By Jennifer Jones, M.S.
When you think of antibody producing animals in the lab you probably think of rabbits, mice, goats, and rats. But what about llamas? Llamas probably aren’t the first animal, or even the fifth animal, that comes to mind when you think of antibody generation, but they’ve recently garnered a lot of attention for their potential to treat COVID-19 through neutralization of the SARS-CoV-2 virus.1 Additionally, they’ve shown potential in combatting other infectious, autoimmune, and inflammatory diseases.2 Some llama antibodies have entered clinical trials for treatment of diseases including rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and breast cancer.2 So, what exactly makes antibodies from llamas and other camelid animals so special?
What are LlaMABody™-Camelid Antibodies?
Camelid antibodies are antibodies produced by members of the Camelidae family which includes llamas, camels, and alpacas.3,4 The Camelidae family generates both conventional antibodies comprised of two heavy chains and two light chains, as well as heavy chain-only antibodies (HCAbs).2-6 HCAbs lack the light chain and the CH1 region but maintain the VHH region containing the antigen-binding domain.6 Recombinant antibody engineering has also enabled the creation of several different types of VHH antibodies. Single domain VHH antibodies, also called Nanobodies®, consist of the antigen binding domain of the heavy chain only.2-5 Bi-valent VHH antibodies are generated by two tandem single domain antibodies targeting different epitopes on the same target or distinct targets.3,6 Additionally, the VHH domain can be fused to IgG (CH2-CH3 constant domains) from a variety of species like llama, mouse, and human to generate scaffold antibodies.5
Camelid antibodies are more often being used in a variety of research applications, from studying protein structure, to drug delivery, to blocking and neutralizing viruses – such as SARS-CoV-2.1,5,6 Bio-Techne offers camelid antibodies, including HCAbs, monomeric, bivalent, and VHH scaffold antibodies, through its LlaMABody™ product line.5
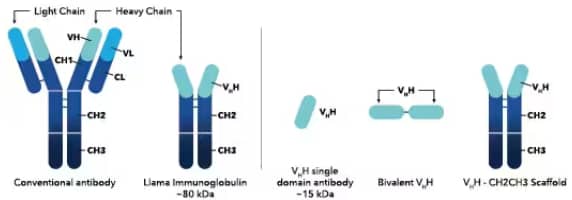
Graphical representation of (left) the conventional antibody and llama immunoglobulin (heavy chain-only antibody) produced by the camelid family and (right) the engineered antibodies including single domain VHH antibodies, bi-valent VHH antibodies, and VHH-IgG scaffold antibodies.
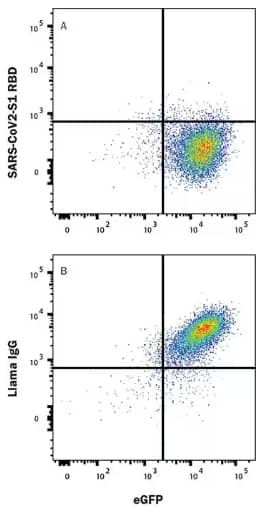
Functional flow cytometry analysis showing the effect of Recombinant SARS-Cov-2 Spike RBD Fc Chimera Protein (Catalog # 10499-CV) binding to HEK293 cell line transfected with recombinant human ACE-2 and eGFP. (Top) Binding is blocked by treatment with Llama Anti-SARS-Cov-2 Spike RBD Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # LMAB12503) but not by (Bottom)Llama IgG1 Control (Catalog # AB-011-C). Protein binding was observed using APC-conjugated Mouse Anti-Human IgG Fc Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB110A).
What Benefits do LlaMABody™ Antibodies Offer?3-6
- Smaller size of single domain VHH antibodies compared to conventional antibodies (15 kDa vs. 150 kDa) allows for detection of epitopes that might not be accessible with traditional antibodies.
- Easier penetration of tissue and cells for more sensitive immunohistochemical and flow cytometry staining.
- Superior stability under intense experimental conditions, including ability to endure a larger range of temperature and pH.
- Unlike conventional antibodies, camelid antibodies do not have solubility or aggregation issues.
- Through our custom LlaMABody™ services, Bio-Techne has improved methods for custom conjugation to single-domain antibodies including biotin, enzymes, and fluorochromes.
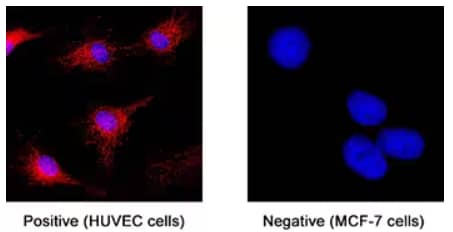
ST2/IL-33R was detected in immersion fixed human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) (positive staining) and MCF‑7 human breast cancer cell line (negative staining) using Llama Anti-Human ST2/IL-33R LlamabodyTM Bivalent VHH HuIgG2 Fusion Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # LMAB108591). Following probing with primary antibody, cells were stained with Anti-Alpaca Alexa Fluor 594 (red) secondary antibody and counterstained with DAPI (blue). ST2/IL-33R expression was specifically localized to cytoplasm.
The small size of llama antibodies and nanobodies make them advantageous for several research areas. More recently, nanobodies have been studied for their application in chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapies.6,7 Both single nanobody and bi-specific nanobody modulated CAR T cells have shown anti-tumor effects and comparable clinical function to traditional single-chain variable fragment (scFv) CAR T cells.7 The ability of bi-specific and multi-specific modulation of nanobodies, along with their small size allowing for increased tissue penetration, makes them great candidates for use in cancer immunotherapies.6 As more studies utilize nanobodies such as LlaMABodies it will be exciting to watch the immunotherapeutic potential and advantages of these tiny antibodies grow.
LlaMABody™ is a trademark of Bio-Techne Corporation.
Nanobody® and Nanobodies® are registered trademarks of Ablynx N.V.

-
Xu, J. et al. (2021) Nanobodies from camelid mice and llamas neutralize SARS-CoV-2 variants. Nature. 595:278-282.
-
Jovčevska, I. & Muyldermans, S. (2020) The Therapeutic Potential of Nanobodies. BioDrugs. 34:11-26.
-
Harmsen, M.M. & De Haard, H.J. (2007) Properties, production, and applications of camelid single-domain antibody fragments. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 77:13-22.
-
Wolfson, W. (2006) Ablynx makes nanobodies from llama bodies. Chem Biol. 13:1243-1244.
-
Bio-Techne. (2020) Bio-Techne Announces Release of a New SARS-CoV-1/2 Spike RBD LlaMABody™ Recombinant Antibody that Blocks Viral Entry.
-
Chanier, T. & Chames, P. (2019) Nanobody Engineering: Toward Next Generation Immunotherapies and Immunoimaging of Cancer. Antibodies (Basel) 8:13.
-
Bao, C. et al. (2021) The Application of Nanobody in CAR-T Therapy. Biomolecules. 11:238.