Recombinant Human Matriptase/ST14 Catalytic Domain, CF Best Seller
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 3946-SEB

Key Product Details
Product Specifications
Source
Gly596-Val855, with an N-terminal Met and 6-His tag
The protein was purified, auto-activated and further purified.
Purity
Endotoxin Level
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Predicted Molecular Mass
SDS-PAGE
Activity
The specific activity is >10,000 pmol/min/μg, as measured under the described conditions.
Reviewed Applications
Read 4 reviews rated 5 using 3946-SEB in the following applications:
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human Matriptase/ST14 Catalytic Domain, CF
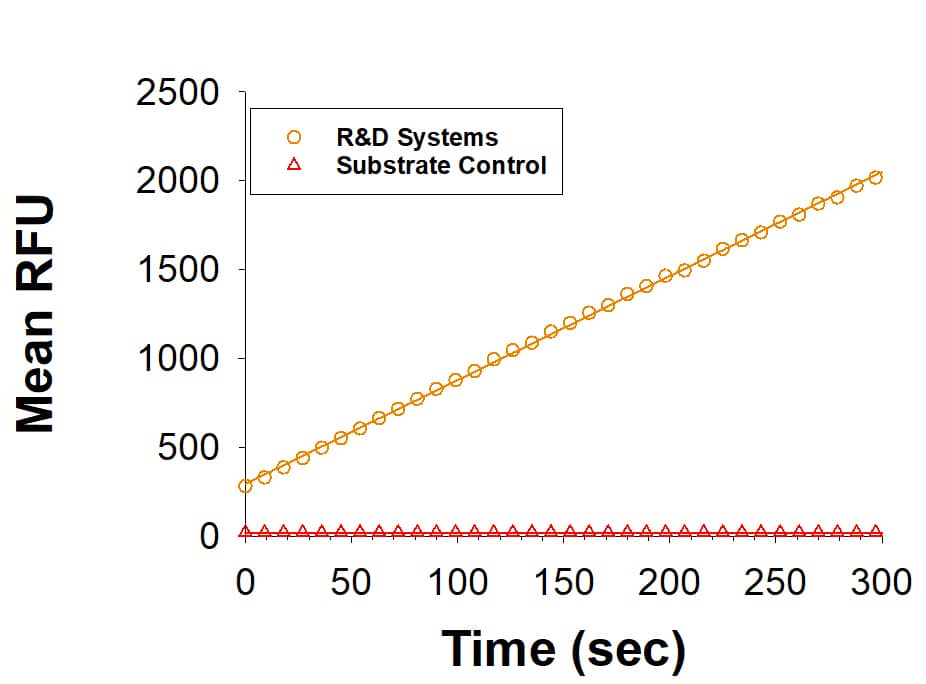
Recombinant Human Matriptase/ST14 Catalytic Domain Enzyme Activity
Recombinant Human Matriptase is measured by its ability to cleave the fluorogenic peptide substrate Boc-QAR-AMC (Catalog # ES014).Formulation, Preparation and Storage
3946-SEB
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution in Tris-HCl and Glycerol. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: Matriptase/ST14
Human matriptase, encoded by the ST14 (suppression of tumorogenicity 14) gene, is also known as tumor associated differentially expressed gene 15 protein/TADG‑15), epithin, and membrane‑type serine protease 1/MT‑SP1 (1). Predicted to have a significant role in tumor biology, matriptase may be a novel target for anti‑cancer therapy (2). However, expressed in most human epithelia, matriptase is also important in several physiological processes (1). For example, it activates prostasin to initiate a protease cascade that is essential for epidermal differentiation (3), and it converts a single‑chain IGFBP-rp1 into the two‑chain form (4). Matriptase is a type II transmembrane serine protease with a complex modular structure (1). The 855 amino acid (aa) sequence of human matriptase consists of a cytoplasmic tail (aa 1‑55), a transmembrane domain (aa 56‑76), and an extracellular portion (aa 77‑855). The latter contains the following domains: SEA (aa 86‑201), two CUBs (aa 214‑334 and 340‑447), four LDLRAs (aa 452‑486, 487‑523, 524‑560, and 566‑603), and a serine protease (aa 615‑855). The physiological activation of the single‑chain zymogen requires the cleavage at the SEA domain within the ER or Golgi, association with HAI-1, which facilitates the transport of the protease to the cell surface, and auto‑cleavage at QAR-V(615)VGG (1). The activated matriptase is inhibited by HAI-1, and the resulting HAI-1 complex can be shed from the cell surface (1). R&D Systems recombinant human (rh) ST14 corresponds to the catalytic domain, and is inhibited effectively by rhHAI-1 and rhHAI-2A (Catalog # http://www.rndsystems.com/product_results.aspx?k=1048-PI">1048‑PI and http://www.rndsystems.com/product_results.aspx?k=1106-PI">1106‑PI).
References
- List, K. et al. (2006) Mol. Med. 12:1.
- Uhland, K. (2006) Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 63:2968.
- Netzel-Arnett, S. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:32941.
- Ahmed, S. et al. (2006) FEBS J. 273:615.
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Matriptase/ST14 Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human Matriptase/ST14 Catalytic Domain, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human Matriptase/ST14 Catalytic Domain, CF
For research use only