Mouse IL-17RC APC-conjugated Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # FAB2270A

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Leu21-Trp465
Accession # AAH04759
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Mouse IL-17RC APC-conjugated Antibody
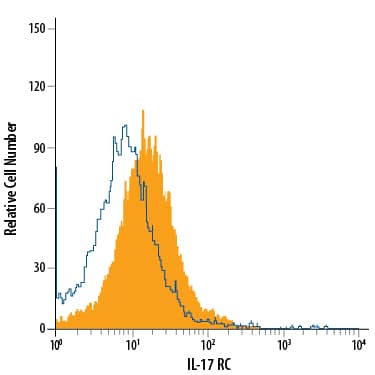
Detection of IL‑17 RC in RAW 264.7 Mouse Cell Line by Flow Cytometry.
RAW 264.7 mouse monocyte/macrophage cell line was stained with Goat Anti-Mouse IL-17 RC APC-conjugated Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB2270A, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # IC108A, open histogram). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.Detection of Mouse IL-17RC by Flow Cytometry
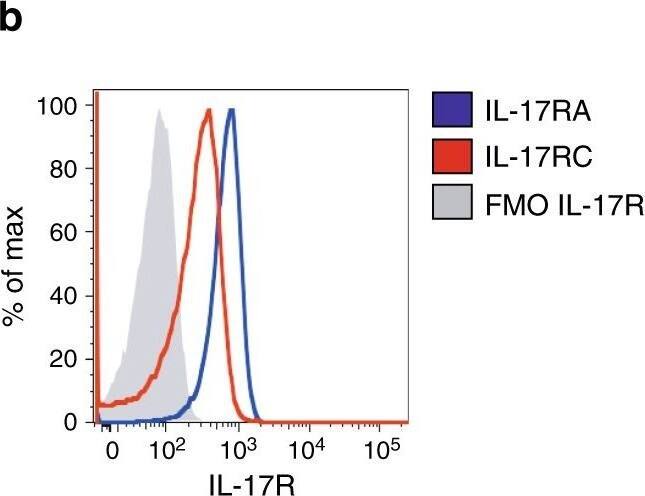
IL-17 promotes STAT-3 phosphorylation in Vk*MYC plasma cells. a Th17 polarization of OT-II splenocytes cultured for 7 days with BM serum obtained from WT, Early-MM and Late-MM Vk*MYC mice, and assessed for intracellular cytokine release by flow cytometry. None and Cytokines refer to the culture condition with or without IL-6, TGF-beta 1, anti-IL-4, and anti-IFN-gamma antibodies, respectively. (None n = 3, Cytokine n = 3, WT n = 6, Vk*MYC Early n = 11, Vk*MYC Late n = 11). Mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Unpaired t test: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. b Plasma cells were also stained with anti-IL-17RA and anti-IL-17RC antibodies (blue and red line respectively) and analyzed by flow-cytometry; FMO (Fluorescence Minus One) sample was not stained for IL-17R (gray histogram). c, d Representative histograms and e quantification of Vk*MYC PCs cultured in the presence of either one of the following stimuli: saturating amounts of IL6 (light blue line) or IL-17 (dark blue line), or BM sera from Early- (red line) or Late-MM (black dotted line), or BM sera from Early-MM and anti-IL17 antibodies (purple line). After culture, plasma cells were analyzed by flow-cytometry for STAT3 phosphorylation (pSTAT3). (IL-6 n = 5, IL-17A n = 5, Vk*MYC Early n = 8, Vk*MYC Early + alphaIL-17A n = 8, Vk*MYC Late n = 8). Mean ± SD of triplicate independent determinations. Unpaired t test: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001 Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30510245), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Detection of Mouse IL-17RC by Flow Cytometry
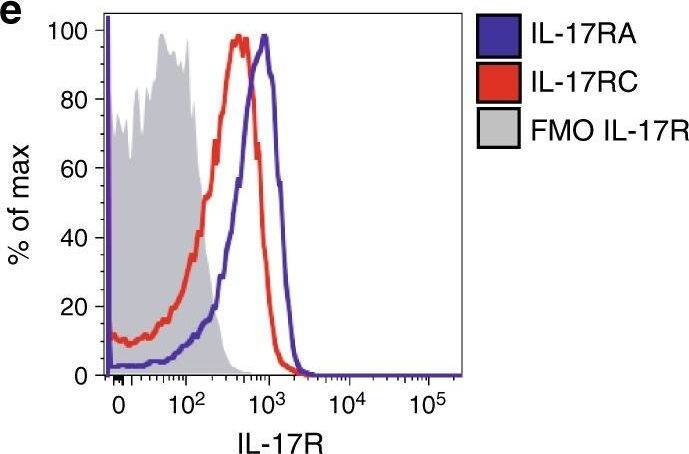
An IL-17-eosinophil axis in the BM of Vk*MYC mice favors disease progression. a Frequency of BM eosinophils (i.e., CD11b+Ly6CintMHC-II−Ly6G−SSChi or CD11b+Siglec-F+ cells) in Vk*MYC IL-17WT and Vk*MYC IL-17KO mice and age- and sex-matched WT littermates. Each dot represents an individual mouse. Mean ± SD of five independent experiments. Unpaired t test: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. b Representative dot plot of IL-6+ cells (gated on CD11b+Siglec-F+ cells) in the BM. c Percentage of IL-6+ cells gated on CD11b+Siglec-F+ cells. Mean ± SD of five independent experiments. Unpaired t test. d Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of IL-6 within Siglec-F+CD11b+ cells. Mean ± SD of five independent experiments. Unpaired t test. e BM derived eosinophils were also stained with anti-IL-17RA and anti-IL-17RC antibodies (blue and red line respectively) and analyzed by flow-cytometry; FMO (Fluorescence Minus One) sample was not stained for IL-17R (gray histogram). f Representative histograms of IL-6 and TNF-alpha production by eosinophils after IL-17A stimulation (red line). FMO samples were not stained for IL-6 or TNF-alpha. g Representative histograms of IL-6 and TNF-alpha production by eosinophils after MCP-3 stimulation (blue line). FMO samples were not stained for IL-6 or TNF-alpha. h IL-6 levels (MFI normalized on FMO sample) in eosinophils cultured alone (None; n = 4), or in the presence of WT (n = 4) or Early-MM (n = 8) or Late-MM (n = 5) BM serum. Mean ± SD of aggregated data from three independent experiments. Unpaired t test. i IL-6 levels (MFI normalized on Early-MM sample) in eosinophils cultured alone (None; n = 5), or in the presence of Early-MM with or without the addition of anti-CCR3 (n = 5) or anti-IL-17A (n = 5). Mean ± SD of aggregated data from three independent experiments. Paired t test. a, c, d Specific n values of biologically independent mice are shown Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30510245), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Mouse IL-17RC APC-conjugated Antibody
Flow Cytometry
Sample: RAW 264.7 mouse monocyte/macrophage cell line
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, 2 to 8 °C as supplied.
Background: IL-17RC
IL-17 receptor C (IL-17 RC; also known as IL-17 RL) is an 85‑110 kDa member of the IL-17 receptor family. This is one of five families, termed IL-17 RA, B, C, D and E, that comprise the cytokine receptor superfamily (1‑6). Not all receptors appear to bind known members of the IL-17 cytokine family. To date, IL-17 RA is reported to bind IL-17A, while IL-17 RB is reported to bind IL-17B and IL-17E (2, 4). Mouse IL-17 RC is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein that is expressed on a variety of nonhematopoietic cell types. Full-length IL-17 RC is synthesized as a 674 amino acid (aa) precursor. It contains a 21 aa signal sequence, a 419 aa extracellular domain (ECD), a 21 aa transmembrane segment, and a 213 aa cytoplasmic region. There are multiple potential N‑linked glycosylation sites in the ECD and potential phosphorylation sites in the cytoplasmic tail. Four mouse variants have been identified that have been designated mIL-17 RC (7). The isoform expressed here as an R&D product is an unusual 567 aa form (8). Its precursor contains a 20 aa signal sequence, a 444 aa extracellular region, a 20 aa transmembrane segment and an 83 aa cytoplasmic tail. When compared to the full length mouse IL-17 RC form, this expressed isoform’s extracellular region shows absolute aa identity, save for an additional 24 aa insert. In the cytoplasmic region, it is highly divergent and shows virtually no aa identity (8‑9). The extracellular region of mouse IL-17 RC shows about 70% aa identity to the equivalent region in human IL-17 RC isoform # 3. IL-17 RC is the cognate receptor for IL-17F (7). In humans, IL-17 RC binds IL-17A with similar affinity, and with IL-17 RA, it forms a definitive receptor for both IL-17A and IL-17F (7). The stoichiometry is unclear; it may form a heterodimer with IL-17 RA, or a heterotrimer with a preexisting IL-17 RA homodimer (4, 7, 10, 11). The heteromeric nature of the receptor may be important given that the predominant form of the IL-17 cytokine is now considered to be an IL-17A:IL-17F heterodimer (4).
References
- Gaffen, S.L. et al. (2006) Vitam. Horm. 74:255.
- Weaver, C.T. et al. (2007) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 25:821.
- Moseley, T.A. et al. (2003) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 14:155.
- Shen, F. and S.L. Gaffen (2008) Cytokine 41:92.
- You, Z. et al. (2006) Cancer Res. 66:175.
- You, Z. et al. (2007) Neoplasia 9:464.
- Kuestner, R.E. et al. (2007) J. Immunol. 179:5462.
- GenBank Accession # AAH04759.
- Haudenschild, D. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277:4309.
- Toy, D. et al. (2006) J. Immunol. 177:36.
- Haudenschild, D.R. et al. (2006) Prostate 66:1268.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional IL-17RC Products
Product Documents for Mouse IL-17RC APC-conjugated Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Mouse IL-17RC APC-conjugated Antibody
For research use only