Recombinant Human NRG1/HRG1-alpha Fc Chimera Protein, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 11353-NR

Key Product Details
Source
Accession #
Structure / Form
Conjugate
Applications
Product Specifications
Source
| Human NRG1/HRG1-alpha (Ser20-Lys241) Accession # AAI50610.1 |
IEGRMD | Human IgG1 (Pro100-Lys330) |
| N-terminus | C-terminus |
Purity
Endotoxin Level
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Predicted Molecular Mass
SDS-PAGE
Activity
The ED50 for this effect is 8.00‑80.0 ng/mL.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human NRG1/HRG1-alpha Fc Chimera Protein, CF
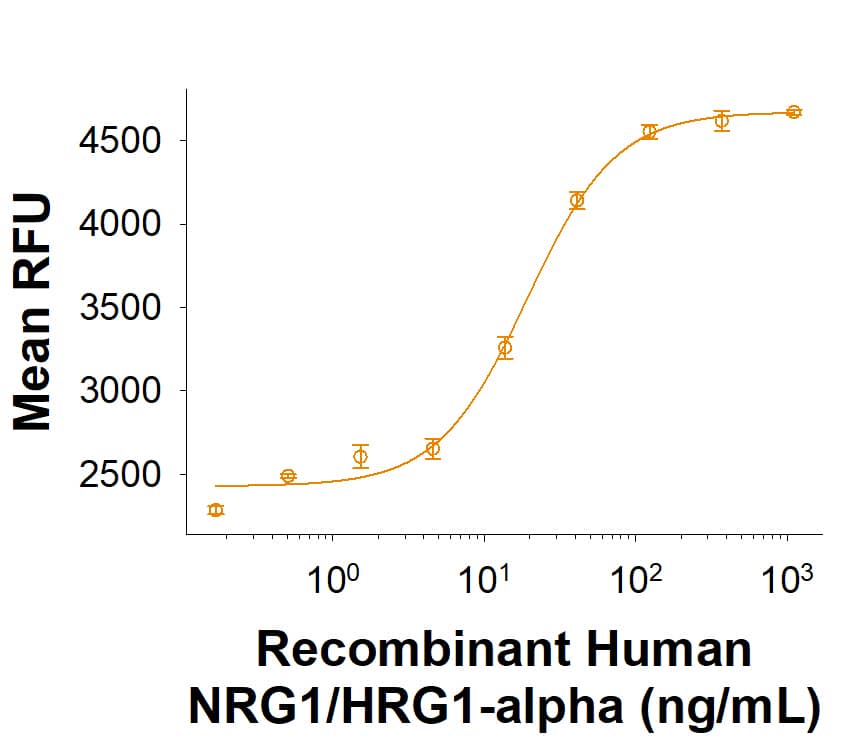
Recombinant Human NRG1/HRG1-alpha Fc Chimera Protein Bioctivity.
Recombinant Human NRG1/HRG1-alpha stimulates cell proliferation on MCF 7 human breast cancer cells. The ED50 for this effect is 8.00-80.0 ng/mL.Recombinant Human NRG1/HRG1-alpha Fc Chimera Protein SDS-PAGE.
2 μg/lane of Recombinant Human NRG1/HRG1-alpha Fc Chimera Protein (Catalog # 11353-NR) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 65-79 kDa and 130-160 kDa, respectively.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
11353-NR
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 500 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: Neuregulin-1/NRG1
The neuregulin family of structurally related glycoproteins comprises products from four distinct but related genes, Nrg-1, Nrg-2, Nrg-3, and Nrg-4. Through alternative splicing or the use of alternative promoters, Nrg-1 encodes more than 14 soluble or transmembrane proteins. The extracellular domain of the transmembrane NRG1 isoforms can be proteolytically cleaved to release soluble growth factors. The alpha- or beta-splice variants differ in their C-terminal region. All NRG1 isoforms contain an EGF-like domain that is required for their direct binding to the ErbB3 or ErbB4 receptor tyrosine kinases. The ErbB3 or ErbB4 subsequently recruits and heterodimerizes with ErbB2, resulting in tyrosine phosphorylation and NRG1 signaling. NRG1 isoforms can be classified into three major subtypes. Type I (Neu Differentiation Factor, NDF; Heregulin, HRG; Acetylcholine Receptor Inducing Activity, ARIA) and type II (Glial Growth Factor, GGF). NRG1s have an immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domain N-terminal to the EGF-like domain. Type I NRG1s differ from type II NRG1s by having a glycosylation-rich domain between the Ig-like and the EGF-like domains. Type III NRG1 (Sensory and Motor neuron-Derived Factor) lacks the Ig-like domain but has a cysteine rich domain (CRD) instead. NRG1 isoforms show distinct spatial and temporal expression patterns. These proteins play important roles during development of both the nervous system and the heart. They have been shown to regulate the selective expression of neurotransmitter receptors in neurons and at the neuromuscular junction, and to promote the differentiation and development of Schwann cells from neural crest stem cells. NRG1s have also been shown to be involved in the establishment of the oligodendroglial lineage.
References
- Lemke, G. (2006) Science STKE 325:pe11.
- Esper, R.M. et al. (2006) Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 51:161.
- Tosato, S. et al. (2005) Schizophr. Bull. 31:613.
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Neuregulin-1/NRG1 Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human NRG1/HRG1-alpha Fc Chimera Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human NRG1/HRG1-alpha Fc Chimera Protein, CF
For research use only