Mouse Dectin-1/CLEC7A Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF1756

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Phe69-Leu244
Accession # Q6QLQ4
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Endotoxin Level
Scientific Data Images for Mouse Dectin-1/CLEC7A Antibody
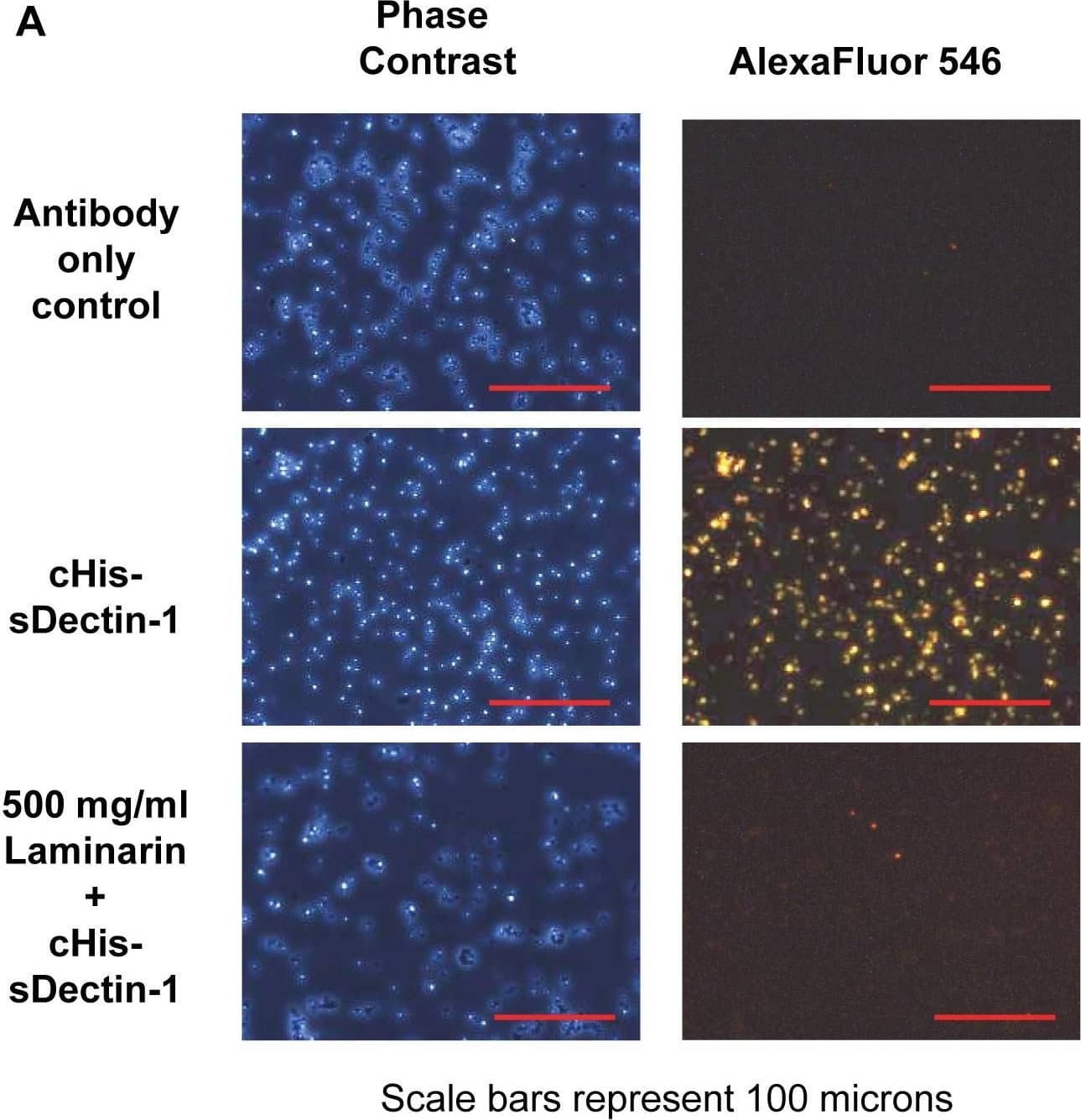
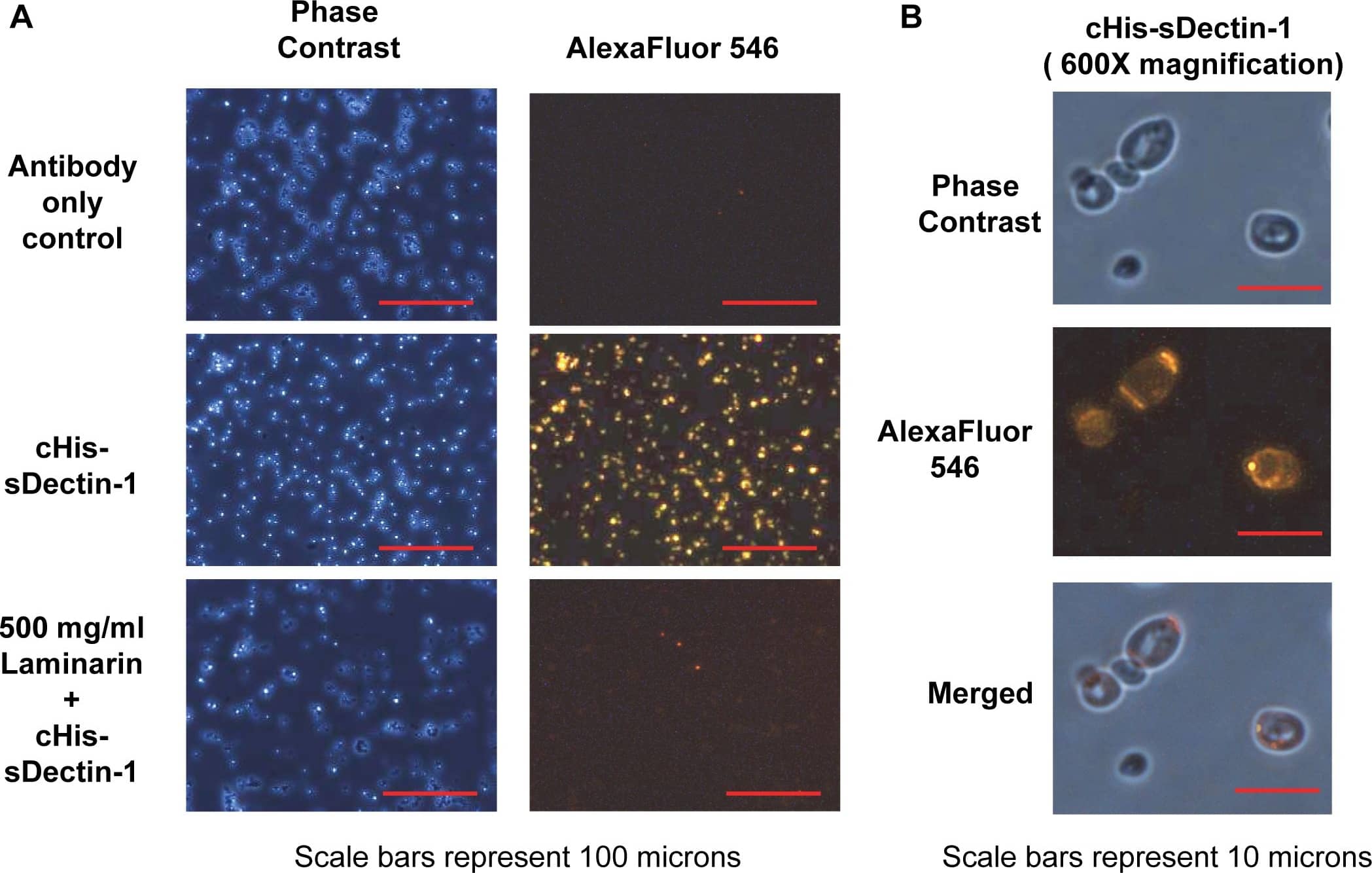
Detection of Yeast Dectin-1/CLEC7A by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
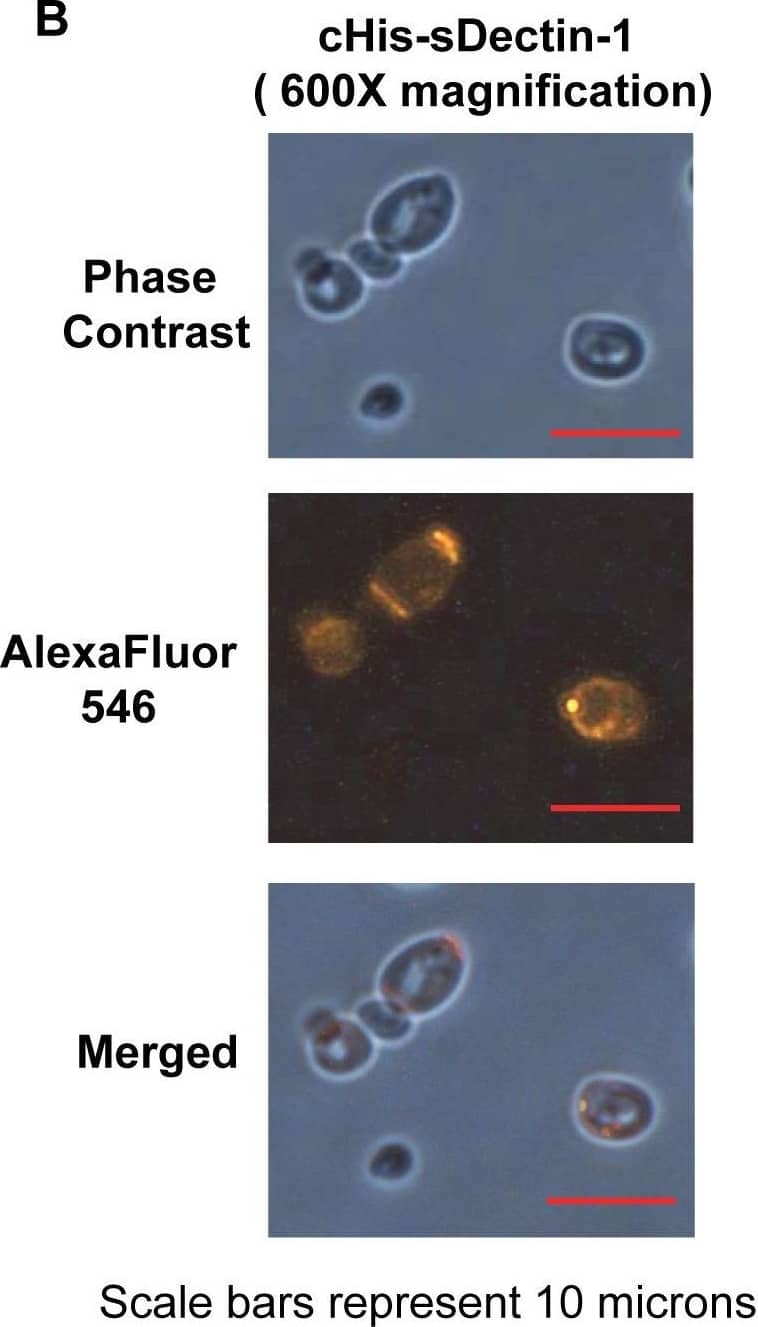
Binding of cHis-sDectin-1 to Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells.Purified cHis-sDectin-1 was diluted to a concentration of 25 µg/ml in blocking buffer with 500 µg/ml, 100 µg/ml or no laminarin. This was added to Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast cells from overnight culture in blocking buffer (PBS with 3% FBS). The cells were then probed with an mDectin-1 goat polyclonal antibody (1∶200; AF1756; R&D Systems) and AlexaFluor546-conjugated anti-goat antibody (1∶100; Catalog Number A-11056; Molecular Probes). After which, the cells were washed with PBS and fixed using 4% paraformaldehyde. The cells were then resuspended in PBS and visualized by phase contrast and fluorescent microscopy at (A) 200× magnification and (B) 600× magnification. Images are cropped or scaled to fit the illustration. cHis-sDectin-1 stained yeast cells was also analyzed by flow cytometry (C). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0052785), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Detection of Yeast Dectin-1/CLEC7A by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
Binding of cHis-sDectin-1 to Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells.Purified cHis-sDectin-1 was diluted to a concentration of 25 µg/ml in blocking buffer with 500 µg/ml, 100 µg/ml or no laminarin. This was added to Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast cells from overnight culture in blocking buffer (PBS with 3% FBS). The cells were then probed with an mDectin-1 goat polyclonal antibody (1∶200; AF1756; R&D Systems) and AlexaFluor546-conjugated anti-goat antibody (1∶100; Catalog Number A-11056; Molecular Probes). After which, the cells were washed with PBS and fixed using 4% paraformaldehyde. The cells were then resuspended in PBS and visualized by phase contrast and fluorescent microscopy at (A) 200× magnification and (B) 600× magnification. Images are cropped or scaled to fit the illustration. cHis-sDectin-1 stained yeast cells was also analyzed by flow cytometry (C). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0052785), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Detection of Yeast Dectin-1/CLEC7A by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
Binding of cHis-sDectin-1 to Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells.Purified cHis-sDectin-1 was diluted to a concentration of 25 µg/ml in blocking buffer with 500 µg/ml, 100 µg/ml or no laminarin. This was added to Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast cells from overnight culture in blocking buffer (PBS with 3% FBS). The cells were then probed with an mDectin-1 goat polyclonal antibody (1∶200; AF1756; R&D Systems) and AlexaFluor546-conjugated anti-goat antibody (1∶100; Catalog Number A-11056; Molecular Probes). After which, the cells were washed with PBS and fixed using 4% paraformaldehyde. The cells were then resuspended in PBS and visualized by phase contrast and fluorescent microscopy at (A) 200× magnification and (B) 600× magnification. Images are cropped or scaled to fit the illustration. cHis-sDectin-1 stained yeast cells was also analyzed by flow cytometry (C). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0052785), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Mouse Dectin-1/CLEC7A Antibody
Blockade of Receptor-ligand Interaction
CyTOF-ready
Flow Cytometry
Sample: RAW 264.7 mouse monocyte/macrophage cell line
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Mouse Dectin-1/CLEC7A (Catalog # 1756-DC)
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Dectin-1/CLEC7A
Dectin-1, also known as CLEC7A and the beta-glucan receptor, is a 43 kDa type II transmembrane C-type lectin that functions in the innate immune response to fungal pathogens. Although Dectin-1 resembles other CLEC molecules structurally, it binds ligands in a calcium-independent manner (1, 2). Mature mouse Dectin-1 is a 244 amino acid (aa) glycoprotein that consists of a short ITAM-containing cytoplasmic tail, a transmembrane segment, and a stalk and carbohydrate recognition domain (CRD) in the extracellular domain (3). The CRD of mouse Dectin-1 shares 61%, 60%, and 87% aa sequence identity with that of bovine, human, and rat Dectin-1, respectively. It shares 25-34% aa sequence identity with the CRD of other subgroup members CLEC-1, CLEC-2, CLEC9A, CLEC12B, LOX-1, and MICL. Mouse Dectin-1 is alternately spliced, generating a variant that lacks the stalk region (4). Mouse Dectin-1 is expressed on monocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils, and on some populations of dendritic cells and T cells (5). It is upregulated on macrophages by GM-CSF, IL-4, or IL-13 and downregulated by dexamethasone, IL-10, or LPS (6). The CRD selectively binds beta-glucan polymers, a major component of yeast and mycobacterial cell walls (7). Yeast beta-glucan is accessible to Dectin-1 only at sites of cell budding, and Dectin-1 does not recognize the filamentous form of yeast (8). Dectin-1 mediates the phagocytosis of zymosan particles and intact yeast (8-10). It co-localizes with TLR2 in the presence of zymosan, and the two receptors cooperate in ligand recognition and the propagation of proinflammatory signaling (9, 11-13). Dectin-1 interaction with the tetraspanin CD37 increases its stability on the cell membrane and inhibits ligand-induced signaling (14). Genetic knockout of Dectin-1 in mice increases their susceptibility to pathogenic infection (15, 16).
References
- Kanazawa, N. (2007) J. Dermatol. Sci. 45:77.
- Brown, G.D. (2006) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6:33.
- Ariizumi, K. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275:20157.
- Heinsbroek, S.E.M. et al. (2006) J. Immunol. 176:5513.
- Taylor, P.R. et al. (2002) J. Immunol. 169:3876.
- Willment, J.A. et al. (2003) J. Immunol. 171:4569.
- Palma, A.S. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:5771.
- Gantner, B.N. et al. (2005) EMBO J. 24:1277.
- Gantner, B.N. et al. (2003) J. Exp. Med. 197:1107.
- Kennedy, A.D. et al. (2007) Eur. J. Immunol. 37:467.
- Brown, G.D. et al. (2003) J. Exp. Med. 197:1119.
- Yadav, M. and J.S. Schorey (2006) Blood 108:3168.
- Suram, S. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:5506.
- Meyer-Wentrup, F. et al. (2007) J. Immunol. 178:154.
- Saijo, S. et al. (2007) Nat. Immunol. 8:39.
- Taylor, P.R. et al. (2007) Nat. Immunol. 8:31.
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Dectin-1/CLEC7A Products
Product Documents for Mouse Dectin-1/CLEC7A Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Mouse Dectin-1/CLEC7A Antibody
For research use only