Recombinant Human MSP/MST1 Protein
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 352-MS

Key Product Details
Source
Accession #
Structure / Form
Conjugate
Applications
Product Specifications
Source
Gln19-Gly711
Purity
Endotoxin Level
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Predicted Molecular Mass
SDS-PAGE
Activity
Recombinant Human MSP/MST1 (Catalog # 352-MS) binds to Recombinant Human MSPR/Ron Protein (Catalog # 1947-MS) with an ED50 of 8.00-40.0 ng/mL.
Reviewed Applications
Read 1 review rated 4 using 352-MS in the following applications:
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human MSP/MST1 Protein
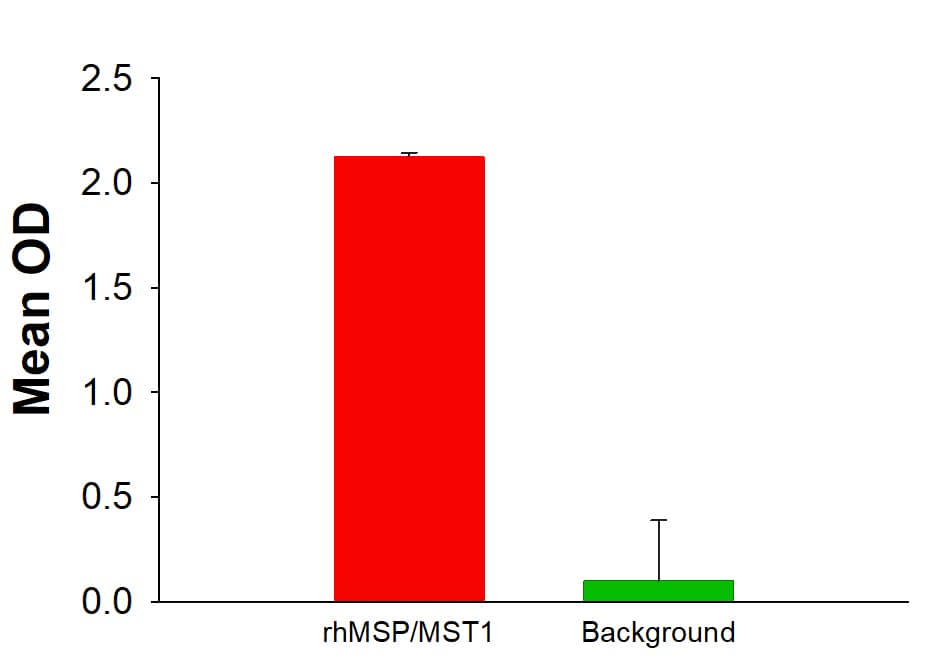
Recombinant Human MSP/MST1 Protein Bioactivity.
Recombinant Human MSP/MST1 Protein (Catalog # 352-MS) activates MSP R/Ron in MDA-MB-453 human breast cancer cells. Recombinant Human MSP/MST1 significantly induced phosphorylation of MSP R/Ron measured by DuoSet IC human phospho-MSP R/Ron kit (DYC1947).Formulation, Preparation and Storage
Carrier Free
What does CF mean?CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
What formulation is right for me?In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
Carrier: 352-MS
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with BSA as a carrier protein. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in sterile PBS containing at least 0.1% human or bovine serum albumin. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Carrier Free: 352-MS/CF
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in sterile PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: MSP/MST1
Macrophage stimulating protein (MSP), also known as HGF-like protein, and scatter factor-2, is a member of the HGF family of growth factors (1). MSP is secreted as an inactive single chain precursor (pro-MSP) that contains a PAN/APPLE-like domain, four kringle domains, and a peptidase S1 domain which lacks enzymatic activity (2). Human MSP shares 79% aa sequence identity with mouse MSP and 44% aa sequence identity with human HGF. Pro-MSP is secreted by hepatocytes under the positive and negative control of CBP in complex with either HNF-4 or RAR, respectively (3). Circulating pro-MSP is proteolytically cleaved in response to tissue injury to yield biologically active disulfide linked heterodimers consisting of a 45 - 62 kDa alpha and a 25-35 kDa beta chain (4, 5). Pro-MSP can be activated by MT-SP1, a transmembrane protease that is expressed on macrophages and is upregulated in many cancers (6). Heterodimeric MSP as well as the isolated beta chain bind to MSP R/Ron with high-affinity, although only heterodimeric MSP can induce receptor dimerization and signaling (7, 8). MSP induces macrophage and keratinocyte proliferation and osteoclast activation (9, 10). It also inhibits LPS- or IFN-induced iNOS and IL-12 expression by macrophages and prevents apoptosis of epithelial cells separated from the ECM (11, 12).
References
- Wang, M.-H. et al. (2002) Scand. J. Immunol. 56:545.
- Han, S. et al. (1991) Biochemistry 30:9768.
- Muraoka, R.S. et al. (1999) Endocrinology 140:187.
- Wang, M.-H. et al. (1996) J. Clin. Invest. 97:720.
- Nanney, L.B. et al. (1998) J. Invest. Dermatol. 111:573.
- Bhatt, A.S. et al. (2007) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 104:5771.
- Wang, M.-H. et al. (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272:16999.
- Danilkovitch, A. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274:29937.
- Wang, M.-H. et al. (1996) Exp. Cell Res. 226:39.
- Kurihara, N. et al. (1998) Exp. Hematol. 26:1080.
- Morrison, A.C. et al. (2004) J. Immunol. 172:1825.
- Liu, Q.P. et al. (1999) J. Immunol. 163:6606.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional MSP/MST1 Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human MSP/MST1 Protein
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human MSP/MST1 Protein
For research use only