Rat MAG/Siglec-4a Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF538

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Gly20-Pro516
Accession # P07722
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Rat MAG/Siglec-4a Antibody
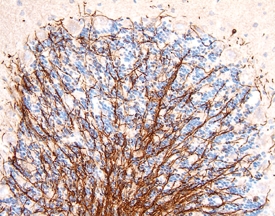
MAG/Siglec-4a in Rat Brain.
MAG/Siglec-4a was detected in perfusion fixed frozen sections of rat brain (cerebellum) using 25 µg/mL Goat Anti-Rat MAG/Siglec-4a Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF538) overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained with the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific labeling was localized to processes of oligodendrocytes. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections.Applications for Rat MAG/Siglec-4a Antibody
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Perfusion fixed frozen sections of rat brain (cerebellum)
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Rat MAG/Siglec-4a Fc Chimera (Catalog # 538-MG)
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: MAG/Siglec-4a
MAG (Myelin-Associated Glycoprotein), a type I transmembrane glycoprotein containing five Ig-like domains in its extracellular domain is an adhesion molecule belonging to the immunoglobin superfamily. Within this superfamily, MAG, CD22, CD33, Schwann cell myelin protein, and sialoadhesin which bind specifically to cell-surface glycan containing sialic acid residues define the I-type sialyl lectin subgroup, also called the sialoadhesin family. Sialoadhesins mediate diverse biological processes through recognition of specific sialyted glycans on cell surface. MAG is expressed on myelinating oligodenrocytes and Schwann cells, and preferentially recognizes alpha2, 3-linked sialic acid on O-linked glycans and gangliosides. MAG exists as two isoforms which differ in the sequence and length of the cytoplasmic tail. The large form (71 kDa) and small form (67 kDa) arise from alternative spliced mRNAs. Although MAG might encounter haematopoietic cells and lymphocytes under pathologic conditions, it would normally be expected to interact with neuronal cells. It has been shown that MAG promotes axonal growth from neonatal DRG neurons and embryonic spinal neurons, but is a potent inhibitor of axonal re-growth from adult DRG and postnatal cerebellar neurons. MAG plays an important role in the interaction between axons and myelin. A soluble form of MAG containing the extracellular domain is released from myelin in large quantities and identified in normal human tissues and in tissues from patients with neurological disorders. This soluble MAG might contribute to the lack of CNS neuron regeneration after injury.
References
- Kelm, S. et al. (1994) Current Biology 4:965.
- McKerracher, L. et al. (1994) Neuron 13:805.
- Tang, S. et al. (1997) Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience 9:333.
- Cai, D. et al. (1999) Neuron 22:89.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional MAG/Siglec-4a Products
Product Documents for Rat MAG/Siglec-4a Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Rat MAG/Siglec-4a Antibody
For research use only