YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free
Novus Biologicals, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # NB110-58358

![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free [NB110-58358] Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free [NB110-58358]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/YAP1-Antibody---BSA-Free-Immunocytochemistry-Immunofluorescence-NB110-58358-img0014.jpg)
Conjugate
Catalog #
Key Product Details
Validated by
Knockout/Knockdown, Biological Validation
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Human, Mouse, Rat, Canine, Zebrafish
Cited:
Human, Mouse, Rat, Canine, Fish - Danio rerio (Zebrafish)
Applications
Validated:
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP), Immunoblotting, Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry, Immunohistochemistry-Frozen, Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin, Immunoprecipitation, Knockdown Validated, Knockout Validated, Simple Western, Western Blot
Cited:
Block/Neutralize, Chemotaxis, Chromatin Immunoprecipitation, IF/IHC, IHC-F, Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry, Immunohistochemistry-Frozen, Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin, Immunoprecipitation, Knockdown Validated, Western Blot
Label
Unconjugated
Antibody Source
Polyclonal Rabbit IgG
Format
BSA Free
Concentration
1.0 mg/ml
Product Specifications
Immunogen
This YAP1 Antibody was developed against a partial recombinant human YAP1 protein expressed in bacteria. , N-terminal GST fusion protein
Reactivity Notes
Use in Human reported in scientific literature (PMID:33737385). Use in Zebrafish reported in scientific literature (PMID:28350986).
Localization
Nuclear
Specificity
Expected reactivity based on immunogen homology: Isoform 4 (100%), Isoform 6 (100%)
Clonality
Polyclonal
Host
Rabbit
Isotype
IgG
Theoretical MW
48 kDa.
Disclaimer note: The observed molecular weight of the protein may vary from the listed predicted molecular weight due to post translational modifications, post translation cleavages, relative charges, and other experimental factors.
Disclaimer note: The observed molecular weight of the protein may vary from the listed predicted molecular weight due to post translational modifications, post translation cleavages, relative charges, and other experimental factors.
Scientific Data Images for YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free [NB110-58358]
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence: YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free [NB110-58358] - Caco-2 cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 minutes and permeabilized in 0.5% Triton X-100 in PBS for 5 minutes. The cells were incubated with YAP1 Antibody (NB110-58358) at 1 ug/ml overnight at 4C and detected with an anti-rabbit DyLight 488 (Green) at a 1:1000 dilution for 60 minutes. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (Blue). Cells were imaged using a 40X objective.
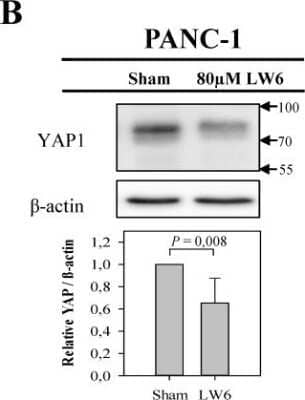
Western Blot: YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free [NB110-58358] - LW6 attenuates the accumulation of cellular YAP1 and its nuclear location. After treating PANC-1 cells with LW6 for 12 hours, LW6 decreased the accumulation of YAP1 when compared to Sham treated cells. n =5 per group. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (//pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31897243/) licensed under a CC-BY license.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free [NB110-58358]
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence: YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free [NB110-58358] - YAP/TAZ signaling is not activated by loss of TRAF3. NT, NF2 KO1, and TRAF3 KO1 cells stained for YAP1 and DAPI. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (//pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33185187/) licensed under a CC-BY license.Applications for YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free
Application
Recommended Usage
Immunoblotting
reported in scientific literature (PMID 28406163)
Immunohistochemistry
1:50-1:200
Immunohistochemistry-Frozen
reported in scientific literature (PMID 28581498)
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin
1:50-1:200
Immunoprecipitation
2-10 ug
Knockdown Validated
reported in scientific literature (PMID 28406163)
Simple Western
1:12.5
Western Blot
1:1000
Application Notes
In Simple Western only 10 - 15 uL of the recommended dilution is used per data point.
See Simple Western Antibody Database for Simple Western validation: Tested in HeLa lysate 0.1 mg/mL, separated by Size, antibody dilution of 1:12.5, apparent MW was 74 kDa. Separated by Size-Wes, Sally Sue/Peggy Sue.
See Simple Western Antibody Database for Simple Western validation: Tested in HeLa lysate 0.1 mg/mL, separated by Size, antibody dilution of 1:12.5, apparent MW was 74 kDa. Separated by Size-Wes, Sally Sue/Peggy Sue.
Reviewed Applications
Read 2 reviews rated 3.5 using NB110-58358 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Immunogen affinity purified
Formulation
PBS
Format
BSA Free
Preservative
0.02% Sodium Azide
Concentration
1.0 mg/ml
Shipping
The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below.
Stability & Storage
Aliquot and store at -20C or -80C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
Background: YAP1
YAP plays a role in the development and progression of multiple cancers as a transcriptional regulator of the Hippo signaling pathway. YAP1 encodes a nuclear effector of the Hippo signaling pathway which is involved in development, growth, repair, and homeostasis to play a pivotal role in controlling cell growth and organ size and has emerged as a key player in tumor suppression (2,3). Deregulation of the Hippo pathway causes tumor formation and malignancy, with YAP being a key oncogenic driver in liver carcinogenesis (2) and may function as a potential target for cancer treatment (3).
References
1. Rueda, E. M., Hall, B. M., Hill, M. C., Swinton, P. G., Tong, X., Martin, J. F., & Poche, R. A. (2019). The Hippo Pathway Blocks Mammalian Retinal Muller Glial Cell Reprogramming. Cell Rep, 27(6), 1637-1649.e1636. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2019.04.047
2. Liu, A. M., Xu, M. Z., Chen, J., Poon, R. T., & Luk, J. M. (2010). Targeting YAP and Hippo signaling pathway in liver cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets, 14(8), 855-868. doi:10.1517/14728222.2010.499361
3.Ye, S., & Eisinger-Mathason, T. S. (2016). Targeting the Hippo pathway: Clinical implications and therapeutics. Pharmacol Res, 103, 270-278. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2015.11.025
Long Name
Yes-associated Protein 1
Alternate Names
YAP2, YAP65, YKI, Yorkie Homolog
Gene Symbol
YAP1
Additional YAP1 Products
Product Documents for YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free
Product Specific Notices for YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free
This product is for research use only and is not approved for use in humans or in clinical diagnosis. Primary Antibodies are guaranteed for 1 year from date of receipt.
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free [NB110-58358] Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free [NB110-58358]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/YAP1-Antibody---BSA-Free-Immunocytochemistry-Immunofluorescence-NB110-58358-img0015.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free [NB110-58358] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free [NB110-58358]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/YAP1-Antibody---BSA-Free-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NB110-58358-img0010.jpg)
![Western Blot: YAP1 AntibodyBSA Free [NB110-58358] Western Blot: YAP1 AntibodyBSA Free [NB110-58358]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/YAP1-Antibody---BSA-Free-Western-Blot-NB110-58358-img0003.jpg)
![Western Blot: YAP1 AntibodyBSA Free [NB110-58358] Western Blot: YAP1 AntibodyBSA Free [NB110-58358]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/YAP1-Antibody---BSA-Free-Western-Blot-NB110-58358-img0012.jpg)
![Western Blot: YAP1 AntibodyBSA Free [NB110-58358] Western Blot: YAP1 AntibodyBSA Free [NB110-58358]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/YAP1-Antibody---BSA-Free-Western-Blot-NB110-58358-img0011.jpg)
![Simple Western: YAP1 AntibodyBSA Free [NB110-58358] Simple Western: YAP1 AntibodyBSA Free [NB110-58358]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/YAP1-Antibody---BSA-Free-Simple-Western-NB110-58358-img0007.jpg)
![Western Blot: YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free [NB110-58358] Knockout Validated: YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free [NB110-58358]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/YAP1-Antibody---BSA-Free-Knockout-Validated-NB110-58358-img0008.jpg)
![Simple Western: YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free [NB110-58358] Knockout Validated: YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free [NB110-58358]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/YAP1-Antibody---BSA-Free-Knockout-Validated-NB110-58358-img0009.jpg)
![Western Blot: YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free [NB110-58358] - YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb110-58358_rabbit-polyclonal-yap1-antibody-31020241535689.jpg)
![Western Blot: YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free [NB110-58358] - YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb110-58358_rabbit-polyclonal-yap1-antibody-310202415371934.jpg)
![Western Blot: YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free [NB110-58358] - YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb110-58358_rabbit-polyclonal-yap1-antibody-310202415291931.jpg)
![Western Blot: YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free [NB110-58358] - YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb110-58358_rabbit-polyclonal-yap1-antibody-310202416235517.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free [NB110-58358] - YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb110-58358_rabbit-polyclonal-yap1-antibody-310202416235539.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free [NB110-58358] - YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb110-58358_rabbit-polyclonal-yap1-antibody-310202416235526.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free [NB110-58358] - YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb110-58358_rabbit-polyclonal-yap1-antibody-310202416235548.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free [NB110-58358] - YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb110-58358_rabbit-polyclonal-yap1-antibody-31020241623554.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free [NB110-58358] - YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb110-58358_rabbit-polyclonal-yap1-antibody-310202416235520.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free [NB110-58358] - YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb110-58358_rabbit-polyclonal-yap1-antibody-310202416235530.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free [NB110-58358] - YAP1 Antibody - BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nb110-58358_rabbit-polyclonal-yap1-antibody-31020241623552.jpg)