What is Ly6G?
Ly6G (Lymphocyte antigen 6 complex locus G6D) is a 21-25kD glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-linked differentiation antigen that is expressed by myeloid-derived cells in a tightly developmentally-regulated manner in the bone marrow. Monocytes express Ly6G transiently during bone marrow development, while Ly6G expression in granulocytes and peripheral neutrophils directly correlates with the cell’s level of differentiation and maturation. This hallmark makes Ly6G a good marker for these particular cell populations. Ly6G has also been implicated in the development of antitumor responses.
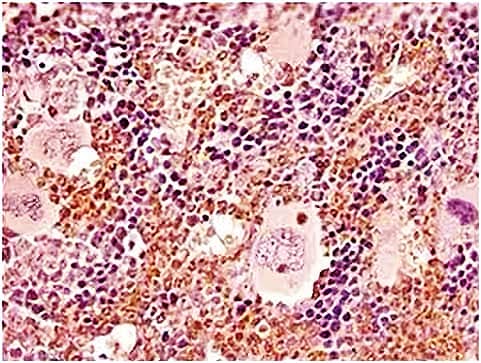
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: Ly-6G/Ly-6C Antibody (RB6-8C5) [NBP2-00441] - Analysis of a FFPE tissue section of mouse bone marrow using 1:200 dilution of Lot A-1 of Ly-6G antibody (clone RB6-8C5). The antibody generated specific staining in a subset of cells in the tested section. The neutrophils (identifiable from typical nuclear morphology) showed stronger signal than the neighboring cells. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of FFPE Tissue Sections
What Does the Ly6G Antibody Tell Us?
Researchers from the Genetics Institute at Andover used the Ly6G antibody to demonstrate that systemic administration of recombinant murine IL-12, as delivered by modified acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells, generates a potent and long-lasting protective immunity in AML patients (PMID: 10590071). Miura et al. relied upon the Ly6G antibody to test the effects of antibodies to KC/Gro alpha and MIP-2 on blocking neutrophil infiltration into kidneys after injury (PMID: 11733364). Their studies found that neutralizing such chemokines and minimizing resultant pathology and damage. Alvarez’s group at the Leloir Institute, Buenos Aires, used the Ly6G antibody to map secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine (SPARC) downstream events in human melanoma cells (PMID: 15958556). Another group found that Toll-like receptor signaling is crucial for Listeria monocytogenes (Lm) bacterial-triggered tumor growth through infection-associated pathways (PMID: 17483348). Their novel work sheds light upon the importance of antibiotic treatment therapy in conjunction with more conventional oncology therapies. Additionally, the Ly6G antibody allowed researchers to examine the role of IL-27 in modulating collagen-induced arthritis (PMID: 21384333). Their rheumatology experiments focused on understanding the MOA of IL-27 and IL-17 and their downstream modulators, with hopes of treating arthritis patients.