Mouse/Rat SOD1/Cu-Zn SOD Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF3787

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Met1-Gln154
Accession # P08228
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Mouse/Rat SOD1/Cu-Zn SOD Antibody
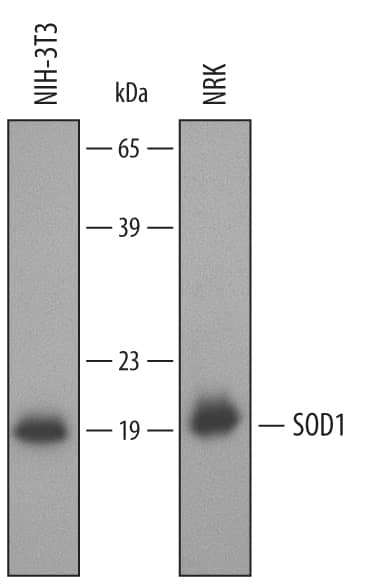
Detection of Mouse/Rat SOD1/Cu-Zn SOD by Western Blot.
Western blot shows lysates of NIH-3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line and NRK rat normal kidney cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 0.2 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Mouse/Rat SOD1/Cu-Zn SOD Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3787) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF017). A specific band was detected for SOD1/Cu-Zn SOD at approximately 19 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted using Immunoblot Buffer Group 2.Applications for Mouse/Rat SOD1/Cu-Zn SOD Antibody
Western Blot
Sample: NIH-3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line and NRK rat normal kidney cell line
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: SOD1/Cu-Zn SOD
Superoxide Dismutases (SODs), originally identified as Indophenoloxidase (IPO), are enzymes that catalyze the converversion of naturally-occuring but harmful superoxide radicals into molecular oxygen and hydrogen peroxide. Superoxide Dismutases 1, SOD1, also known as Cu/Zn SOD, soluble SOD, and IPO-A, is a soluble, cytoplasmic 16 kDa homodimer. Each SOD1 monomer binds one Cu2+ and Zn2+ ion. Three isozymes of SOD have been identified and are functionally related but have very modest sequence homology. SOD1 shares 23% and 27% sequence identity with SOD2 and SOD3, respectively. Mouse SOD1 is 97% aa identcal to rat SOD1. Mutations in SOD1 have been suggested to be the cause of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). The ALS-causing mutations of SOD1 are scattered throughout the protein and provide no clear functional or structural clues to the underlying disease mechanism. The oligomerization hypothesis suggests that mutant SOD1 proteins become misfolded and consequently oligomerize into high molecular weight aggregates that result in the death of motor neurons. The oxidative damage hypothesis suggests that loss of function mutations in SOD1 result in the intracellular accumulation of the superoxide radical, leading to free radical-mediated damage, the release of cytochrome c, and apoptosis.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional SOD1/Cu-Zn SOD Products
Product Documents for Mouse/Rat SOD1/Cu-Zn SOD Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Mouse/Rat SOD1/Cu-Zn SOD Antibody
For research use only