Recombinant Human PD-L1/B7-H1 Fc Chimera Protein, CF Best Seller
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 156-B7

Key Product Details
Source
Accession #
Structure / Form
Conjugate
Applications
Product Specifications
Source
| Human PD-L1 (Phe19-Thr239) Accession # Q9NZQ7 |
DIEGRMD | Human IgG1 (Pro100-Lys330) |
| N-terminus | C-terminus |
Purity
Endotoxin Level
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Predicted Molecular Mass
SDS-PAGE
Activity
The ED50 for this effect is 0.075-0.75 μg/mL.
Reviewed Applications
Read 21 reviews rated 4.9 using 156-B7 in the following applications:
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human PD-L1/B7-H1 Fc Chimera Protein, CF
Recombinant Human PD-L1/B7-H1 Fc Chimera Protein SEC-MALS.
Recombinant human B7-H1/Fc (Catalog # 156-B7) has a molecular weight (MW) of 135.0 kDa as analyzed by SEC-MALS, suggesting that this protein is a homodimer. MW may differ from predicted MW due to post-translational modifications (PTMs) present (i.e. Glycosylation).Bioactivity of PD-L1 Protein
Recombinant Human PD-L1 / B7-H1 Fc Chimera (Catalog # 156-B7) inhibits anti-CD3 antibody-induced IL-2 secretion in human T lymphocytes. The ED50 for this effect is 0.075-0.75 µg/mL in the presence of Goat Anti-Human IgG Fc Polyclonal Antibody (G-102-C).Binding of Human PD-1 to PD-L1/B7-H1 by surface plasmon resonance (SPR).
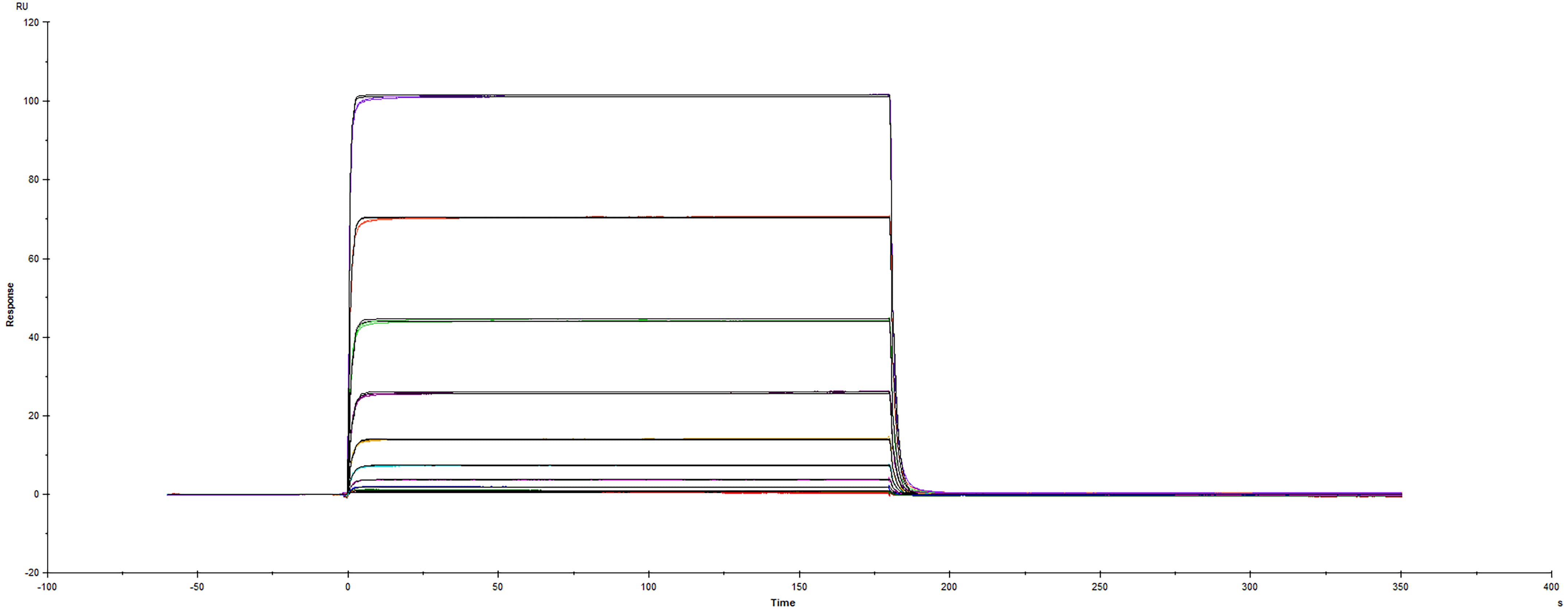
Recombinant Human PD-L1/B7-H1 Fc protein (Catalog # 156-B7) was immobilized on a Biacore Sensor Chip CM5, and binding to Recombinant Human PD-1 His protein (8986-PD) was measured at a concentration range between 6.0 nM and 3.05 uM. The double-referenced sensorgram was fit to a 1:1 binding model to determine the binding kinetics and affinity, with an affinity constant of KD=1.70 uM.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
156-B7
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS and NaCl. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in sterile PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: PD-L1/B7-H1
PD-L1, also known as B7-H1, PDL1, is one of the ligands for PD-1 and plays a critical role in the regulation of T cell immunity (1-6). The PD-1:PD-L1 interaction initiates a negative signaling cascade in T cells leading to inhibition of T cell activation (2, 5, 7, 8). PD-L1 provides a molecular stop signal to the adaptive immune system helping to distinguish between self and foreign antigens. PD-L1 also plays a role in the development of immune tolerance by promoting T cell anergy (1, 5) and enhancing regulatory T cell development (8). In addition, PD-L1 favors the development of anti-inflammatory IL-10 and IL-22 producing dendritic cells (7, 9) and inhibits the development of Th17 cells (8). Many cancers exhibit upregulated PD-L1 protein expression, and several cancers with high levels of PD-L1 have been associated with increased tumor aggressiveness and poor prognosis. Using new therapeutics that block the PD-L1:PD-1 interaction has proven successful in the clinic for many cancer types and has sparked great interest in the field of cancer immunotherapy.
The PD-L1 protein is an approximately 65 kDa transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the B7 family of immune regulatory molecules (10). Mature human PD-L1 protein consists of a 220 amino acid (aa) extracellular domain (ECD) with two immunoglobulin-like domains, a 21 aa transmembrane segment, and a 31 aa cytoplasmic domain (11). Within the ECD, human PD-L1 shares 73% and 74% aa sequence identity with mouse and rat B7-H1, respectively. Alternative splicing generates additional isoforms that either lack the first Ig-like domain or are truncated within the second Ig-like domain (12). PD-L1 is expressed on inflammatory-activated immune cells including macrophages, T cells, and B cells (10, 13, 14, 16) keratinocytes (9, 11), endothelial and intestinal epithelial cells (2, 9), as well as a variety of carcinomas and melanoma (12, 16).
References
- Tsushima, F. et al. (2007) Blood 110:180.
- Mazanet, M.M. and C.C.W. Hughes (2002) J. Immunol. 169:3581.
- Azuma, T. et al. (2008) Blood 111:3635.
- Butte, M.J. et al. (2008) Mol. Immunol. 45:3567.
- Park, J.-J. et al. (2010) Blood 116:1291.
- Ritprajak, P. et al. (2010) J. Immunol. 184:4918.
- Chen, L. et al. (2007) J. Immunol. 178:6634.
- Herold, M. et al. (2015) J. Immunol. 195:3584.
- Scandiuzzi, L. et al. (2014) Cell Rep. 6:625.
- Ceeraz, S. et al. (2013) Trends Immunol. 34:556.
- Dong, H. et al. (1999) Nat. Med. 5:1365.
- Frigola, X. et al. (2011) Clin. Cancer Res. 17:1915.
- Tamura, H. et al. (2001) Blood 97:1809.
- Kuang, D.-M. et al. (2014) J. Clin. Invest. 124:4657.
- Cao, Y. et al. (2010) Cancer Res. 71:1235.
- Dong, H. et al. (2002) Nat. Med. 8:793.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional PD-L1/B7-H1 Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human PD-L1/B7-H1 Fc Chimera Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human PD-L1/B7-H1 Fc Chimera Protein, CF
For research use only