Recombinant Human follistatin-resistant Activin A,AF Protein
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # Qk035
Human/Mouse/Rat Animal-Free

Key Product Details
Source
E. coli
Conjugate
Unconjugated
Applications
Bioactivity
Product Specifications
Source
E. coli-derived Activin A protein
Purity
Single species with expected mass
Endotoxin Level
<0.10 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method.
Predicted Molecular Mass
26 kDa (dimer)
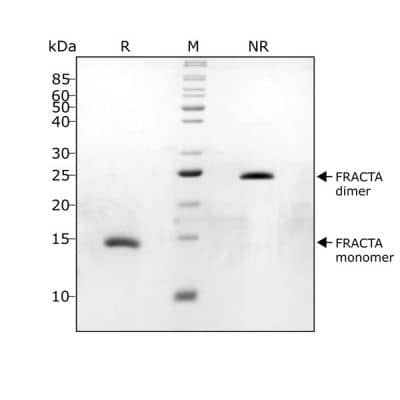
SDS-PAGE
Dimeric follistatin-resistant Activin A protein only
Activity
No significant difference between EC50 of reference and test lots
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human follistatin-resistant Activin A,AF Protein
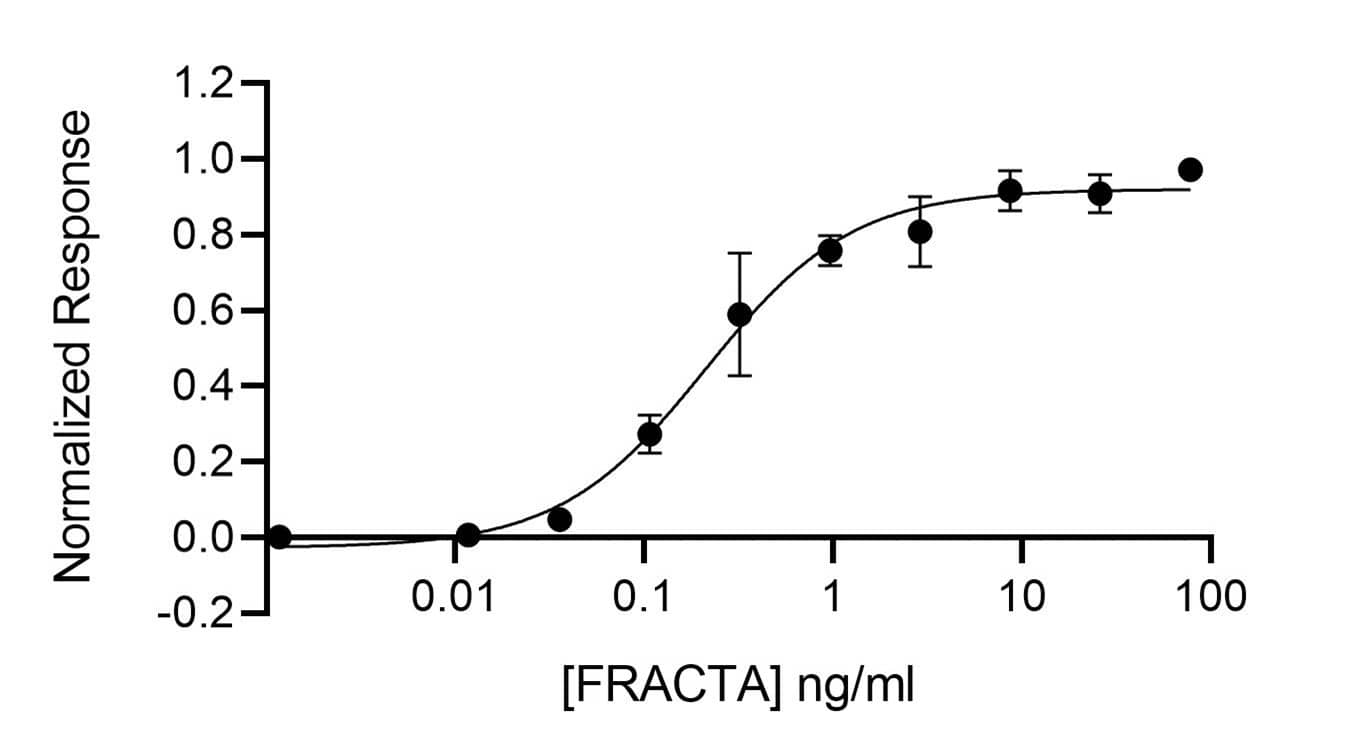
Recombinant Human follistatin-resistant Activin A,AF Protein Bioactivity
Activin A protein activity is determined using an activin-responsive firefly luciferase reporter in HEK293T cells. EC50 for wild-type activin A (Qk001) = 0.228 ng/ml (8.776 pM), EC50 for follistatin-resistant activin A (FRACTA, Qk035) = 0.212 ng/ml (8.2 pM).Recombinant Human follistatin-resistant Activin A,AF Protein SDS-PAGE
FRACTA migrates as a single band at 24 kDa in non-reducing (NR) and 13 kDa as a single monomeric species upon reduction (R). No contaminating protein bands are visible.Purified recombinant protein (1 µg) was resolved using 15% w/v SDS-PAGE in reduced (+ beta-mercaptothanol, R) and non-reduced conditions (NR) and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
Qk035
| Formulation | Lyophilized from acetonitrile/TFA |
| Reconstitution | Resuspend in 10mM HCl at >100 µg/ml, prepare single use aliquots, add carrier protein if desired. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped lyophilized at ambient temperture, on ice blocks or dry ice. Shipping at ambient temperture does not affect the bioactivity or stability of the protein. Upon reciept, store immediately at the conditions stated below. |
| Stability & Storage | Store lyophilized protein between -20 and -80 °C until the date of expiry. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. |
Background: Activin A
Activin A exerts its biological activities by binding to the type 2 serine/threonine kinase Activin RIIA which then noncovalently associates with the type 1 serine/threonine kinase Activin RIB/ALK-4 (7, 11). Signaling through this receptor complex leads to Smad activation and regulation of activin-responsive gene transcription (7, 11). The bioactivity of Activin A is regulated by a variety of mechanisms (11). BAMBI, Betaglycan, and Cripto are cell‑associated molecules that function as decoy receptors or limit the ability of Activin A to induce receptor complex assembly (12‑14). The intracellular formation of Activin A can be prevented by the incorporation of the betaA subunit into Activin AC or Inhibin A (3, 10). And the bioavailability of Activin A is restricted by its incorporation into inactive complexes with alpha2-Macroglobulin, Follistatin, and FLRG (15, 16).
Activin A is involved in the differentiation of various cell
and tissue types. The induction of definitive endoderm by Activin A is required
in differentiation protocols of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) (17, 18).
In vitro models of human gametogenesis use prolonged Activin A supplementation
to human embryonic stem cells for differentiation into human primordial germ
cell-like cells (19). Activin A can also be used to maintain cells in vitro, as
is the case for iPSC-derived nephron cells that can then be used in disease
modeling, drug screening and in regenerative medicine (20).
Activin A is an
important factor for tumor cells to evade the immune system as Activin A can
act on surrounding immune cells to decrease their antitumor activity (21).
Activin A also promotes migration and growth of tumors, making it a target for
cancer therapies (22). Specifically, research has shown that interfering with
Activin A activity can assist in overcoming CD8 T-cell exclusion and
immunotherapy resistance (23). In bone marrow-derived stem cell transplants for
treatment of diabetes, Activin A enhances migration and homing of stem cells
towards pancreatic lineage (24).
References
- Kumanov, P. et al. (2005) Reprod. Biomed. Online 10:786.
- Maeshima, A. et al. (2008) Endocr. J. 55:1.
- Rodgarkia-Dara, C. et al. (2006) Mutat. Res. 613:123.
- Werner, S. and C. Alzheimer (2006) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 17:157.
- Xu, P. and A.K. Hall (2006) Dev. Biol. 299:303.
- Shav-Tal, Y. and D. Zipori (2002) Stem Cells 20:493.
- Chen, Y.G. et al. (2006) Exp. Biol. Med. 231:534.
- Gray, A.M. and A.J. Mason (1990) Science 247:1328.
- Mason, A.J. et al. (1996) Mol. Endocrinol. 10:1055.
- Thompson, T.B. et al. (2004) Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 225:9.
- Harrison, C.A. et al. (2005) Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 16:73.
- Onichtchouk, D. et al. (1999) Nature 401:480.
- Gray, P.C. et al. (2002) Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 188:254.
- Kelber, J.A. et al. (2008) J. Biol. Chem. 283:4490.
- Phillips, D.J. et al. (1997) J. Endocrinol. 155:65.
- Schneyer, A. et al. (2003) Endocrinology 144:1671.
- Ghorbani-Dalini, S. et al. (2020) 3 Biotech. 10:215.
- Mennen, R. H. et al. (2022) Reprod Toxicol. 107:44.
- Mishra, S. et al. (2021) Stem Cells. 39:551.
- Tanigawa, S. et al. (2019) Stem Cell Reports 13:322.
- Cangkrama, M. et al. (2020) Trends Mol. Med. 26:1107.
- Ries, A. et al. (2020) Expert Opin. Ther. Targets. 24:985.
- Pinjusic, K. et al. (2022) J. Immunother. Cancer. 10:e004533.
- Dadheech, N. et al. (2020) Stem Cell Res. Ther. 11:327.
Alternate Names
activin AB alpha polypeptide, Activin beta-A chain, erythroid differentiation factor, Erythroid differentiation protein, follicle-stimulating hormone-releasing protein, FSH-releasing protein, inhibin beta A chain, inhibin beta A subunit, Inhibin, beta-1
Gene Symbol
INHBA
Additional Activin A Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human follistatin-resistant Activin A,AF Protein
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human follistatin-resistant Activin A,AF Protein
The above product was manufactured, tested and released by R&D System's contract manufacturer, Qkine Ltd, at 1 Murdoch House, Cambridge, UK, CB5 8HW. The product is for research use only and not for the diagnostic or theraputic use.
For research use only
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...