Human Uteroglobin/SCGB1A1 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF4218

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Glu22-Asn91
Accession # NP_003348
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Endotoxin Level
Scientific Data Images for Human Uteroglobin/SCGB1A1 Antibody
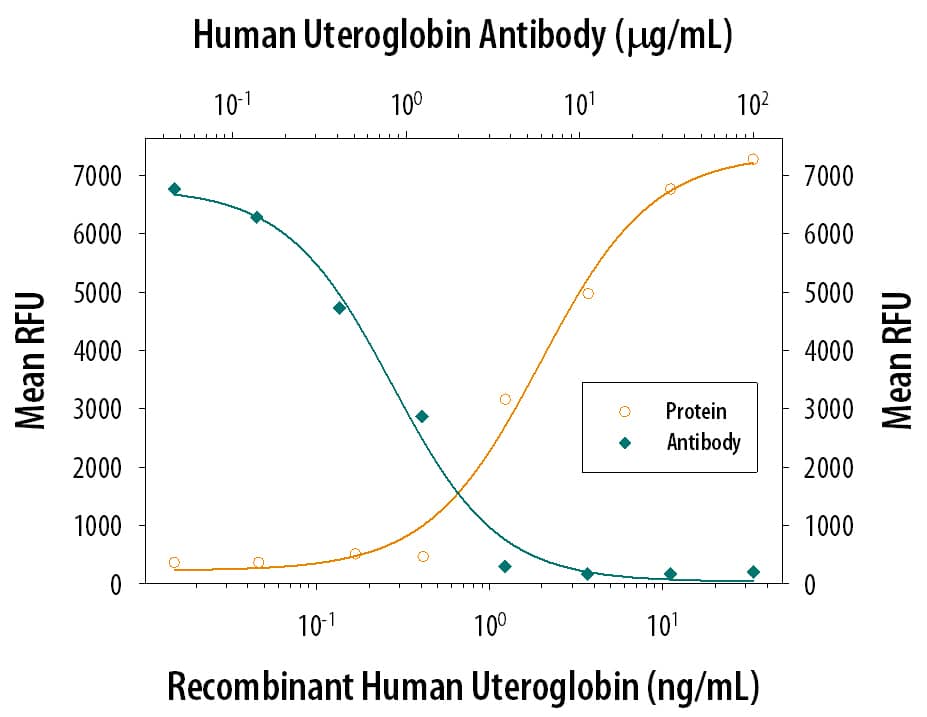
Cell Adhesion Mediated by Uteroglobin and Neutralization by Human Uteroglobin Antibody.
Recombinant Human Uteroglobin (Catalog # 4218-UT), immobilized onto a microplate, supports the adhesion of A549 human lung carcinoma cell line in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). Adhesion elicited by Recombinant Human Uteroglobin (5 µg/mL) is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Human Uteroglobin Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF4218). The ND50 is typically 0.3‑1.2 µg/mL.Uteroglobin/SCGB1A1 in Human Endometrial Cancer Tissue.
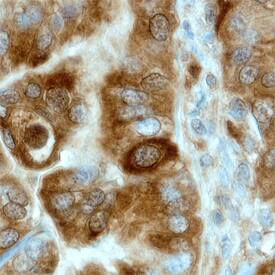
Uteroglobin/SCGB1A1 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human endometrial cancer tissue using Human Uteroglobin/SCGB1A1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF4218) at 3 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (Catalog # CTS013). Tissue was stained using the Anti-Sheep HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS019) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm of epithelial cells. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.Applications for Human Uteroglobin/SCGB1A1 Antibody
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections in human endometrial cancer tissue
Neutralization
Reviewed Applications
Read 1 review rated 5 using AF4218 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Uteroglobin/SCGB1A1
Uteroglobin, also called Clara cell secretory, phospholipid binding, 10 kDa or 16 kDa protein (CCSP, CCPBP, CC10 or CC16, respectively) is a small, non‑glycosylated secreted protein of the secretoglobin superfamily, (designated 1A, member 1) (1‑3). Its name is derived from its very high expression in the pre‑implantation uterus. It is produced by the non-ciliated, non-mucous secretory cells that predominate in lung bronchioles (Clara cells), and other non-ciliated epithelia that communicate with the external environment (1‑3). Expression is induced by steroid hormones such as estrogen, and enhanced by the non-steroid hormone prolactin (1). Uteroglobin is found in blood, urine and other body fluids (1). Human Uteroglobin cDNA encodes a 21 amino acid (aa) signal sequence and a 70 aa mature protein. It shares 53-56% aa identity with mouse, rat, bovine, canine, equine or rabbit Uteroglobin, and is active in mice (4). The mature protein forms a disulfide-linked head-to-tail homodimer of 16 kDa (2, 5). This homodimer is thought to form a binding pocket that binds hydrophobic ligands such as phospholipids, progesterone and retinols (5). Sequestering of prostaglandins and leukotrienes is anti-inflammatory, while sequestering of carcinogens such as polychlorinated bisphenols is anti-tumorigenic (6‑8). Other immunoregulatory activities of Uteroglobin include cell migration inhibition (by binding the chemotaxis-related formyl peptide receptor FPR2 on dendritic cells), and the inhibition of T cell differentiation to a Th2 phenotype (9). A single nucleotide polymorphism of Uteroglobin, A38G, confers increased risk of asthma (10). Transglutaminase can crosslink Uteroglobin, either to itself or to other proteins such as the adhesion molecule fibronectin (3, 11). Binding of fibronectin to Uteroglobin in the kidney is thought to protect against nephropathy, while binding of the lipocalin-1 receptor has been reported to suppress cancer cell motility and invasion (12, 13).
References
- Mukherjee, A.B. et al. (2007) Endocr. Rev. 28:707.
- Singh, G. et al. (1988) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 950:329.
- Mantile, G. et al. (1993) J. Biol. Chem. 268:20343.
- Wang, S-Z. et al. (2003) J. Immunol. 171:1051.
- Umland, T.C. et al. (1994) Nat. Struct. Biol. 1:538.
- Mandal, A.K. et al. (2004) J. Exp. Med. 199:1317.
- Watson, T.M. et al. (2001) Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 281:L1523.
- Yang, Y. et al. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279:29336.
- Ray, R. et al. (2006) FEBS Lett. 580:6022.
- Martin, A.C. et al. (2006) Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 173:617.
- Antico, G. et al. (2006) J. Cell Physiol. 207:553.
- Zheng, F. et al. (1999) Nat. Med. 5:1018.
- Zhang, Z. et al. (2006) Gene 369:66.
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Uteroglobin/SCGB1A1 Products
Product Documents for Human Uteroglobin/SCGB1A1 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human Uteroglobin/SCGB1A1 Antibody
For research use only