Endotoxin Level
Scientific Data Images for Human TfR (Transferrin R) Antibody
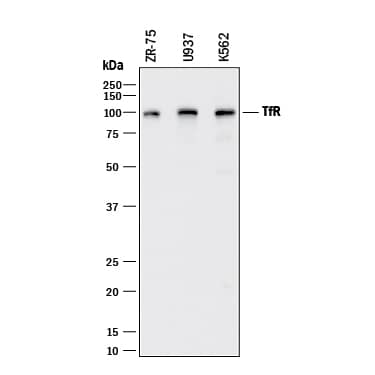
Detection of Human TfR (Transferrin R) by Western Blot.
Western blot shows lysates of ZR-75 human breast cancer cell line, U937 human histiocytic lymphoma cell line, and K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 0.25 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human TfR (Transferrin R) Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2474) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF017). A specific band was detected for TfR (Transferrin R) at approximately 95 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.TfR (Transferrin R) in Human Liver.
TfR (Transferrin R) was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human liver using Goat Anti-Human TfR (Transferrin R) Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2474) at 5 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific labeling was localized to the plasma membrane of hepatocytes. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.Detection of Mouse TfR (Transferrin R) by Western Blot
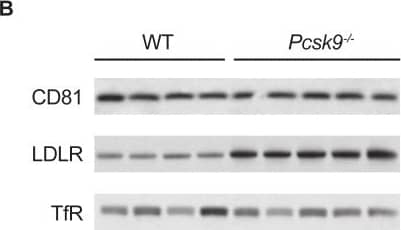
Effect of Pcsk9 deletion on LDLR and CD81 levels in age- and sex-matched Pcsk9-/- mice (n = 5) and their wild type littermates (n = 4).Shown are (A) mean ± SE serum LDL-C levels and (B) Western blot analysis of CD81 and LDLR levels in liver extracts with TfR as loading control, in animals sacrificed after a 4-hour fast. Lanes in panel B represent samples from individual mice. LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDLR, low-density lipoprotein receptor; PCSK9, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9; SE, standard error; TfR, transferrin receptor; wt, wild type. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0154498), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Human TfR (Transferrin R) Antibody
Blockade of Receptor-ligand Interaction
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human bladder, breast, and liver
Western Blot
Sample: ZR‑75 human breast cancer cell line, U937 human histiocytic lymphoma cell line, and K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line
Reviewed Applications
Read 3 reviews rated 4.3 using AF2474 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: TfR (Transferrin R)
The Transferrin Receptor (TfR or TfR-1, designated CD71) is a type 2 transmembrane glycoprotein expressed on erythroid progenitors, muscle cells and proliferating cells as a 188 kDa disulfide-linked homodimer of 95 kDa monomers (1-4). As the major mediator of cellular iron uptake, it binds and internalizes diferric transferrin, allowing iron release at the low pH of the endosome (2, 5). The human TfR cDNA encodes 760 amino acids (aa) including a 67 aa N-terminal intracellular domain, a 21 aa transmembrane domain, and a 672 aa extracellular domain (ECD) with helical, peptidase (nonfunctional), and ligand binding domains, including an RGD potential integrin binding site (5). Human TfR ECD shares 75 - 80% aa identity with mouse, rat, feline, canine, equine, porcine and bovine TfR. A 679 aa alternately spliced form begins at aa 82 and is presumably secreted, while in an 804 aa form, 44 aa are inserted at aa 518 within the peptidase region (6). Most soluble TfR (sTfR) arises from trypsin proteolysis at aa 100, producing the circulating form of TfR (3). sTfR concentration in plasma or serum is proportional to total TfR and can be increased by iron deficiency (3). Erythroid progenitors, which use iron for hemoglobin synthesis, normally account for the bulk of total body TfR production (3). Since rapidly growing cells require iron to replicate DNA, cancer cells can express up to 5-fold more TfR than quiescent cells in the surrounding tissue (2, 4). Antibody targeting of TfR can inhibit tumor cell proliferation and induce apoptosis (2, 4). The hereditary hemochromatosis protein HFE competes with diferric transferrin for binding to TfR, and targets TfR for degradation rather than recycling (2, 5). TfR has been reported to have ferritin-independent functions in T cell development, immunological synapse formation and galectin-3-mediated cell death, and to be a cell entry receptor for New World hemorrhagic fever arenaviruses (2, 4, 7).
References
- Schneider, C. et al. (1984) Nature 311:675.
- Daniels, T.R. et al. (2006) Clin. Immunol. 121:144.
- Skikne, B.S. (2008) Am. J. Hematol. 83:872.
- Macedo, M.F. and M. deSousa (2008) Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets 7:41.
- Aisen, P. (2004) Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 36:2137.
- Entrez protein Accession # EAW53671, EAW53672.
- Radoshitzky, S.R. et al. (2007) Nature 446:92.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
Additional TfR (Transferrin R) Products
Product Documents for Human TfR (Transferrin R) Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human TfR (Transferrin R) Antibody
For research use only