Mouse Siglec-F Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB17061

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Asp18-Thr437
Accession # Q920G3
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Endotoxin Level
Scientific Data Images for Mouse Siglec-F Antibody
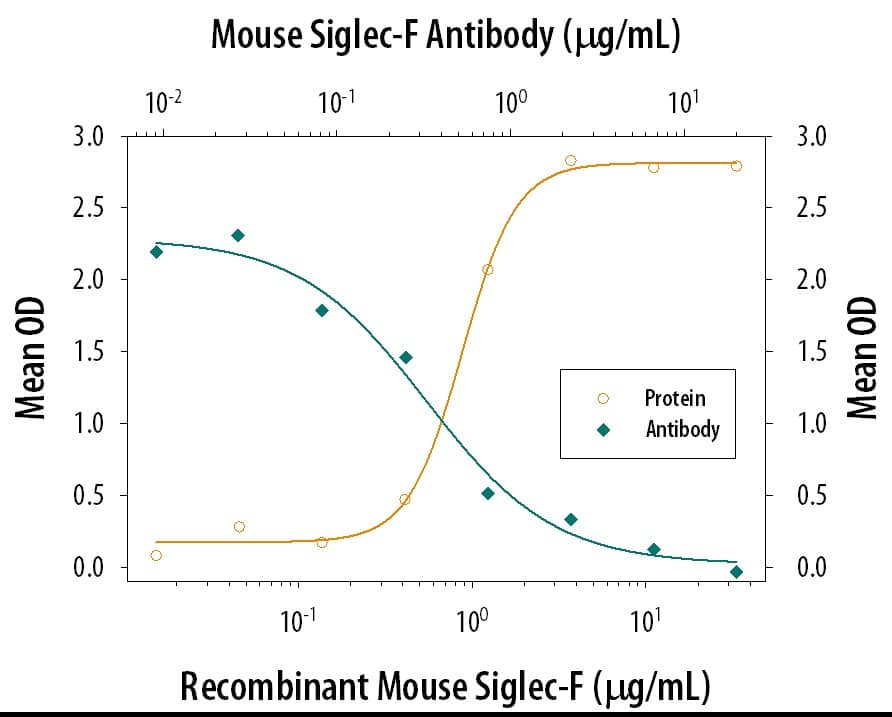
Cell Adhesion Mediated by Siglec-F and Neutralization by Mouse Siglec-F Antibody.
Recombinant Mouse Siglec-F Fc Chimera (Catalog # 1706-SF), immobilized onto a microplate, supports the adhesion of human red blood cells in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). Adhesion elicited by Recombinant Mouse Siglec-F Fc Chimera (5 µg/mL) is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Mouse Siglec-F Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB17061). The ND50 is typically 0.1-0.5 µg/mL.Applications for Mouse Siglec-F Antibody
Neutralization
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Siglec-F
Siglecs (1) (sialic acid binding Ig-like lectins) are I-type (Ig-type) lectins (2) belonging to the Ig superfamily. They are characterized by an N-terminal Ig-like V-type domain which mediates sialic acid binding (3), followed by varying numbers of Ig-like C2-type domains (1, 4). Eleven human Siglecs have been cloned and characterized (1, 4). They are sialoadhesin/CD169/Siglec-1, CD22/Siglec-2, CD33/Siglec-3, Myelin-Associated Glycoprotein (MAG/Siglec-4a) and Siglec 5 to 11 (4‑6). To date, no Siglec has been shown to recognized any cell surface ligand other than sialic acids, suggesting that interactions with glycans containing this carbohydrate are important in mediating the biological functions of Siglecs. Siglec 5 to 11 share a high degree of sequence similarity with CD33/Siglec-3 both in their extracellular and intracellular regions. They are collectively referred to as CD33-related Siglecs. One remarkable feature of the CD33-related Siglecs is their differential expression pattern within the hematopoietic system (4, 5). This fact, together with the presence of two conserved immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motifs (ITIMs) in their cytoplasmic tails, suggests that CD33-related Siglecs are involved in the regulation of cellular activation within the immune system.
Mouse Siglec-F cDNA encodes a 569 amino acid polypeptide with a hydrophobic signal peptide, an N-terminal Ig-like V-type domain, three Ig-like C2-type domains, a transmembrane region and a cytoplasmic tail (7). The expression of Siglec-F is restricted to the cells of myelomonocytic lineage. Mouse Siglec-F is likely an ortholog of human Siglec-5. Unlike many human CD33-related Siglecs, which show similar binding to both alpha2,3- and alpha2,6-linked sialic acids, mouse Siglec-F preferentially recognize alpha2,3-linked sialic acid.
References
- Crocker, P.R. et al. (1998) Glycobiology 8:v.
- Powell, L.D. et al. (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270:14243.
- May, A.R. et al. (1998) Mol. Cell 1998. 1:719.
- Crocker, P.R. and A. Varki (2001) Trends Immunol. 22:337.
- Crocker, P.R. et al. (2001) Immunology 103:137.
- Angata, T. et al. (2002) J. Biol Chem. 277:24466.
- Angata, T. et al. (2001) J. Biol Chem. 276:45128.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Siglec-F Products
Product Documents for Mouse Siglec-F Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Mouse Siglec-F Antibody
For research use only