Recombinant Human Klotho beta Protein, CF Best Seller
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 5889-KB

Key Product Details
Product Specifications
Source
Phe53-Leu997, with a C-terminal 10-His tag
Purity
Endotoxin Level
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Predicted Molecular Mass
SDS-PAGE
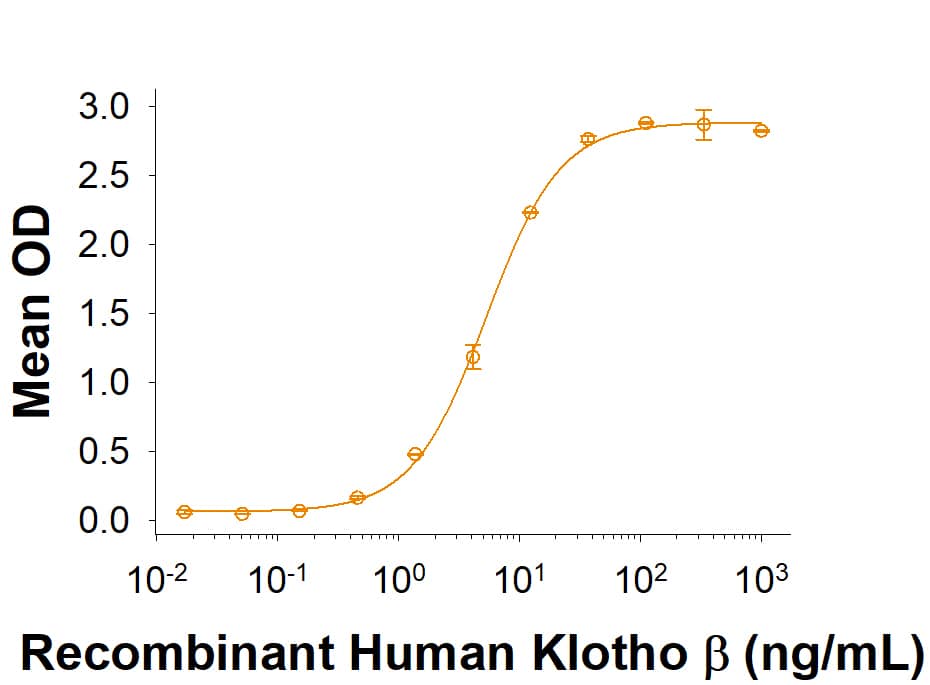
Activity
When Recombinant Human FGF-21 (Catalog # 2539-FG) is immobilized at 1 µg/mL (100 µL/well), Recombinant Human Klotho beta His-tag (Catalog # 5889-KB) binds with an ED50 of 2.5-20 ng/mL.
Reviewed Applications
Read 3 reviews rated 5 using 5889-KB in the following applications:
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human Klotho beta Protein, CF
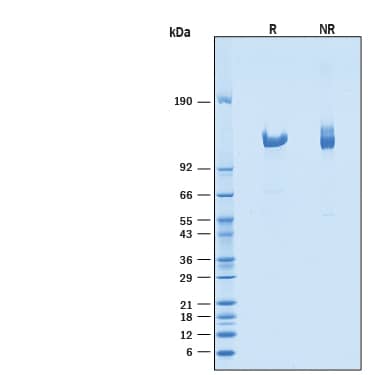
Recombinant Human Klotho beta Protein SDS-PAGE
1 μg/lane of Recombinant Human Klotho beta was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing a single band at 113-125 kDa.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
5889-KB
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS, Glycerol and EDTA. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with dry ice or equivalent. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: Klotho beta
Klotho beta, a divergent structural member of the glycosidase I superfamily, is expressed primarily in the liver and pancreas, with lower expression in adipose tissue (1, 2). Like Klotho, Klotho beta facilitates binding between FGF19 subfamily members and their receptors via formation of a ternary complex (3). The Klotho beta mediated interaction of human FGF19 (mouse FGF15) with FGF Receptor 4 in the liver negatively regulates bile acid synthesis by controlling the secretion of two key bile acid synthase genes, cholesterol 7-alpha hydroxylase (Cyp7a1) and sterol 12-alpha hydroxylase (Cyp8b1) (2-5). Klotho beta is also a cofactor for the interaction of FGF21 with FGF Receptor 1c in adipocytes, which allows FGF21 to stimulate GLUT1 expression, upregulating adipocyte insulin-dependent glucose uptake (2-4, 6). The 1043 amino acid (aa) type I transmembrane protein is composed of a 51 aa signal sequence, a 943 aa extracellular domain (ECD) containing two glycosidase-like regions, a 21 aa transmembrane domain, and 28 aa intracellular tail. Since Klotho-related proteins lack critical active site Glu residues present in beta-glycosidases, it was initially unclear whether they were functional enzymes (1, 7). However, glucuronidase activity has since been demonstrated for Klotho, indicating that physiologically relevant enzymatic activity for Klotho beta is also possible (8). The extracellular domain shares 79%, 87%, 87% and 67% identity with mouse, equine, canine and rat Klotho beta, respectively. The low identity with rat reflects aa discordance within rodent ECD.
References
- Mian, I. S. (1998) Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 24:83.
- Kurosu, H. and M. Kuro-o (2009) Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 299:72.
- Ito, S. et al. (2005) J. Clin. Invest. 115:2202.
- Kurosu, H. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282:26687.
- Lin, B. C. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282:27277.
- Ogawa, Y. et al. (2007) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 104:7432.
- Chang, Q. et al. (2005) Science 310:490.
- Goetz, R. et al. (2007) Mol. Cell. Biol. 27:3417.
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Klotho beta Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human Klotho beta Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human Klotho beta Protein, CF
For research use only