Rat IL-1 alpha/IL-1F1 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF500

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Ser115-Ser270
Accession # P16598
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Endotoxin Level
Scientific Data Images for Rat IL-1 alpha/IL-1F1 Antibody
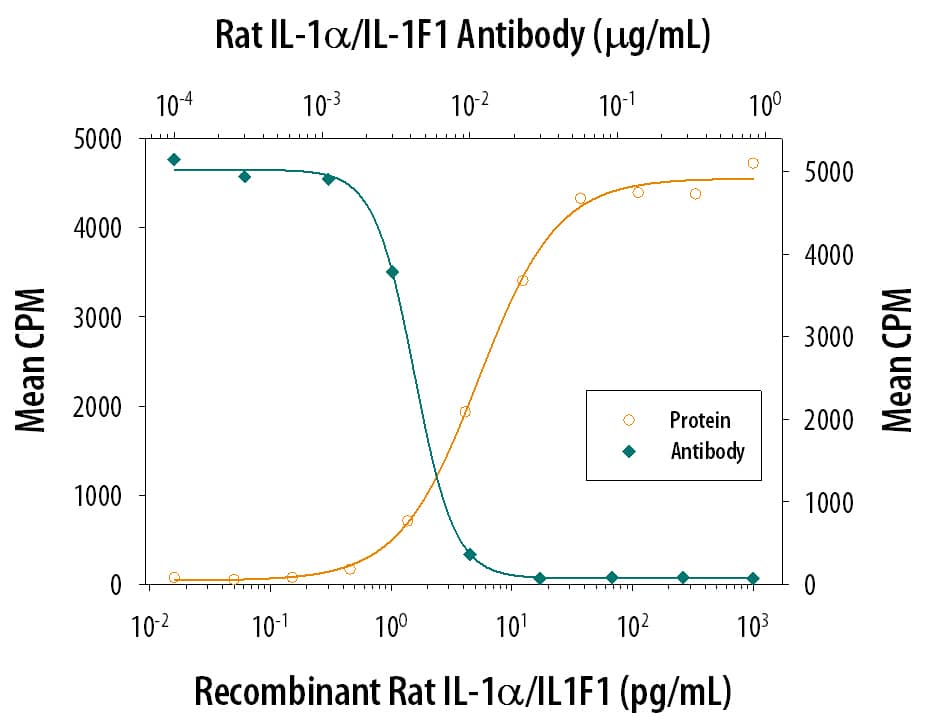
Cell Proliferation Induced by IL‑1 alpha/IL‑1F1 and Neutralization by Rat IL‑1 alpha/IL‑1F1 Antibody.
Recombinant Rat IL-1a/IL-1F1 (Catalog # 500-RL) stimulates proliferation in the the D10.G4.1 mouse helper T cell line in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). Proliferation elicited by Recombinant Rat IL-1a/IL-1F1 (50 pg/mL) is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Goat Anti-Rat IL-1a/IL-1F1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF500). The ND50 is typically 0.003-0.009 µg/mL.Applications for Rat IL-1 alpha/IL-1F1 Antibody
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Rat IL-1 alpha/IL-1F1 (Catalog # 500-RL)
Neutralization
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: IL-1 alpha/IL-1F1
Interleukin 1 (IL-1) is a name that designates two proteins, IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta, which are the products of distinct genes, but which show approximately 25% amino acid (aa) sequence identity and which recognize the same cell surface receptors. Although IL-1 production is generally considered to be a consequence of inflammation, evidence suggests that IL-1 is also temporally upregulated during bone formation and the menstrual cycle and can be induced in response to nervous system stimulation. In response to classic stimuli produced by inflammatory agents, infections or microbial endotoxins, a dramatic increase in the production of IL-1 by macrophages and various other cells is seen. Cells in particular known to produce IL-1 include osteoblasts, monocytes, macrophages, keratinocytes, Kupffer cells, hepatocytes, thymic and salivary gland epithelium, Schwann cells, fibroblasts, and glia (oligodendroglia, astrocytes, and microglia).
IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta are both synthesized as 31 kDa precursors that are subsequently cleaved into proteins with molecular weights of approximately 17,000 Da. Neither precursor contains a typical hydrophobic signal peptide sequence and most of the precursor form of IL-1 alpha remains in the cytosol of cells, although there is evidence for a membrane-bound form of the precursor form of IL-1 alpha. The IL-1 alpha precursor reportedly shows full biological activity in the EL-4 assay. Among various species, the aa sequence of mature IL-1 alpha is conserved 60‑70% and human IL-1 has been found to be biologically active on murine cell lines. Both forms of IL-1 bind to the same receptors, designated type I and type II. Evidence suggests that only the type I receptor is capable of signal transduction and that the type II receptor may function as a decoy, binding IL-1 and thus preventing binding of IL-1 to the type I receptor.
References
- Dower, S.K. and J.Z. Sims, (1994) Guidebook to Cytokines and Their Receptors, Nicola, N.A., ed., Oxford University Press, New York p. 17.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional IL-1 alpha/IL-1F1 Products
Product Documents for Rat IL-1 alpha/IL-1F1 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Rat IL-1 alpha/IL-1F1 Antibody
For research use only