By Natalia Gurule, PhD
What is IRE1 alpha?
Inositol- requiring enzyme type 1 alpha (IRE1α) is a serine/threonine kinase that is one of the three transducers within the unfolded protein response (UPR) signaling pathway which becomes activated upon accumulation of misfolded proteins within the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).1 IRE1α contains two domains, the N- terminal domain that senses misfolded proteins within the ER lumen and the C- terminal domain that signals through serine/threonine kinase and endoribonuclease domains within the cytoplasm to initiate the UPR response.2 Mechanistically, IRE1α is known to induce apoptosis and target cytosolic RNAs for degradation upon conditions of ER stress.3 IRE1α-dependent apoptosis is induced through two mechanisms: the first is regulated through alternative splicing of the transcription factor x-box binding protein 1 (XBP1), and the second is via activation of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway, which occurs under severe stress.4
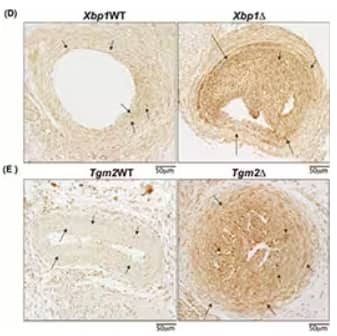
Immunohistochemical analysis showing (D) Xbp1WT and Xbp1Δ and (E) Tgm2WT and Tgm2Δ carotid artery tissue sections probed with Rabbit anti-IRE1 alpha Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # NB100-2324) for total IRE1α. Increased IRE1 alpha expression is observed in neointima in situ in carotid artery sections of deficient mice. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0212235) licensed under a CC-BY license.
IRE1α: A major player in cellular response to disease
IRE1 (inositol-requiring enzyme 1 or ERN1) has been implicated in physiological processes and pathogenesis of multiple diseases including cancer, neurodegenerative, inflammatory, and metabolic diseases.5,6 Many of these diseases are associated with accumulation of misfolded proteins while also exhibiting an increase in IRE1 activity, providing rationale for pharmacological targeting of IRE1α. A study by Tognarelli and colleagues described upregulation of IRE1α activity and downstream XPB1 splicing in dendritic cells (DCs) infected with herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2).7 Recent findings show that endonuclease activity of IRE1 was responsible for viability of DCs infected with HSV-2.8 Furthermore, they demonstrate that inhibition of IRE1α endonuclease activity in mice infected with HSV enhanced the ability of DCs to migrate to the lymph nodes and activate virus-specific T cell responses.
IRE1α also has a role in modulating susceptibility to host cell apoptosis in response to HSV and vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV). Interestingly, loss of XBP1 in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) caused upregulation of IRE1α enzymatic activity.9 Using this model, cells infected with either HSV or VSV were not only unable to undergo apoptosis, but viral replication was also increased. A common pharmacologic strategy to inhibit IRE1α activity is to use compounds that block the RNAse enzymatic activity of IRE1α. One such study found using a selective IRE1α nuclease inhibitor sensitized infected cells to apoptosis and decreased viral replication, indicating that RNAse activity of IRE1α is capable of contributing to apoptosis resistance.10 Taken together, these findings define a functional role for IRE1α in cellular responses to viral infections such as HSV, VSV, and hepatitis C virus (HCV).
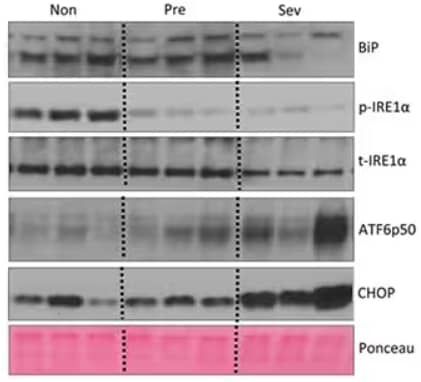
Western Blot analysis showing expression of hepatic ER stress markers Bip, IRE1a (phospho-, p; total, t), ATF6p50, and CHOP during cachexia progression in the liver of non, pre and severely cachectic mice. (Non=non-cachetitc Apc Min/+; Sev =severely chachetic Apc Min/+). Rabbit anti-IRE1 alpha [p Ser724] Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog #NB100-2323) was used to examine p-IREa expression where expression is reduced during cachexia progression. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https //doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0119888) licensed under a CC-BY license.
Natalia Gurule, PhD
Dr. Gurule is a postdoctoral fellow at National Jewish Health. She studies pathways that regulate inflammation upon infection in leukemia and myeloid dysplastic syndromes.
-
Hiramatsu, N. (2015) Multiple Mechanisms of Unfolded Protein Response-Induced Cell Death Am J Pathol 185:1800-1808.
-
Siwecka, N. et al. (2021) The Structure, Activation and Signaling of IRE1 and Its Role in Determining Cell Fate Biomedicines 9:156.
-
Kaser, A. et al. (2008) XBP1 links ER stress to intestinal inflammation and confers genetic risk for human inflammatory bowel disease Cell 134:743-756.
-
Tavernier, Q. et al. (2018) Regulation of IRE1 RNase activity by the Ribonuclease inhibitor 1 (RNH1) Cell Cycle 17:1901-1916.
-
Zhao, N. et al. (2018) Pharmacological targeting of MYC-regulated IRE1/XBP1 pathway suppresses MYC-driven breast cancer J Clin Invest 128:1283-1299.
-
Rosen, D.A. et al. (2019) Modulation of the sigma-1 receptor-IRE1 pathway is beneficial in preclinical models of inflammation and sepsis [published correction appears in Sci Transl Med. 2019 Mar 27;11(485):] Sci Transl Med
-
Retamal-Díaz, A. et al. (2017) US6 Gene Deletion in Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 Enhances Dendritic Cell Function and T Cell Activation Front Immunol 8:1523.
-
Tognarelli, E.I. et al. (2022) Pharmacological Inhibition of IRE-1 Alpha Activity in Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 and Type 2-Infected Dendritic Cells Enhances T Cell Activation Front Immunol
-
Fink, S.L. et al. (2017) IRE1α promotes viral infection by conferring resistance to apoptosis Sci Signal
-
Cross, B.C. et al. (2012) The molecular basis for selective inhibition of unconventional mRNA splicing by an IRE1-binding small molecule Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:869-878.