Mouse DC-SIGN/CD209 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB83451

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Accession # FJ168685
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Mouse DC-SIGN/CD209 Antibody
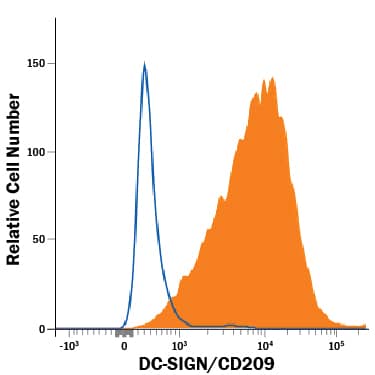
Detection of DC‑SIGN/CD209 in CHO Chinese Hamster Cell Line Transfected with Mouse DC-SIGN/CD209 by Flow Cytometry.
CHO Chinese hamster ovary cell line transfected with mouse DC-SIGN/CD209 was stained with Mouse Anti-Mouse DC-SIGN/CD209 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB83451, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody Mouse IgG2C, followed by Allophycocyanin-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0101B).Applications for Mouse DC-SIGN/CD209 Antibody
CyTOF-ready
Flow Cytometry
Sample: CHO Chinese hamster ovary cell line transfected with mouse DC-SIGN/CD209
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: DC-SIGN/CD209
Human DC-Sign (Dendritic Cell-Specific ICAM-3 Grabbing Nonintegrin), also known as CD209, is a member of the chromosome 19 C-type lectin family that includes DC-SIGN, DC-SIGN-related protein, CD23 and LSECtin (1). DC-SIGN was initially reported to be a 46 kDa, 404 amino acid (aa) type II transmembrane protein that contained a 40 aa cytoplasmic N-terminus, a 21 aa transmembrane segment, and a 343 aa extracellular C-terminus (2). The extracellular region contains a distal, 115 aa Ca++-dependent carbohydrate-binding lectin domain and a membrane-proximal linker segment that is composed of seven 23 aa repeats (2, 3). The lectin domain is believed to preferably bind mannose, either within the context of ICAM-3 (on T cells) or ICAM-2 (on endothelial cells) (2, 4, 5). DC-SIGN expression appears to be limited to dendritic cells (DC) and macrophages (6), and DC interaction with the ICAMs both aids DC cell trafficking and immunological synapse formation (7). Since the original report on DC-SIGN, multiple splice forms have been discovered, generating both membrane-bound and soluble forms (3). There are eight type A isoforms, all of which begin with the same 15 aa of exon 1a. Four contain the transmembrane region of exon II, and four do not (i.e., are soluble). Among these eight type A isoforms, only three retain the entire 343 aa found in the full length form described in reference #2 (the full length form is referred to as type I mDC-SIGN1A) (3). Five additional isoforms utilize an alternate start site, and these are referred to as type B isoforms. These all show a 35 aa cytoplasmic domain. One also has a transmembrane segment; four do not. Two of the five contain full, unspliced extracellular regions (3). All of this suggests enormous complexity in DC-SIGN biology. DC-SIGN is not well conserved across species. Human and mouse show little overall aa identity. In the lectin domain, however, human DC-SIGN shares 68% aa identity with mouse DC-SIGN (8). Human and rhesus monkey DC-SIGN share 91% aa identity over the entire extracellular region (8).
References
- Liu, W. et al. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279:18748.
- Curtis, B.M. et al. (1992) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:8356.
- Mummidi, S. et al. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276:33196.
- Su, S.V. et al. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279:19122.
- Cambi, A. et al. (2005) Cell. Microbiol. 7:481.
- Serrano-Gomez, D. et al. (2004) J. Immunol. 173:5635.
- Geijtenbeek, T.B.H. and Y. van Kooyk (2003) Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 276:32.
- Baribaud, F. et al. (2001) J. Virol. 75:10281.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional DC-SIGN/CD209 Products
Product Documents for Mouse DC-SIGN/CD209 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Mouse DC-SIGN/CD209 Antibody
For research use only