Kit Summary
For the differentiation of Th17 cells from a preparation of naïve CD4+ T cells.
Key Benefits
- Generate a 20-fold increase of Th17 polarized cells
- Contains high quality bioactive proteins
- Provides optimized reagents needed to induce Th17 differentiation
- Includes straightforward procedures
- Does not require specialized instrumentation
Why Differentiate Th17 Cells In Vitro?
T helper type 17 (Th17) cells are a subset of CD4+ effector T cells that promote cell-mediated immune responses against extracellular bacteria and fungi. Differentiation into the Th17 lineage is promoted by cytokines such as TGF-beta and IL-6, while their survival and expansion are dependent on IL-21 and IL-23. Th17 cells secrete TNF-alpha, IL-6, IL-9, IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-21, IL-22, and (human) IL-26/AK155. Th17 polarized cells are present in low abundance in normal human peripheral blood. In vitro differentiation of Th17 cells from the larger naïve CD4+ T cell population provides increased numbers of Th17 cells to facilitate downstream research.
Kit Contents
This kit contains the following optimized proteins and reagents to drive efficient differentiation of naïve CD4+ T cells into Th17 polarized cells.
- Mouse Anti-Human CD3 Antibody
- Mouse Anti-Human CD28 Antibody
- Human Th17 Reagent 1
- Human Th17 Reagent 2
- Human Th17 Reagent 3
- Human Th17 Reagent 4
- Human Th17 Reagent 5
- Reconstitution Buffer 1
- Reconstitution Buffer 2
- Reconstitution Buffer 3
- 20X Wash Buffer
The quantity of the components in the kit is sufficient to differentiate one 24-well plate, or approximately 2.5-5 x 106 naïve CD4+ T cells, and generate a 20-fold increase of Th17 polarized cells within your starting CD4+ T cell population.
Stability and Storage
Store the unopened kit at 2 to 8 °C. After opening the kit, Mouse Anti-Human CD3 Antibody, Mouse Anti-Human CD28 Antibody, and Human Th17 Reagents 1-5 can be stored at 2-8 °C under sterile conditions for up to 30 days or at -20 °C to -70 °C in a manual defrost freezer for up to 3 months. Reconstitution Buffer 1, Reconstitution Buffer 2, Reconstitution Buffer 3, and 20X Wash Buffer may be stored under sterile conditions for up to 3 months at 2 to 8 °C. Do not use beyond the expiration date of the kit.
Data Examples
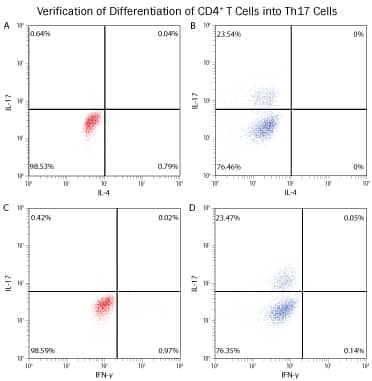
| Intracellular Cytokine Staining of Differentiated Human Th17 Cells. Flow cytometry data showing human peripheral blood naïve CD4+ T cells without (A, C) and with (B, D) a 10-day differentiation using reagents included in this kit. On day 10 of differentiation, the cells were stimulated with Cell Activation Cocktail (Tocris®, Catalog # 5476) and stained with APC-conjugated Mouse Anti-Human IL-17 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # IC317A), PE-conjugated Mouse Anti-Human IFN-gamma Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # IC285P) and a Fluorescein-conjugated Mouse Anti-Human IL-4 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # IC204F). Quadrants were placed based on isotype control-stained samples. |
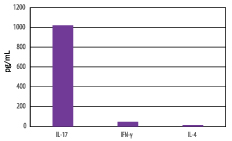
| Th17-differentiated Human CD4+ Cells Secrete IL-17. Human peripheral blood naïve CD4+ T cells were differentiated for 10 days under Th17 polarization conditions using reagents included in this kit. On day 10, cell culture supernatant was collected and cytokine expression was determined using the Human IL-17 Quantikine® ELISA Kit (Catalog # D1700), the Human IFN-gamma Quantikine® ELISA Kit (Catalog # DIF50), and the Human IL-4 Quantikine® ELISA Kit (Catalog # D4050). |
T helper type 17 (Th17) cells are involved in the immune response mounted against specific fungi and extracellular bacteria. In mice, Th17 cells develop from naive CD4+ T cells in the presence of TGF-beta and IL-6. These cytokines induce the STAT3-dependent expression of IL-21, IL-23 R, and the transcription factor, ROR gamma t. IL-21 and IL-23 regulate the establishment and clonal expansion of Th17 cells, while ROR gamma t-induced gene expression leads to the secretion of IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-22. Cytokines secreted by Th17 cells stimulate chemokine secretion by resident cells, leading to the recruitment of neutrophils and macrophages to sites of inflammation. These cells, in turn, produce additional cytokines and proteases that further exacerbate the immune response. In contrast to mouse Th17 differentiation, Th17 polarization in humans requires IL-1 beta, IL-6, IL-21, and IL-23, but seems to be less dependent upon TGF-beta. One other notable difference is that human Th17 cells secrete IL-26, an IL-10 family cytokine without a murine homologue. Cytokines produced by Th17 cells can have both beneficial and pathogenic effects. While they play a central role in eliminating harmful microbes, persistent secretion of Th17 cytokines promotes chronic inflammation and may be involved in the pathogenesis of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and inflammatory bowel disorders.