Mouse PDGF R alpha Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB3221

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Applications
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Leu25-Glu524
Accession # P26618.3
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Mouse PDGF R alpha Antibody
PDGF R alpha in NIH-3T3 Mouse Cell Line.
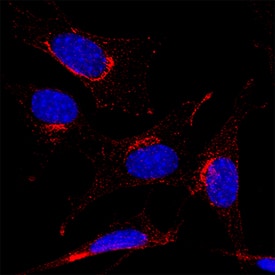
PDGF R alpha was detected in immersion fixed NIH-3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line using Rat Anti-Mouse PDGF R alpha Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB3221) at 8 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Rat IgG Secondary Antibody (red; NL013) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cell surface. Staining was performed using our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Non-adherent Cells.PDGF R alpha in 13 d.p.c. mouse embryos.
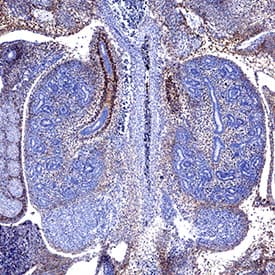
PDGF R alpha was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of 13 d.p.c. mouse embryos using Rat Anti-MousePDGF R alpha Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB3221) at 5 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Rat IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (VC005). Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (CTS013). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to embryonic kidney. Staining was performed using our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.Applications for Mouse PDGF R alpha Antibody
Immunocytochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed NIH‑3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of 13 d.p.c. mouse embryos
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: PDGF R alpha
PDGF R alpha (platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha) is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein in the class III subfamily of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK) (1-3). PDGF R alpha and PDGF R beta can form homo- or hetero-dimeric receptors when engaged by dimers of the PDGF family of growth factors, which include disulfide-linked homodimers of PDGF-A, B, C or D, or the heterodimer PDGF-AB that is mainly found in human platelets. While multiple in vitro ligand-receptor combinations have been identified, in vivo evidence indicates that PDGF R alpha primarily binds PDGF-AA and PDGF-CC, while PDGF R beta primarily binds PDGF-BB and probably PDGF-DD. Like all class III RTKs, the extracellular domain (ECD) of mouse PDGF R alpha (amino acids 25-525) contains five immunoglobulin-like domains, while the intracellular region contains a split tyrosine kinase domain (aa 593‑954). Within the ECD, mouse PDGF R alpha shares 85%, 93%, 84%, 84%, and 81% amino acid sequence identity with human, rat, equine, canine and bovine PDGF R alpha respectively. PDGF R alpha autophosphorylates upon dimerization, activating signaling cascades in PI 3-kinase Ras-MAP kinase, and PLC-gamma pathways (1, 2). Signaling is down‑regulated by SHP-2 phosphatase activity and by receptor endocytosis and lysosomal degradation. PDGF R alpha is expressed at low levels in most mesenchymal cells, but is strongly expressed in oligodendrocyte, lung, skin and intestinal progenitor cells and induced by inflammation or growth in culture (1-3). During development, mesenchymal cells expressing PDGF R alpha respond to local gradients of epithelially produced PDGF-AA or PDGF-CC during formation of the cranial and cardiac neural crest, retina, gonads, lung alveoli, intestinal villi, skin, hair follicles, skeleton, teeth, palate, and interstitial kidney mesenchyme (1, 4). Deletion of PDGF R alpha in mice severely impairs mesenchymal derivatives in both embryo and extraembryonic tissues, and high or low PDGF R alpha signaling in humans may result in spina bifida or cleft palate‑type malformations. Postnatally, PDGF R alpha is implicated in gliomas and fibrotic disorders of lung, heart and skin (scleroderma) (5- 7).
References
- Andrae, J. et al. (2008) Genes Dev. 22:1276.
- Heldin, C-H. and B. Westermark (1999) Physiol. Rev. 79:1283.
- Do, M.S. et al. (1992) Oncogene 7:1567.
- Klinghoffer, R.A. et al. (2002) Dev. Cell 2:103.
- Martinho, O. (2009) Br. J. Cancer 101:973.
- Olson, L.E. and P. Soriano (2009) Dev. Cell 16:303.
- Baroni, S.S. et al. (2006) N. Engl. J. Med. 354:2667.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional PDGF R alpha Products
Product Documents for Mouse PDGF R alpha Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Mouse PDGF R alpha Antibody
For research use only