TLR4 Antibody (HTA125) - BSA Free
Novus Biologicals, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # NB100-56723
Clone HTA125 was used by HLDA to establish CD designation.

![Western Blot: TLR4 Antibody (HTA125)BSA Free [NB100-56723] Western Blot: TLR4 Antibody (HTA125)BSA Free [NB100-56723]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/TLR4-Antibody-HTA125-Western-Blot-NB100-56723-img0023.jpg)
Conjugate
Catalog #
Forumulation
Catalog #
Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Human, Mouse, Canine
Cited:
Human, Mouse, Rat, Canine
Applications
Validated:
Block/Neutralize, CyTOF-ready, Flow (Cell Surface), Flow Cytometry, Functional, Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry, Immunohistochemistry Whole-Mount, Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin, Immunoprecipitation, In vitro assay, Western Blot
Cited:
Block/Neutralize, ELISA, Flow (Cell Surface), Flow Cytometry, Functional Assay, Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin, Immunoprecipitation, In vitro assay, Western Blot
Label
Unconjugated
Antibody Source
Monoclonal Mouse IgG2A Clone # HTA125
Format
BSA Free
Concentration
1.0 mg/ml
Product Specifications
Immunogen
This TLR4 Antibody (HTA125) was developed by immunizing mice with Ba/F3 cell line expressing human TLR4 cell surface antigen.
Reactivity Notes
Mouse reactivity reported in scientific literature (PMID: 28219705).
Clonality
Monoclonal
Host
Mouse
Isotype
IgG2A
Theoretical MW
95.7 kDa.
Disclaimer note: The observed molecular weight of the protein may vary from the listed predicted molecular weight due to post translational modifications, post translation cleavages, relative charges, and other experimental factors.
Disclaimer note: The observed molecular weight of the protein may vary from the listed predicted molecular weight due to post translational modifications, post translation cleavages, relative charges, and other experimental factors.
Scientific Data Images for TLR4 Antibody (HTA125) - BSA Free
Western Blot: TLR4 Antibody (HTA125)BSA Free [NB100-56723]
Western Blot: TLR4 Antibody (HTA125) [NB100-56723] - Untransfected 293T cells probed with the monoclonal antibody against TLR4 (NB100-56723, Lane 1), TLR4 transfected 293T cells probed with the TLR4 monoclonal antibody (Lane 2), and with antibodies affinity-purified against the celiac peptide (Lane 3). TLR4 transfected 293T cells probed with TLR4 monoclonal (biotin) antibody (Lane 4) and probed first with affinity-purified anti-peptide antibodies, followed by an incubation with biotin-labelled anti-TLR4 monoclonal antibody (Lane 5). Human plasmocytoid dendritic cells probed with TLR4 monoclonal antibody (Lane 6), human monocytes probed with TLR4 monoclonal antibody (Lane 7) and with affinity-purified anti-peptide antibodies (Lane 8). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (//doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0030358) licensed under a CC-BY license.
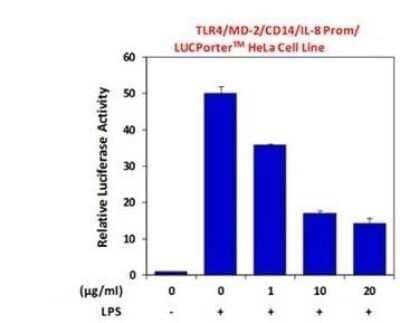
Block/Neutralize: TLR4 Antibody (HTA125) [NB100-56723] - Human monocyte-derived DCs were pre-incubated wit TLR-neutralizing antibodies including TLR4 antibody (NB100-56723) for 1 h. Afterwards, DCs were infected with H. pylori G27 (MOI 5) and the levels of the costimulatory molecule CD86 and the maturation marker CD83 were analyzed by FACS on CD11c+ cells 24 h post-infection. Data are presented as mean +/- SD of five independent experiments. *p<=0.05, **p<=0.005, ***p<=0.0005. Asterisks on top of bars indicate significance relative to non-neutralized, H. pylori-primed control cells. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (//doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0104804) licensed under a CC-BY license.
Flow Cytometry: TLR4 Antibody (HTA125) - BSA Free [NB100-56723]
Flow Cytometry: TLR4 Antibody (HTA125) [NB100-56723] - Analysis using Azide/BSA FREE version of NB100-56727. Cell surface analysis of TLR4 in stable HEK293/hTLR4 cells using this antibody. Secondary antibody goat anti-mouse IgG-PE at 0.25ug/10^6 cells. Both stable HEK293/hTLR4 and HEK293/Vector cell lines were equally stained.Applications for TLR4 Antibody (HTA125) - BSA Free
Application
Recommended Usage
Flow (Cell Surface)
reported in scientific literature (PMID 17015691)
Flow Cytometry
0.25 ug / 10^6 cells
Functional
reported in scientific literature (PMID 25412776)
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence
reported in scientific literature (PMID 27744428)
Immunohistochemistry Whole-Mount
reported in scientific literature (PMID 26610398)
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin
reported in scientific literature (PMID 24529879)
Immunoprecipitation
1:10-1:500
In vitro assay
reported in scientific literature (PMID 24676500)
Western Blot
1 - 2 ug/ml. Use reported in scientific literature (PMID 28546218)
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Protein G purified
Formulation
PBS
Format
BSA Free
Preservative
0.02% Sodium Azide
Concentration
1.0 mg/ml
Shipping
The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below.
Stability & Storage
Store at 4C short term. Aliquot and store at -20C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
Background: TLR4
TLR4 signaling occurs through two distinct pathways: The MyD88 (myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88)-dependent pathway and the MyD88-independent (TRIF-dependent, TIR domain-containing adaptor inducing IFN-beta) pathway (3, 5-7). The MyD88-dependent pathway occurs mainly at the plasma membrane and involves the binding of MyD88-adaptor-like (MAL) protein followed by a signaling cascade that results in the activation of transcription factors including nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) that promote the secretion of inflammatory molecules and increased phagocytosis (5-7). Conversely, the MyD88-independent pathway occurs after TLR4-MD2 complex internalization in the endosomal compartment. This pathway involves the binding of adapter proteins TRIF and TRIF-related adaptor molecule (TRAM), a signaling activation cascade resulting in IFN regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) translocation into the nucleus, and secretion of interferon-beta (INF-beta) genes and increased phagocytosis (5-7).
Given its expression on immune-related cells and its role in inflammation, TLR4 activation can contribute to various diseases (6-8). For instance, several studies have found that TLR4 activation is associated with neurodegeneration and several central nervous system (CNS) pathologies, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and Huntington's disease (6, 7). Furthermore, TLR4 mutations have been shown to lead to higher rates of infections and increased susceptibility to sepsis (7-8). One potential therapeutic approach aimed at targeting TLR4 and neuroinflammation is polyphenolic compounds which include flavonoids and phenolic acids and alcohols (8).
Alternative names for TLR4 includes 76B357.1, ARMD10, CD284 antigen, CD284, EC 3.2.2.6, homolog of Drosophila toll, hToll, toll like receptor 4 protein, TOLL, toll-like receptor 4.
References
1. Vaure, C., & Liu, Y. (2014). A comparative review of toll-like receptor 4 expression and functionality in different animal species. Frontiers in immunology. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2014.00316
2. Park, B. S., & Lee, J. O. (2013). Recognition of lipopolysaccharide pattern by TLR4 complexes. Experimental & molecular medicine. https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2013.97
3. Krishnan, J., Anwar, M.A., & Choi, S. (2016) TLR4 (Toll-Like Receptor 4). In: Choi S. (eds) Encyclopedia of Signaling Molecules. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-6438-9_592-1
4. Botos, I., Segal, D. M., & Davies, D. R. (2011). The structural biology of Toll-like receptors. Structure. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2011.02.004
5. Lu, Y. C., Yeh, W. C., & Ohashi, P. S. (2008). LPS/TLR4 signal transduction pathway. Cytokine. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2008.01.006
6. Leitner, G. R., Wenzel, T. J., Marshall, N., Gates, E. J., & Klegeris, A. (2019). Targeting toll-like receptor 4 to modulate neuroinflammation in central nervous system disorders. Expert opinion on therapeutic targets. https://doi.org/10.1080/14728222.2019.1676416
7. Molteni, M., Gemma, S., & Rossetti, C. (2016). The Role of Toll-Like Receptor 4 in Infectious and Noninfectious Inflammation. Mediators of inflammation. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6978936
8. Rahimifard, M., Maqbool, F., Moeini-Nodeh, S., Niaz, K., Abdollahi, M., Braidy, N., Nabavi, S. M., & Nabavi, S. F. (2017). Targeting the TLR4 signaling pathway by polyphenols: A novel therapeutic strategy for neuroinflammation. Ageing research reviews. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2017.02.004
Long Name
Toll-like Receptor 4
Alternate Names
CD284, hta125, hta125 tlr4
Gene Symbol
TLR4
Additional TLR4 Products
Product Documents for TLR4 Antibody (HTA125) - BSA Free
Product Specific Notices for TLR4 Antibody (HTA125) - BSA Free
This product is for research use only and is not approved for use in humans or in clinical diagnosis. Primary Antibodies are guaranteed for 1 year from date of receipt.
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...

![Flow Cytometry: TLR4 Antibody (HTA125) - BSA Free [NB100-56723] Flow Cytometry: TLR4 Antibody (HTA125) - BSA Free [NB100-56723]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/TLR4-Antibody-HTA125-Flow-Cytometry-NB100-56723-img0011.jpg)
![Flow Cytometry: TLR4 Antibody (HTA125) - BSA Free [NB100-56723] Flow Cytometry: TLR4 Antibody (HTA125) - BSA Free [NB100-56723]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/TLR4-Antibody-HTA125-Flow-Cytometry-NB100-56723-img0016.jpg)
![Flow Cytometry: TLR4 Antibody (HTA125) - BSA Free [NB100-56723] Flow Cytometry: TLR4 Antibody (HTA125) - BSA Free [NB100-56723]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/TLR4-Antibody-HTA125-Flow-Cytometry-NB100-56723-img0014.jpg)