Recombinant Human Mindin His-tag Protein, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 11539-SP

Key Product Details
Product Specifications
Source
Mouse myeloma cell line, NS0-derived human Mindin protein
Glu32-Val331, with a C-terminal 6-His tag
Glu32-Val331, with a C-terminal 6-His tag
Purity
>90%, by SDS-PAGE visualized with Silver Staining and quantitative densitometry by Coomassie® Blue Staining.
Endotoxin Level
<0.10 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method.
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Glu 32
Predicted Molecular Mass
34 kDa
SDS-PAGE
38-44 kDa, under reducing conditions
Activity
Measured
by its ability to bind fluorescein-conjugated E. coli Bioparticles. The ED50
for this effect is 0.200-2.40 μg/mL.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human Mindin His-tag Protein, CF
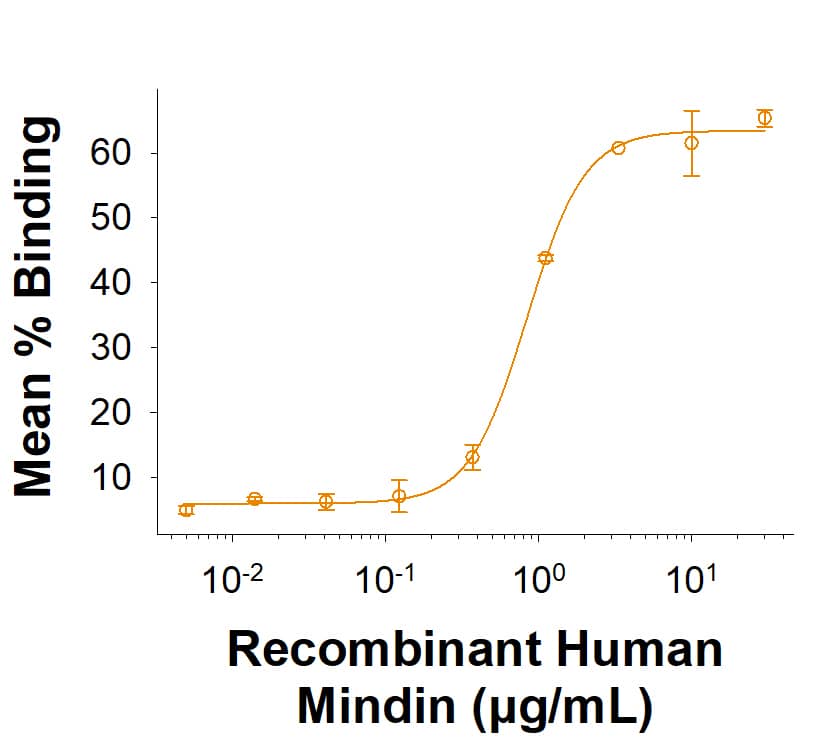
Recombinant Human Mindin His-tag Protein Binding Activity.
Recombinant Human Mindin His-tag Protein (Catalog # 11539-SP) binds to fluorescein-conjugated E. coli Bioparticles. The ED50 for this effect is 0.200-2.40 μg/mL.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
11539-SP
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute lyophilized material at 250 μg/mL in sterile PBS. For liquid material, refer to CoA for concentration. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: Mindin
References
- Li, Y. et al. (2009) EMBO J. 28:286.
- He, Y.W. et al. (2004) Nat. Immunol. 5:88.
- Jia, W. et al. (2008) J. Immunol. 180:6255.
- Li, H. et al. (2006) EMBO J. 25:4097.
- Jia, W. et al. (2005) Blood 106:3854.
- Li, Z. et al. (2009) J. Leukoc. Biol. 85:124.
- Tighe, R.M. et al. (2011) J. Allergy Ther. 2011 (Suppl. 1). pii: 001.
- Feinstein, Y. et al. (1999) Development 126:3637.
- Yan, L. et al. (2011) Cardiovasc. Res. 92:85.
- Bian, Z.Y. et al. (2012) J. Mol. Med. (Berl.) 90:895.
- Wang, L. et al. (2013) Exp. Neurol. 247:506.
- Simon, I. et al. (2007) Gynecol. Oncol. 106:112.
- Murakoshi, M. et al. (2011) Exp. Diabetes Res. 2011:486305.
- Lucarelli, G. et al. (2013) J. Urol. 190:2271.
Alternate Names
DIL1, RG-1, SPON2, Spondin 2
Gene Symbol
SPON2
UniProt
Additional Mindin Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human Mindin His-tag Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human Mindin His-tag Protein, CF
For research use only
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...