Recombinant Rat VEGF 164 Protein
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 564-RV

Key Product Details
Source
Accession #
Structure / Form
Conjugate
Applications
Product Specifications
Source
Ala27-Arg190
Purity
Endotoxin Level
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Predicted Molecular Mass
SDS-PAGE
Activity
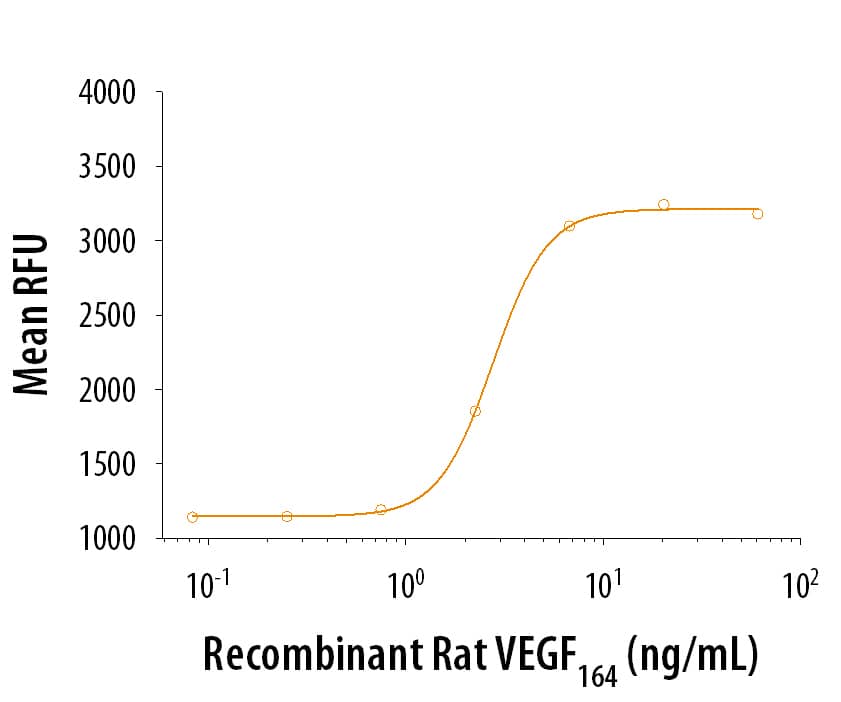
The ED50 for this effect is 0.75-3.75 ng/mL.
Reviewed Applications
Read 1 review rated 5 using 564-RV in the following applications:
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Rat VEGF 164 Protein
Recombinant Rat VEGF 164 Protein Bioactivity
Recombinant Rat VEGF164(Catalog # 564‑RV) stimulates cell proliferation in HUVEC human umbilical vein endothelial cells in a dose-dependent manner. The ED50 is 0.75-3.75 ng/mL.Recombinant Rat VEGF 164 Protein SDS-PAGE
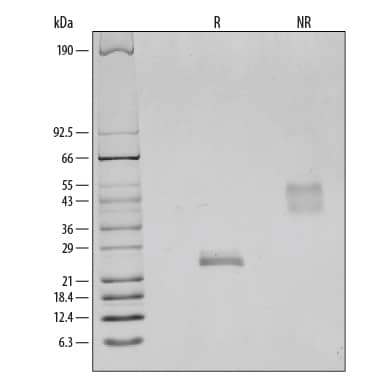
1 μg/lane of Recombinant Rat VEGF164was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by silver staining, showing bands at 25 kDa and 54 kDa, respectively.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
Carrier Free
What does CF mean?CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
What formulation is right for me?In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
Carrier: 564-RV
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with BSA as a carrier protein. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in sterile PBS containing at least 0.1% human or bovine serum albumin. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Carrier Free: 564-RV/CF
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in sterile PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: VEGF
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF or VEGF-A), also known as vascular permeability factor (VPF), is a potent mediator of both angiogenesis and vasculogenesis in the fetus and adult (1-3). It is a member of the PDGF family that is characterized by a cysteine-knot structure formed by eight conserved cysteine residues (4). Alternately spliced isoforms of 121, 145, 165, 183, 189, and 206 amino acids (aa) have been identified in humans, with 120, 164 and 188 aa isoforms found in rat and mouse (2, 4). Isoforms other than VEGF120 and VEGF121 contain basic heparin-binding regions and are not freely diffusible (4). Rat VEGF164 shares 97% aa sequence identity with corresponding regions of mouse, 88% with human and bovine, 89% with porcine and canine, and 90% with feline and equine VEGF, respectively. VEGF binds the type I transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinases VEGF R1 (also called Flt-1) and VEGF R2 (Flk-1/KDR) on endothelial cells (4). Although affinity is highest for binding to VEGF R1, VEGF R2 appears to be the primary mediator of VEGF angiogenic activity (3, 4). Human VEGF165 binds the semaphorin receptor, neuropilin-1 and promotes complex formation with VEGF R2 (5). VEGF is required during embryogenesis to regulate the proliferation, migration, and survival of endothelial cells (3, 4). In adults, VEGF functions mainly in wound healing and the female reproductive cycle (3). Pathologically, it is involved in tumor angiogenesis and vascular leakage (6, 7). Circulating VEGF levels correlate with disease activity in autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus (8). VEGF is induced by hypoxia and cytokines such as IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, oncostatin M and TNF-alpha (3, 4, 9).
References
- Conn, G. et al. (1990) J. Biol. Chem. 87:2628.
- Ishii, H. et al. (2001) Arch. Oral Biol. 46:77.
- Byrne, A.M. et al. (2005) J. Cell. Mol. Med. 9:777.
- Robinson, C.J. and Stringer, S.E. (2001) J. Cell. Sci. 114:853.
- Pan, Q. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282:24049.
- Weis, S.M. & D.A. Cheresh (2005) Nature 437:497.
- Thurston, G. (2002) J. Anat. 200:575.
- Carvalho, J.F. et al. (2007) J. Clin. Immunol. 27:246.
- Angelo, L.S. & R. Kurzrock (2007) Clin. Cancer Res. 13:2825.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional VEGF Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Rat VEGF 164 Protein
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Rat VEGF 164 Protein
For research use only