Recombinant Cynomolgus/Rhesus EMMPRIN/CD147 Fc Protein, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 10797-EM
aa 138-327

Key Product Details
Source
CHO
Accession #
Structure / Form
Disulfide-linked homodimer
Conjugate
Unconjugated
Applications
Bioactivity
Product Specifications
Source
Chinese Hamster Ovary cell line, CHO-derived EMMPRIN/CD147 protein
| Cynomolgus/Rhesus EMMPRIN/CD147 (Glu138-Ala327) Accession # XP_005587353.1 |
IEGRMD | Human IgG1 (Pro100-Lys330) |
| N-terminus | C-terminus |
Purity
>95%, by SDS-PAGE visualized with Silver Staining and quantitative densitometry by Coomassie® Blue Staining.
Endotoxin Level
<0.10 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method.
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Glu138
Predicted Molecular Mass
47 kDa
SDS-PAGE
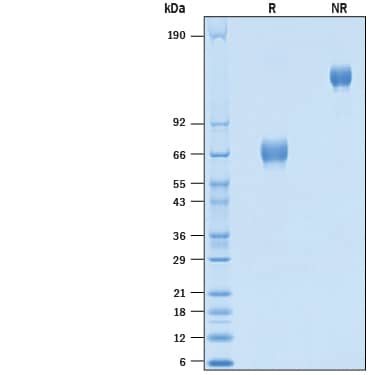
63 - 72 kDa, under reducing conditions.
Activity
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA.
When Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Fc Chimera (Catalog # 10499-CV) is immobilized at 1 µg/mL (100 µL/well), Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey EMMPRIN/CD147 Fc Chimera (Catalog # 10797-EM) binds with an ED50 of 1.50-12.0 µg/mL.
When Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Fc Chimera (Catalog # 10499-CV) is immobilized at 1 µg/mL (100 µL/well), Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey EMMPRIN/CD147 Fc Chimera (Catalog # 10797-EM) binds with an ED50 of 1.50-12.0 µg/mL.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Cynomolgus/Rhesus EMMPRIN/CD147 Fc Protein, CF
Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey EMMPRIN/CD147 Fc Chimera Protein Binding Activity.
When Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Fc Chimera (10499-CV) is immobilized at 1 µg/mL (100 µL/well), Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey EMMPRIN/CD147 Fc Chimera (Catalog # 10797-EM) binds with an ED50 of 1.50-12.0 µg/mL.Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey EMMPRIN/CD147 Fc Chimera Protein SDS-PAGE.
2 μg/lane of Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey EMMPRIN/CD147 Fc Chimera Protein (Catalog # 10797-EM) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 63-72 kDa and 120-140 kDa, respectively.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
10797-EM
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with dry ice or equivalent. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: EMMPRIN/CD147
References
- Gabison, E. E. et al. (2005) Biochimie 87:361.
- Yurchenko, V. et al. (2006) Immunology 117:301.
- Kasinrerk, W. et al. (1992) J. Immunol. 149:847.
- Iacono, K.T. et al. (2007) Exp. Mol. Pathol. 83:283.
- Hanna, S. M. et al. (2003) BMC Biochem. 4:17.
- Liao, C-G. et al. (2011) Mol. Cell. Biol. 31:2591.
- Riethdorf, S. et al. (2006) Int. J. Cancer 119:1800.
- Braundmeier, A. G. et al. (2006) J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 91:2358.
- Tang, Y. et al. (2006) Mol. Cancer Res. 4:371.
- Quemener, C. et al. (2007) Cancer Res. 67:9.
- Wilson, M. C. et al. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280:27213.
- Xu, D. and M. E. Hemler, (2005) Mol. Cell. Proteomics 4:1061.
- Tang, W. et al. (2004) Mol. Biol. Cell 15:4043.
- Zhao, P. et al. (2010) Cancer Sci. 101:387.
- Dai, J. et al. (2009) BMC Cancer 9:337.
- Li, Y. et al. (2012) J. Biol. Chem. 287:4759.
- Hibino, T. et al. (2013) Cancer Res. 73:172.
- Arora, K. et al. (2005) J. Immunol. 175:517.
- Pushkarsky, T. et al. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280:27866.
- Egawa, N. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:37576.
- Sidhu, S. S. et al. (2004) Oncogene 23:956.
Long Name
Extracellular Matrix Metalloproteinase Inducer
Alternate Names
Basigin, BSG, CD147
Gene Symbol
BSG
UniProt
Additional EMMPRIN/CD147 Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Cynomolgus/Rhesus EMMPRIN/CD147 Fc Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Cynomolgus/Rhesus EMMPRIN/CD147 Fc Protein, CF
For research use only
Loading...
Loading...