IL-17 Family Cytokines

IL-17 Family Cytokines, Receptors, and Signaling Pathways
The IL-17 cytokine family consists of IL-17A, IL-17B, IL-17C, IL-17D, IL-17E/IL-25, and IL-17F. These proteins are secreted by multiple different cell types and primarily promote pro-inflammatory immune responses. IL-17A was the first member of the IL-17 family of cytokines to be cloned, followed by homology-based cloning of the other five IL-17 family members, which share 16–50% amino acid sequence identity with IL-17A. Members of this cytokine family contain five spatially conserved cysteine residues at their C-terminal ends and form a cysteine-knot fold structure. Members of the IL-17 cytokine family are secreted primarily as disulfide-linked homodimers, with the exception of IL-17B, which is secreted as a non-covalent homodimer and IL-17A/F, which is secreted as a heterodimer.
IL-17 Family Receptors
Signaling by IL-17 family cytokines is mediated by members of the IL-17 receptor family. This family includes five members, IL-17 R/IL-17RA, IL-17B R/IL-17RB, IL-17RC, IL-17RD/SEF, and IL-17RE. These receptor subunits are type I transmembrane proteins that contain two extracellular fibronectin type III-like domains and a cytoplasmic SEF/IL-17R/TIR (SEFIR) domain. Members of the IL-17 receptor family oligomerize to form functional receptor complexes that mediate downstream signaling.
IL-17A
IL-17A signals through a receptor complex consisting of IL-17 RA and IL-17 RC. IL-17A is predominantly expressed by Th17 cells and is involved in promoting immune responses against extracellular bacteria and fungi. Binding of IL-17A to its receptor recruits the intracellular adaptor proteins, ACT1, TRAF-3, and TRAF-6, leading to downstream activation of a series of intracellular kinases that drive the NF kappa B-, AP-1-, and C/EBP-dependent expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and anti-microbial peptides. While IL-17A signaling is intended to protect the host against invading pathogens, it needs to be tightly regulated as IL-17A overexpression has been shown to be associated with chronic inflammatory disorders, autoimmune diseases, and cancer.
IL-17B
IL-17B is secreted as a noncovalent homodimer and signals through a receptor complex consisting of IL-17B R/IL-17RB and an unknown receptor subunit. IL-17B is primarily produced by neutrophils, germinal center B cells, neurons, and chondrocytes, and has been found to be overexpressed in the inflammatory cartilage of a rheumatoid arthritis mouse model. High level expression of either IL-17 B or its receptor IL-17B R/IL-17RB has also been linked to a poor prognosis in breast, pancreatic, and gastric cancer. Most of what is currently known about the signaling pathways activated downstream of IL-17B R/IL-17RB is based primarily upon activation of the receptor by IL-17E/IL-25, which binds to a receptor complex composed of IL-17RA and IL-17B R/IL-17RB. When both IL-17B and IL-17E/IL-25 are present, IL-17B inhibits the ability of IL-17E/IL-25 to bind to IL-17 RA-IL-17B R/IL-17RB receptor complexes and reduces its ability to promote the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in epithelial cells. This suggests that under certain conditions, IL-17B may negatively regulate IL-17E/IL-25 signaling.
IL-17C
IL-17C is primarily produced by epithelial cells and immune cells such as CD4+ T cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages at sites of inflammation. IL-17C binds to a receptor complex consisting of IL-17 RA and IL-17 RE. Autocrine signaling by IL-17C in epithelial cells stimulates the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and anti-microbial peptides and is thought to play a central role in the establishment of protective barriers in the skin and intestine. Similar to IL-17A and IL-17B, overexpression of IL-17C has deleterious effects. IL-17C has been shown to be overexpressed in patients with psoriatic skin lesions and atopic dermatitis. Additionally, it is up-regulated in the synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, in tissue from patients with intestinal bowel disease, and in several forms of cancer.
IL-17D
Similar to other IL-17 family cytokines, IL-17D has the ability to induce the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, but its receptor and the context in which it functions have yet to be characterized. IL-17D is expressed in a variety of different tissues, including brain, skeletal muscle, adipose tissue, lung, heart, and pancreas. Additionally, it is expressed at low levels in resting CD4+ T cells and CD19+ B cells, but not in activated immune cell types. As little is currently known about the biological activity of IL-17D, the role that it may play in disease pathogenesis is also not well understood. IL-17D has been detected in rheumatoid nodules of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, but its expression was found to be decreased in psoriatic skin lesions. IL-17D has also been described to be involved in promoting the early immune response to viral infections, and to have anti-tumor effects due to its ability to induce the expression of MCP-1, which promotes the recruitment of natural killer cells and M1 macrophage development at tumor sites.
IL-17E
IL-17E, also known as IL-25, signals through a receptor complex consisting of IL-17 RA and IL-17B R/IL-17RB. IL-17E shares only 16% sequence homology with IL-17A, making it the most divergent member of the IL-17 cytokine family. It is produced by a variety of different cell types including endothelial cells, epithelial cells, T cells, dendritic cells, group 2 ILCs (ILC2 cells), macrophages, and eosinophils. While IL-17E signaling activates intracellular signaling pathways that are similar to IL-17A, IL-17E primarily promotes Th2- and Th9-type immune responses. As a result, IL-17E is involved in providing protection against parasitic helminths and may also contribute to the development of allergic asthma. Although IL-17E has also been suggested to have pathogenic effects in inflammatory skin disorders such as psoriasis and atopic dermatitis, it has also been found to suppress Th17-mediated autoimmune diseases in mouse models of rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis.
IL-17F
Compared with the other IL-17 family cytokines, IL-17F shares the highest homology with IL-17A. IL-17F is frequently co-expressed with IL-17A, and can either form IL-17F homodimers or heterodimers with IL-17A. Similar to IL-17A, IL-17F homodimers and IL-17A/F heterodimers signal through a receptor complex composed of IL-17RA and IL-17RC. Likewise, they both induce the in vitro expression of a similar set of pro-inflammatory genes as IL-17A, although IL-17F displays reduced potency compared to both IL-17A and IL-17A/F. IL-17F expression has been found to be elevated in patients with atopic dermatitis and psoriasis, as well as in patients with multiple sclerosis and Crohn’s disease.
Bio-Techne offers a wide selection of products for IL-17 family research including R&D Systems™ bioactive recombinant human and mouse proteins for most of the IL-17 family cytokines and receptors, along with single and multianalyte immunoassays for monitoring immune responses. In addition, we offer antibodies against IL-17 family cytokines, receptors, and intracellular signaling molecules that are validated for one or more of the following applications: blocking/neutralization, Western blot, flow cytometry, and immunohistochemistry.
IL-17 Family Cytokines and Receptors - Products by Molecule
| IL-17/IL-17A | IL-17A/F Heterodimer | IL-17B | IL-17C | IL-17D | IL-17E/IL-25 |
| IL-17F | IL-17B R/IL-17 RB | IL-17 RC | IL-17 RD/SEF | IL-17 RE |
IL-17 Cytokine Family Intracellular Signaling - Products by Molecule
R&D Systems Human Cell-Expressed Recombinant Human IL-17A Displays Higher Activity than a Leading Competitor's Recombinant Human IL-17A Protein

R&D Systems Recombinant Human IL-17A Displays Higher Activity than a Leading Competitor’s Recombinant Human IL-17A Protein. The HT-29 human colon adenocarcinoma cell line was treated with increasing concentrations of R&D Systems HEK293-derived Recombinant Human IL-17A (Catalog # 7955-IL; blue line) or with human cell-derived recombinant human IL-17A from another company (red line). The bioactivity of the recombinant proteins was assessed by measuring CXCL1/GRO alpha secretion using the Human CXCL1/GRO alpha DuoSet™ ELISA Development Kit (R&D Systems, Catalog # DY275). The activity of the R&D Systems protein was approximately 2.5-fold greater than the leading competitor's protein.
Detection of CD4+IL-17/IL-17A+ Mouse Splenocytes by Flow Cytometry
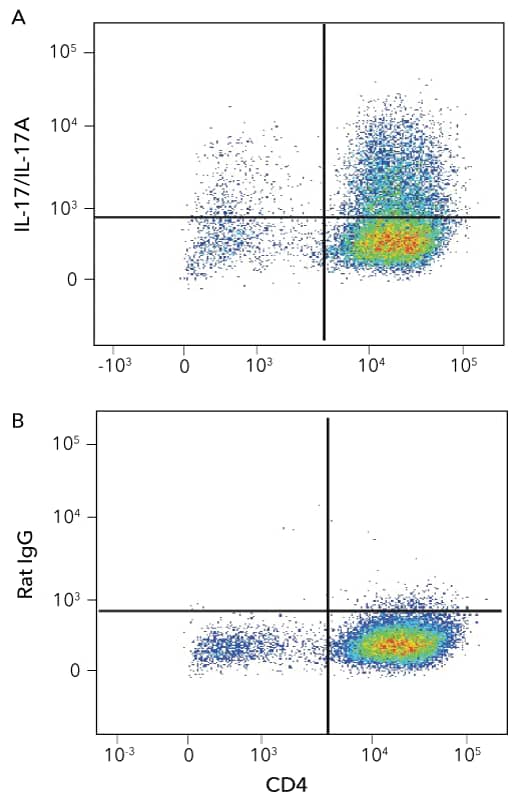
Detection of IL-17/IL-17A in Mouse Splenocytes by Flow Cyotmetry. Mouse splenocytes stimulated to induce Th17 cells were stained with an APC-conjugated Rat Anti-Mouse CD4 Monoclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # FAB554A) and either a (A) PE-conjugated Rat Anti-Mouse IL-17/IL-17A Monoclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # IC7211P) or a (B) PE-conjugated Rat IgG2B Isotype Control Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # IC013P). To facilitate intracellular staining, cells were fixed and permeabilized using the FlowX FoxP3 Fixation and Permeabilization Buffer Kit (R&D Systems, Catalog # FC012).
CXCL1/GRO alpha Secretion Induced by R&D Systems Recombinant Human IL-17E/IL-25 and Neutralization by a Goat Anti-Human IL-17E/IL-25 Polyclonal Antibody

IL-17E-induced CXCL1/GRO alpha Secretion is Neutralized Using a Goat Anti-Human IL-17E/IL-25 Polyclonal Antibody. The HT-29 human colon adenocarcinoma cell line was treated with the indicated concentrations of Recombinant Human IL-17E/IL-25 (R&D Systems, Catalog # 1258-IL) and CXCL1/GRO alpha secretion was measured using the Human CXCL1/GRO alpha DuoSet™ ELISA Development Kit (R&D Systems, Catalog # DY275; orange line). The ED50 for this effect is typically 0.25-1.5 ng/mL. The stimulatory effect induced by 5 ng/mL Recombinant Human IL-17E/IL-25 was neutralized by treating the cells with increasing concentrations of a Goat Anti-Human IL-17E/IL-25 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # AF1258; blue line). The ND50 for this effect is typically 0.04-0.24 ug/mL.
IL-6 Secretion Induced by R&D Systems Recombinant Human IL-17F and Neutralization by a Mouse Anti-Human IL-17F Monoclonal Antibody

IL-17F-induced IL-6 Secretion is Neutralized Using a Mouse Anti-Human IL-17F Monoclonal Antibody. The NIH-3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line was treated with the indicated concentrations of Recombinant Human IL-17F (R&D Systems, Catalog # 1335-INS) and IL-6 secretion was measured using the Mouse IL-6 Quantikine™ ELISA Kit (R&D Systems, Catalog # M6000B; red line). The ED50 for this effect is typically 2-10 ng/mL. The stimulatory effect induced by 25 ng/mL Recombinant Human IL-17F was neutralized by treating the cells with increasing concentrations of a Mouse Anti-Human IL-17F Monoclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # MAB13352; blue line). The ND50 for this effect is typically 0.1-0.6 ug/mL.
Featured Products for IL-17 Cytokine Family Research

Immunoassays for Detecting IL-17 Family Cytokines
Immunoassays for Detecting IL-17 Family Cytokines
From our complete, ready-to-use Quantikine™ ELISA Kits to our multiplex Luminex® Assays and fully automated Simple Plex™ Assays, you can count on our immunoassays to deliver accurate, reproducible, high-quality data for every experimental sample that you test.

Proteome ProfilerTM Human Phospho-Kinase Antibody Array
Proteome ProfilerTM Human Phospho-Kinase Antibody Array
The Proteome Profiler Human Phospho-Kinase Antibody Array offers a simple and inexpensive method to simultaneously detect the phosphorylation of 37 different kinases in a single sample, using chemiluminescence and standard Western blotting equipment. Utilize this multiplex membrane-based assay to explore the signaling pathways activated by IL-17 family cytokines.

Bulk Proteins
Bulk Proteins
If your experiments require large quantities of a particular protein, contact us for a bulk quote. We have the capacity and the expertise to scale up the production of any protein to meet your needs, and we offer economical pricing on bulk orders.
Featured Resources for IL-17 Cytokine Family Research

IL-17 Cytokine Family Product Guide
IL-17 Cytokine Family Product Guide
Download this guide to see a complete listing of our products for IL-17 cytokine family research. We offer bioactive recombinant human and mouse proteins for most of the IL-17 family ligands and receptors, along with antibodies validated for multiple applications including blocking/neutralization, flow cytometry, Western blotting, and IHC, and both single and multianalyte immunoassays.

Cytokine Signaling Pathways
Cytokine Signaling Pathways
Cytokines activate a diverse array of intracellular signaling pathways that can induce processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, and inflammation. Explore the signaling pathways that are activated by different cytokine families, the primary target cells that they affect, and the biological effects that they mediate using our interactive signaling pathways.

Signaling Pathways in Mouse Th17 Differentiation Poster
Signaling Pathways in Mouse Th17 Differentiation Poster
Th17 cells are a subset of CD4+ effector T cells that is required for host defense against specific fungi and extracellular bacteria. Use this poster to learn more about the signaling pathways that promote the differentiation of naïve CD4+ T cells into Th17 cells and some of the cell surface markers and transcription factors that distinguish Th17 cells from other T helper cell subtypes.