Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody [HRP]
Novus Biologicals, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # NB7539


Conjugate
Catalog #
Key Product Details
Validated by
Knockout/Knockdown
Species Reactivity
Mouse
Applications
ELISA, Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry, Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin, Western Blot
Label
HRP
Antibody Source
Polyclonal Goat IgG
Concentration
1.0 mg/ml
Product Specifications
Immunogen
This Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody [HRP] was developed against mouse IgG-heavy and light chain.
Specificity
By immunoelectrophoresis and ELISA this Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody [HRP] reacts specifically with mouse IgG and with light chains common to other mouse immunoglobulins. No antibody was detected against non-immunoglobulin serum proteins.
Clonality
Polyclonal
Host
Goat
Isotype
IgG
Scientific Data Images for Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody [HRP]
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody [HRP] [NB7539] - FFPE serial sections of human stomach carcinoma. Primary Antibody: Mouse anti-p53 (Clone DO-1) used at a dilution of 1:100. Secondary Antibody: Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody [HRP] Conjugated used at a dilution of 1:200 (5ug/ml). Detection: DAB
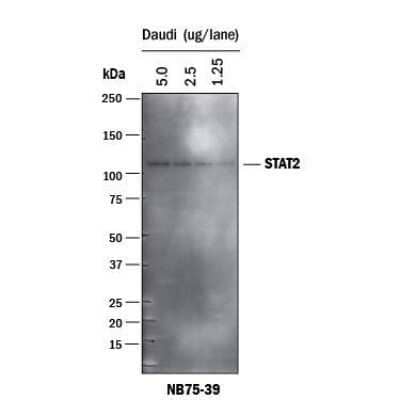
Western Blot: Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody [HRP] [NB7539] - This Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody [HRP] used for detection of beta-Actin in human pancreatic cancer cell lines. Image from verified customer review.
Applications for Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody [HRP]
Application
Recommended Usage
ELISA
1:10000-1:1000000
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence
1:50 - 1:500
Immunohistochemistry
1:40 - 1:400
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin
1:40 - 1:400
Western Blot
1:5000-1:50000
Reviewed Applications
Read 1 review rated 5 using NB7539 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Immunogen affinity purified
Formulation
Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS) containing 0.2% BSA
Preservative
0.05% Pro-Clean 400
Concentration
1.0 mg/ml
Shipping
The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below.
Stability & Storage
Store at 4C. Do not freeze.
Background: IgG (H+L)
The 4 IgG subclasses, sharing 95% amino acid identity, include IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4 for humans and IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, and IgG3 for mice. The relative abundance of each human subclass is 60% for IgG1, 32% for IgG2, 4% for IgG3, and 4% for IgG4. In an IgG deficiency, there may be a shortage of one or more subclasses (4).
References
1. Painter RH. (1998) Encyclopedia of Immunology (Second Edition). Elsevier. 1208-1211
2. Chapter 9 - Antibodies. (2012) Immunology for Pharmacy. Mosby 70-78
3. Schroeder H, Cavacini, L. (2010) Structure and Function of Immunoglobulins. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 125(2 0 2): S41-S52. PMID: 20176268
4. Vidarsson G, Dekkers G, Rispens T. (2014) IgG subclasses and allotypes: from structure to effector functions. Front Immunol. 5:520. PMID: 25368619
Additional IgG (H+L) Products
Product Documents for Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody [HRP]
Product Specific Notices for Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody [HRP]
This product is for research use only and is not approved for use in humans or in clinical diagnosis. Secondary Antibodies are guaranteed for 1 year from date of receipt.
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...