Recombinant Human Cadherin-9 Fc Chimera Protein, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 9984-CA

Key Product Details
Source
Accession #
Structure / Form
Conjugate
Applications
Product Specifications
Source
| Human Cadherin-9 (Gly54-Ala615) Accession # Q9ULB4 |
IEGRMD | Human IgG1 (Pro100-Lys330) |
| N-terminus | C-terminus |
Purity
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Predicted Molecular Mass
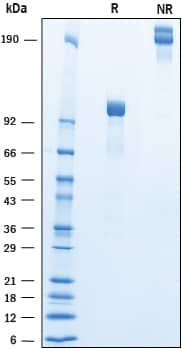
SDS-PAGE
Activity
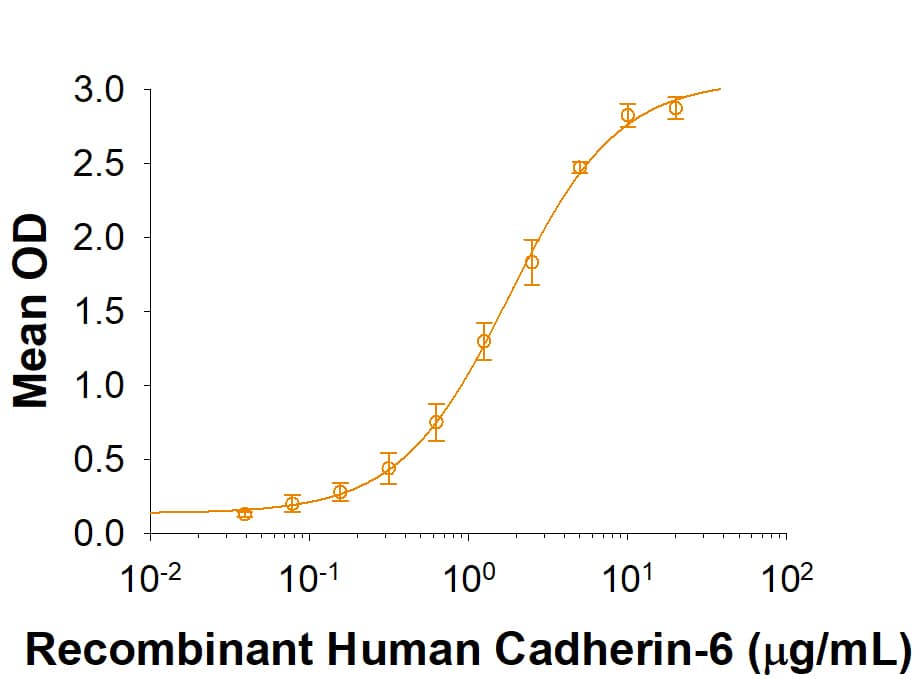
When Recombinant Human Cadherin-9 Fc Chimera is immobilized at 1 μg/mL, 100 μL/well, Recombinant Human Cadherin‑6/KCAD Fc Chimera (Catalog # 2715-CA) binds with an ED50 of 0.6-3.6 μg/mL.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human Cadherin-9 Fc Chimera Protein, CF
Recombinant Human Cadherin-9 Fc Chimera Protein Binding Activity
When Recombinant Human Cadherin 9 Fc Chimera is immobilized at 1 µg/mL, 100 µL/well, Recombinant Human Cadherin-6/KCAD Fc Chimera (Catalog # 2715-CA) binds with an ED50 of 0.6-3.6 µg/mL.Recombinant Human Cadherin-9 Fc Chimera Protein SDS-PAGE
2 μg/lane of Recombinant Human Cadherin-9 was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 92-106 kDa and 180-210 kDa, respectively.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
9984-CA
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 250 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage |
|
Background: Cadherin-9
Cadherin-9 (CDH9) is a member of the larger Cadherin superfamily of cell surface glycoproteins originally identified as proteins mediating cell-cell adhesion (1). In humans, there are more than 100 cadherin members divided into distinct families and numerous sub-families (1-3). Cadherins share a general structural architecture with an extracellular domain (ECD) containing 2 or more extracellular Ca2+ binding cadherin repeat (EC) domains, a single-pass transmembrane section, and a short cytoplasmic tail (1-3). Cadherins function by forming homophilic binding interactions through these EC domains to generate both trans and cis dimers (1-3). Human CDH9 is categorized as a classical cadherin, containing 5 EC domains, and the ECD shares 94% amino acid sequence identity with the ECD of both mouse and rat CDH9, respectively. Cadherins are found in diverse cell types and have been implicated as essential for the morphogenesis and homeostasis of multiple tissues and organs (1-3). Human CDH9 functions primarily in the central nervous system and is expressed in DG and CA3 neurons. Loss of CDH9 expression leads to defects in synapse formation and differentiation of specific neural circuits. (4). Additionally, disruption to CDH9 and CDH10 genes has been linked to autism spectrum disorders (5, 6). CDH9 expression has been identified in human kidney, and it has been used as a cell surface marker for fibroblasts (7). Recently, CDH9 has been reported as a potential suppressor of cancer metastasis (8).
References
- Gumbiner, B.M. (2005) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6:622.
- Hirano S and Takeichi M. (2012) Physiol Rev. Apr; 92(2):597.
- Nollet et al. (2000) J Mol Biol. Jun. 9; 299(3):551.
- Williams ME et al. (2011) Neuron. Aug. 25; 71(4):640.
- Wang K. et al. (2009) Nature 459, 528.
- Inoue YU and, Inoue T. (2016) Sci Rep. 6:31227.
- Thedieck, C. et al. (2007) PLoS One. 2(8):e657.
- Yan G. et al. (2017) Scientific Reports volume 7, 10023.
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Cadherin-9 Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human Cadherin-9 Fc Chimera Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human Cadherin-9 Fc Chimera Protein, CF
For research use only